First Aid
advertisement

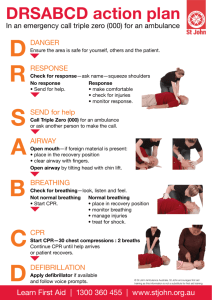
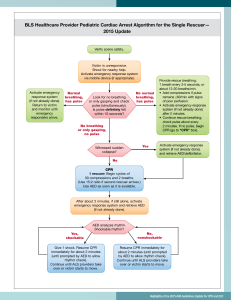
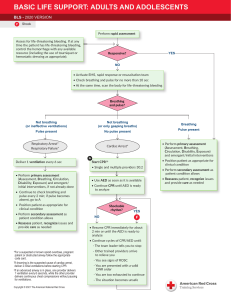
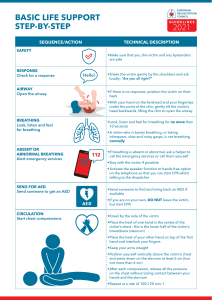
First Aid What Is First Aid? Immediate, temporary care given to a person who has become sick or who has been injured Takes place until proper medical authority arrive Emergency Action Plan Primary Survey 3 C’s = Check, Call, Care • Check – scene safety You don’t want to make more victims! – Check the immediate surroundings for possible dangers; move victim only if life is threatened • Check victim... – Check consciousness – gently tap and ask, “Are you OK?” – Check the victim for poisoning Emergency Action Plan cont. º Call • Call 911 immediately if victim shows any life-threatening conditions • Answer 911 operator’s questions and follow directions calmly and completely º Care • Be prepared to provide first aid • Control severe bleeding • Prepare to perform CPR Making the Call to 911 • Give location of emergency (exact address, city or town, nearby intersections, building #, floor, apt.) • Telephone # from which call is being made • Caller’s name • What happened • # of victims • Condition of victims • First aid given Universal Precautions • Be responsible – protect yourself and the victim! • Wear disposable gloves if coming into contact with body fluids • Use a plastic face shield or mask with a one-way valve • Wash your hands with soap and warm water after providing first aid Shock • Usually accompanies severe injury or emotional upset • Circulation system fails to send blood to all parts of the body Signs – ► cool, clammy skin ► pale face ►confusion ► nausea ► vomiting ► rapid breathing Choking • When food or any other object becomes lodged in a person’s airway, this person may choke • Unless the object is dislodged within minutes, the person can die Signs: a person may bring one or both hands to the throat, gasp for air or turn blue CPR = Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation • When blood does not circulate, the brain and other vital organs do not receive O2 Signs of a cardiac arrest –Unconsciousness –No signs of breathing –No signs of circulation CPR • 2010 Guidelines – C, A, B (Compressions, Airway, Breathing) – If not CPR certified, provide “Hands-Only” CPR CPR Certified: – Begin immediately with 30 compressions, 2” deep – Open the airway, deliver 2 breaths AED • Automated External Defibrillator (AED) • An AED can check a person’s heart rhythm. It can recognize a rhythm that requires a shock. • It can advise the rescuer when a shock is needed. • The AED uses voice prompts, lights and text messages to tell the rescuer the steps to take. Burns • 1st Degree – superficial – top layers of skin ex. Sunburn – takes 5-6 days to heal (use sunscreen with an SPF of 15 or more) • 2nd Degree – top several layers of skin, blisters & blotchy – takes 3-4 weeks to heal • 3rd Degree – destroys all layers of skin as well as nerves, muscles, fat, and bones Heat Exhaustion/Heat Stroke • Heat Exhaustion – exposed to high temps - Signs: skin that is cool, moist or pale, headache, dizziness, nausea, heavy sweating, weakness • Heat Stroke – body systems become so overheated = stop functioning – life threatening – Signs: confusion, red, hot, dry skin, shallow breathing Frostbite/Hypothermia • Frostbite – freezing of body parts * lack of feeling in the affected area, skin that appears waxy or discolored and is cold to the touch • Hypothermia – body temp falls below 95° * shivering, numbness or weakness, glassy stare, confusion Open Wounds - Bleeding • Abrasion – damage to outer layers of skin • Laceration – caused by a sharp object; deep cuts result in heavy bleeding and may damage nerves, blood vessels or soft tissue • Puncture – wound caused by a pin, splinter, or other pointed object piercing the skin • Avulsion – tissue is separated partly or completely from a person’s body Dislocation - Fracture • Dislocation – Displacement or separation of a bone from its normal position at a joint • Fracture – chip, crack, or break in bone – Closed = skin intact Open = piece of bone sticks out through skin symptoms: swelling, inability to move joint or pain when moving, tenderness Strains & Sprains •Strain – muscles have been overworked – Symptoms: dull pain that worsens with movement, swelling •Sprain – injury to tissues surrounding a joint – Symptoms: popping sound or tearing sensation, swelling, tenderness, discoloration Poison Poisons can enter the body by 4 routes: Ingestion, Inhalation, Injection, Absorption • Ingestion – most swallowed poisons are household cleaners and medications • Inhalation: Carbon Monoxide, Ammonia • Injected Poison – insect stings and bites • Absorption – Plants and chemicals