AG 10-6 to 10
advertisement

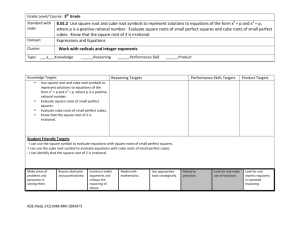
Unit 2 Assignment guide Math 8A– Weeks of 10/06 to 10/10 and 10/13 – 10/17 Exponents and Equations In this unit, students build upon their work with whole-number exponents in Grades 5 and 6, by extending the properties of exponents to include rational and irrational numbers, including numbers in scientific notation. Students strategically choose and efficiently implement procedures to solve linear equations in one variable, understanding that when they use the properties of equality and the concept of logical equivalence, they maintain the solutions of the original equation. Students also use linear equations to represent, analyze, and solve a variety of problems. Monday October 06 MCC.8.EE.2 Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x 2 = p and x3 = p, where p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Know that √2 is irrational. EQ: What patterns and structures can I identify when looking at relationships among rational and irrational numbers? WU: Make a list of the first 15 perfect squares and the first 5 perfect cubes CW: Models of Cubes Handout HW: Finish the packet Tuesday October 7/Wednesday October 8 Students will either go on the Walking Tour of Roswell on Tuesday or Wednesday morning, depending upon which team they are on. The day they do not go on the tour, this will be their assignment. Students in the afternoon will have review activities. MCC.8.EE.2 Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x2 = p and x3 = p, where p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Know that √2 is irrational. EQ: What patterns and structures can I identify when looking at relationships among rational and irrational numbers? WU: Make a list of the first 15 perfect squares and the first 5 perfect cubes CW: QR code review of Irrational/Rational Numbers, square and cube roots HW: Make a 20 questions study guide for another student to complete Thursday October 3 MCC.8.EE.2 Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x 2 = p and x3 = p, where p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Know that √2 is irrational. MCC.8.NS.1 Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion; for rational numbers show that the decimal expansion repeats eventually, and convert a decimal expansion which repeats eventually into a rational number. MCC.8.NS.2 Use rational approximations of irrational numbers to compare the size of irrational numbers, locate them approximately on a number line diagram, and estimate the value of expressions (e.g., π 2). EQ: What patterns and structures can I identify when looking at relationships among rational and irrational numbers? CW: Review for irrational number quiz 3 HW: Practice 3 – 1 and √𝑐𝑢𝑏𝑒 𝑟𝑜𝑜𝑡 Worksheets EVEN problems only Friday October 4 MCC.8.EE.2 Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x 2 = p and x3 = p, where p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Know that √2 is irrational. MCC.8.NS.1 Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion; for rational numbers show that the decimal expansion repeats eventually, and convert a decimal expansion which repeats eventually into a rational number. MCC.8.NS.2 Use rational approximations of irrational numbers to compare the size of irrational numbers, locate them approximately on a number line diagram, and estimate the value of expressions (e.g., π 2). EQ: How can I show mastery of rational and irrational numbers, square and cube roots and locating them on a number line diagram to estimate the value of the expressions CW: Quiz 3 of Unit 2 HW: None Unit 2 Assignment guide Math 8A– Week of 10/13 to 10/17 Monday October 13 School Holiday Tuesday October 14 Teacher Workday Wednesday October 15 MCC.8.EE.7 Solve linear equations in one variable. EQ: How can algebraic expressions be used to model, analyze and solve mathematical situations? WU: BK p 73 # 19 - 25 CW: BK Lesson 2 – 1 Solve One-Step equations by adding and subtracting p. 77 – 81 CW and HW: pp 80, 81 # 2-60 Even Thursday October 16 MCC.8.EE.7b Solve linear equations with rational number coefficients, including equations whose solutions require expanding expressions using the distributive property and collecting like terms. EQ: How can algebraic expressions be used to model, analyze and solve mathematical situations? WU: BK p 82 # 79 – 87 CW: BK Lesson 2 – 2 Solving Equations by Multiplying or Dividing pp 84 – 89 CW and HW: BK pp 87, 88 #2-60 Even Friday October 17 MCC.8.EE.7b Solve linear equations with rational number coefficients, including equations whose solutions require expanding expressions using the distributive property and collecting like terms. EQ: How can algebraic expressions be used to model, analyze and solve mathematical situations? WU: BK p 90 #95 - 104 CW: BK 2-3 Solving Two-Step and Multi-Step Equations p. 92-96 CW and HW: BK p. 96, 97 # 2 – 44 Even