Powerpoint Cells Ch 3
advertisement

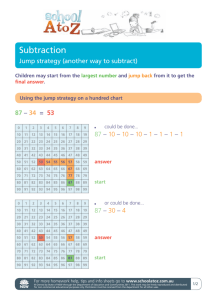
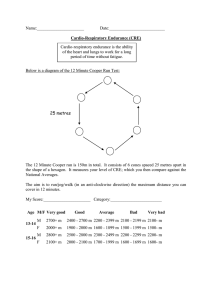
Cell Biology Structure and Function Jump to first page Cell Theory List the contributions of the following to the development of cell theory. Anton van Leeuwenhoek Hooke Schleiden Schwann and Virchow State the cell theory Jump to first page Microscope Microscope first made in 1600’s Anton van Leeuwenhoek, a dutch biologist saw tiny water organisms Jump to first page Robert Hooke Englishman Observed slices of cork under microscope Named spaces “cells”, because they looked like a monastery room. Jump to first page Matthias Schleiden German botanist Found all plants are made of cells. Jump to first page Theodor Schwann Found all animals are made of cells. Jump to first page Rudolf Virchow 1855 of Germany Found all cells arise from the division of pre-existing cells. OR Jump to first page Cell Theory All living things are composed of cells, whether one or trillions. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. All cells come from pre-existing cells. Jump to first page Review page 180 Jump to first page Microscopes Compound Light Microscope Uses lenses to bend light rays Has an objective lens (5x,10x,20x,40x,60x,80x, 100x) Has an eye piece lens (10x) Jump to first page Transmission electron Uses negative electron microscope charges to make an image on a screen 50,000x magnification Jump to first page Scanning Electron Microscope False color images Sprays metal dust on object. Metal gives off electrons which are detected and drawn on screen Jump to first page Glowing Fluorescent protein Taken from jellyfish Mitochondria Attached to DNA and produces a glowing protein that allows tracking of proteins in cells. Jump to first page Cell structure Identify and give the function of the cell structures. Compare the structure of the cell membrane to the cell wall. Distinguish between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Jump to first page Prokaryotes No nucleus Contain DNA, strings like spaghetti Contain tiny spheres called ribosomes Jump to first page Eukaryotes Have a nucleus containing DNA Contain many membrane bound organelles Jump to first page http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/NSC/13-cells.htm Jump to first page Cell Structures Jump to first page Cell membrane Jump to first page Cell Membrane Regulates what goes out and comes in. door, phone, trash, groceries Made of a double layer of phospholipids Jump to first page Membrane continued... Stationary Proteins are stuck in the bilayer Carbohydrates stick to proteins to serve as identifiers to other cells Free moving proteins are doors which pump molecules in or out (Alleys for molecules to exit and enter the cell) Jump to first page Cell Wall Found in plants, algae, some bacteria. Made of 2 or more layers. Protects, supports, surrounds cell membrane Porous (has holes) to allow water, oxygen, and carbon dioxide to pass. Jump to first page Wall Layers 1st layer is between 2 cells. Buffer layer Made of cellulose & pectin Pectin is a sticky glue Cellulose is elastic Jump to first page 2nd wall layer Trees have Seconary cell wall Made of cellulose and lignin lignin provides rigidity Jump to first page Cell walls stain Purple for Gram Positive Staphylococcus Red for Gram Negative E coli Jump to first page Nucleus Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) don’t have a nucleus Eukaryotic cells have nucleus Directs cell activity (Boss) reproduction production of proteins, lipids, enzymes, carbohydrates, and other nucleic acids Jump to first page Nucleus continued... Contains DNA blue print for construction of body long chain of DNA = chromosome 2-5 micrometers in diameter Surrounded by 2 membranes called the Nuclear Envelope. Contains dozens of pores (doors to nucleus) Jump to first page Inside the nucleus Nucleolus Contains RNA- serves as copier of DNA Ribosomes- aid in protein production 6 feet of Chromosomes bunched and attached to special round proteins Half of DNA is passed to offspring Jump to first page RNA Three types Messenger RNA Single strand that takes the copy of DNA to make proteins Transfer RNA Attaches an amino acid to a triplet of bases on messenger RNA. Ribosomal RNA Helps the amino acid, tRNA, mRNA hold together Jump to first page Cytoplasm Area between nucleus and cell membrane Contains many structures floating in a liquid gel Contains carbohydrates, proteins, amino acids, lipids, water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and enzymes. Jump to first page Endoplasmic Reticulum Long structure that helps make and store proteins. The factory of the cell Two types Rough E.R. Studded with Ribosomes- makes proteins. Smooth E.R. makes lipids and stores proteins. Jump to first page Golgi Apparatus Transports proteins, hormones, carbohydrates outside the cell. Blob shaped The truckers of the cell Jump to first page Lysosome Blob structure that cleans up wastes and invaders by engulfing and digesting them. Janitor of the cell Jump to first page Vacuole Stores water for plant cells. Very large in plants Animal cells have smaller vacuoles. These gather excess water and transport it out of the cell. Jump to first page Mitochondria Rod shaped Have folds inside where energy is produced. Have their own DNA Passed to children through the mother Jump to first page Plastids Store pigments or starch Chloroplasts in plants store green chlorophyll for photosynthesis Jump to first page Centrioles Made of protein Cylinders that are used during cell reproduction. Act as anchors or winches Jump to first page Cytoskeleton Provides support, made of protein Microtubules Microfilaments Jump to first page Review page 193 Jump to first page