Cell Cycle WS Answers
advertisement

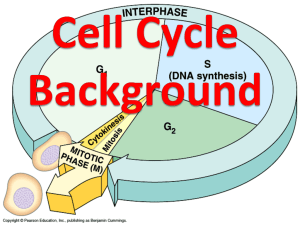
Name:_______________________ Date:________________________ Class:________________________ Stage 1: Interphase (p. 96) 1. The regular sequence of growth and division that cells undergo is called the __cell cycle____________. 2. List three things that the cell is doing during interphase. a._grows__________________________________________ b. __copies DNA_________________________________________ c. ___prepares to divide into 2 new cells________________________________________ 3. Circle the letter of the specific process during which cell copies DNA. a. Interphase b. Cytokinesis c. Replication d. Division Stage 2: Mitosis (p.97-99) 4. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about mitosis. a. The cell makes a copy of its DNA b. The cell membrane pinches in around the middle of the cell *Did you choose this answer? Why or why not? c. The cell’s nucleus divides into two new nuclei d. One copy of DNA is distributed into each daughter cell Match the phases of mitosis with the events that occur in each. Event ___C 5. The centromeres split and chromatids separate __A_6. The chromatin condenses to form chromosomes __D_7. A new nuclear envelope forms around each region of chromosomes __B_8. The chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. Phase a. prophase b. metaphase c. anaphase d. telophase 9. Label the parts of the structure in the diagram below. Stage 3: Cytokinesis (p.100) 10. During cytokinesis the__cytoplasm_________________ divides, distributing the organelles into each of the two new cells. 11. Is the following true of false? During cytokinesis in plant cells, the new cell membrane forms before the new wall does. ___True_____________________________ Structure and Replication of DNA(pp. 101-102) 12. Why does a cell make a copy of its DNA before mitosis occurs? ____So that each new daughter cell will have a complete copy (set) of DNA_______________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 13. Circle the letter of each molecule that makes up the DNA ladder. a. Deoxyribose b. Glucose c. Phosphate d. Oxygen Cell Division Understanding Main Ideas Fill in the blanks in the table below. Then answer the questions that follow in the space provided. Phases of Mitosis Event Phase Prophase 15.______Metaphase_________________________ 14._______Chromatin condenses to form chromosomes, nuclear envelope breaks down__________________ Chromosomes attach to spindle fibers. Anaphase 16. ____centomeres split and chromosomes /chromatids seperate______________________ 17._____Telophase__________________________ New nuclear envelope forms 18. Which stage of the cell cycle usually lasts longest? __Interphase__________________________________________________________________________ 19. During which stage of the cell cycle does DNA replication occur? ___Interphase_________________________________________________________________________ 20. During which stage of the cell cycle does the cell membrane pinch the cell in two? ______Cytokinesis______________________________________________________________________ Building Vocabulary Match each term with its definition by writing the correct letter in the blank. _C___21. Regular sequence of growth and a. interphase division that cells undergo b.mitosis _A_22. First stage of the cell cycle c. cell cycle _E__23. Process in which DNA is copied d. cytokinesis _B_24. Stage of the cell cycle during which e. replication The cell’s nucleus divides f. chromosome _F_25. Doubled rod of condensed chromatin _D_26. Final stage of the cell cycle Cytokinesis in Plant cells and Animal cells Recall that all plant cells have a rigid cell wall. Because of this rigid cell wall, cytokinesis in plant cells in different from cytokinesis in animal cells. Study the figures below to see how cytokinesis differs in plant cells and animal cells. In animal cells, as daughter cells pinch into two cells, there is a space between the cells called a furrow. As the furrow gets increasingly narrow, the spindle fibers are pressed into a tight bundle, called a stem body. The stem body eventually is cut in two as the new cell membranes fuse together. In plant cells, pockets of cell-wall material, called vesicles, line up across the middle of the cell. The vesicles fuse together in two sheets to form new cell walls and cell membranes between the daughter cells. Answer the following questions using the information above. 1. How does the furrow form in an animal cell? What is the furrow’s role in cell division? As daughter cells pinch into two cells, there is a space between the cells called a furrow. As the furrow gets increasingly narrow, called a stem body two new cell membranes fuse together. 2. What causes the stem body to form in an animal cell? What happens to the stembody when the cell divides? The spindle fibers are pressed into a tight bundle creating the stem body. body eventually is cut in two as the new cell membranes fuse together. 3. What are vesicles? Which part of the plant cell do vesicles develop into? In plant cells, pockets of cell-wall material. The cell wall and the cell membrane. The stem 4. If you observed a cell under a microscope during cytokinesis how could you tell whether it was a plant cell or an animal cell?