Michael Foucault: Discipline and Punish
advertisement

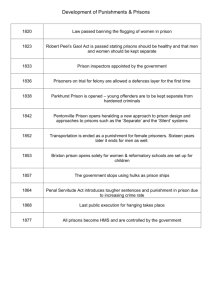
Department of Criminal Justice California State University - Bakersfield CRJU 100 Introduction to Criminal Justice Dr. Abu-Lughod, Reem Ali The History of Control Before there were prisons: No CJS to punish and deal with violators Family, tribes enforcing laws Blood feuds Corporal Punishment: Revenge Physical harm on body relatively equal to crime committed 1) Torture: disembowelment or impaling but now solitary confinement Michael Foucault: Discipline and Punish: The Birth of the Prison Torture as justice 2) Flogging (whipping) Leather thongs 3) Branding: Assuring community offender has been punished Repeat offenders branded on their forehead Women wore identification on clothing 4) Mutilation Eye for eye 5) Humiliation: Verbal or physical 6) Shock Death: Hanging Psychological torture ECONOMIC PUNISHMENT: 1) The Galley: Ships powered by prisoners and slaves 2) Workhouses: bad living conditions and treatment. 1779 Penitentiary Act passed, reform legislation to address living conditions. Did not work but gave feds authority to oversee prison system 3) Exile and transportation: exchange of labor for money Prisons in America: replaced workhouses A) Control in Colonies: all housed together. The Quakers movement in Pennsylvania: incarceration and hard labor preferable to corporal punishment Walnut Street Jail: no women housed with men Used as military prison ion Revolutionary War. Was converted into nation’s 1st penitentiary housing serious offenders. Set tone for formal prisons Castle Island: another modern pen Development of the Pen: Two systems: 1) Pennsylvania and Auburn Penn: known as Cherry Hill Separate and silent Solitary confinement Then overcrowding Auburn in NY Congregate and silent: eat and work together but locked in isolation and no face-to-face contact AGE OF REFORM: 1860-1900 Charles Dickens toured Penns and criticized it Yes for reform Irish system of reform: Punish but focus on reintegration Developed 3 systems: 1) Alexander Maconochie: making inmate trustworthy to soc 2 beliefs: cruelty will create problems and must focus on reintegration Instituted indeterminate sentences Marks of commendation system 2) Sir Walter Crofton: Ticket of leave, conditional release under police supervision 3) Zebulon Brockway: Crofton and Maconochie’s models at the reformatory in Elmira, NY. Used 3-grade program for first time offender No supervision after release. If in solitary confinement then bread and water only for months Prison Labor and Public Works: 1900-1930 work as beneficial Keep them out of trouble Rehab and offset cost of incarceration Make goods used by state government, e.g.office furniture Today: clean highway trash, dressed in prison attire for humiliation Age of Rehabilitation: Very important goal of CJS esp since 1930s Criminologists and correctional practitioners perceived criminality in a different manner “germ theory of medicine” Rehab not fully accomplished: Lack of resources Consensus Medical model: flawed Retributive Era: 1970s to present Mov’t away from rehab 1960s events caused change E.g. political movement: minorities, youth and women challenged how soc treated them, and inmates challenged conditions and confinement Courts had “hands off” policy in matters concerning prison operation 1960s: more constitutional rights Black Panther Party and Black Muslims wanted legitimacy of their political orgs Change from rehab to retribution 1) 2) 3) Determinate sentences Voluntary treatment Abolition of parole: no early release although not fully accomplished: critics “soft on crime” CAPITAL PUNISHMENT : Method of social control Controversial Courts limited execution on mentally ill for deterrence and understanding Supporters to death penalty: Deterrent: specific and general deterrence Just deserts model: for soc justice Retribution model: eye for an eye Against death penalty: Old testament of Bible “thou shall not kill” Deterrence Barbaric Racial biases Social class Innocence