Lecture1_notes_2006
advertisement

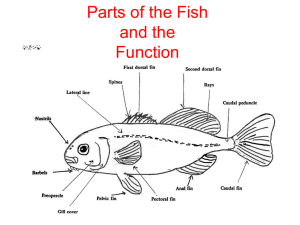
What is a Fish? • • • • • Poikilothermic – body temperature is identical to surrounding water Chordates – have developmental characteristics of all vertebrates Appendages developed as fins Chief respiratory organs are gills Body generally covered with scales “A fish is an aquatic vertebrate with gills and with limbs in the shape of fins” (Nelson 1994) There are over 25,000 fish species, so there are exceptions to these general characteristics. Fish vs. Fishes “This tank is full of fish.” “The ocean is full of fishes.” Anatomical Terminology Functional Morphology in Fishes Functional Morphology – “the study of form and structure in animals as related to the functions of the various body parts” W.A. Gosline, 1971 From P.W. Webb, 1984 Acceleration Specialists – Adaptations for Ram Feeding Flexible Body Thick Caudal Peduncle Large Gape Maxilla may or may not be excluded from gape Posterior-placed Median Fins Cruising Specialists – Adaptations for Sustained Swimming Terminal Mouth Finlets Fusiform Body bluefin tuna – Thunnus thynnus Lunate Tail Caudal Keels Narrow Caudal Peduncle Maneuvering Specialists – Adaptations for Suction Feeding Laterally Compressed Body Small Gape Maxilla Excluded From Gape Laterally Positioned Pectoral Fins Adaptations for Bottom Dwellers Barbels Inferior Mouth Dorso-ventrally Compressed Body Adaptations for Surface Dwellers Superior Mouth Counter-color Shading Fish Identification: Color … ? Fathead Minnow (Pimephales promelas) Fish Identification: Size… ? Fish Identification : Patterns white bass (Morone chrysops) - stripes yellow perch (Perca flavescens) - bars northern pike (Esox lucius) - spots Fish Identification : Patterns red drum (Sciaenops ocellatus) - eye spot white shark (Carcharodon carcharias) -counter-color shading Fish Identification: Fins Spiny Dorsal Fin (protection, steering, braking) Soft Dorsal Fin (forward propulsion, steering, braking) Caudal Fin (forward propulsion) Anal Fin (forward propulsion) Pectoral Fin (braking, steering, propulsion) Pelvic Fin (braking, steering) Adipose Fin (Ictaluridae, Salmonidae) Pelvic fins in thoracic position (derived state) Pelvic fins in abdominal position (more primitive) Fish Identification: Shapes Forked Fins vs. Rounded Body streamlined vs. deep Scales vs. diamond round superior Mouth inferior terminal vs. vs. Fish Identification : Unique Features Barbels Teeth Northern Pike Tadpole Madtom Scales Lateral line Brook Stickleback Golden Shiner Fish Scale Types Fish Scale Types