MTT Exam Competency 001
advertisement

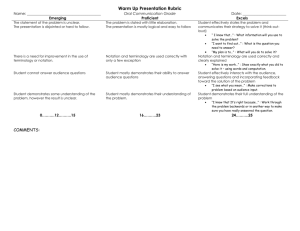
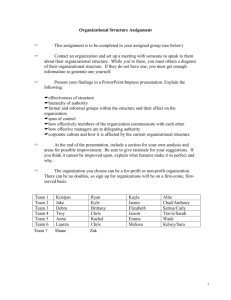
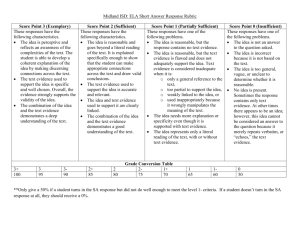
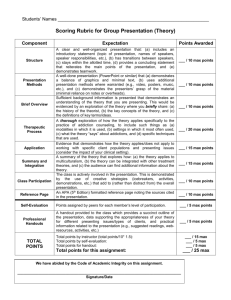
MTT Exam Competency 001 Robert W. Young, Jr. University of Texas, Brownsville Competency 001 The Master Technology Teacher demonstrates knowledge and application of technology-related terminology and concepts, hardware, software, data-input strategies, and ethical practices, and knows how to acquire, analyze, and evaluate digital information from the Internet and other sources. The Master Technology Teacher: 1. 2. 3. 4. Knows technology-related terminology and concepts. Demonstrates an understanding of the appropriate use of hardware components and software applications. Knows how to use input and output devices when using selected digital technologies (e.g., text, graphics, animation, video, sound, Internet applications). Identifies and demonstrates knowledge of how to create, use, manipulate, and exchange digital file formats (e.g., text, image, video, audio) between applications and/or platforms. The Master Technology Teacher: 5. 6. 7. 8. Demonstrates knowledge of criteria (e.g., quality, appropriateness, effectiveness, efficiency) for evaluating productivity and authoring tools for selection, acquisition, and use. Knows how to facilitate the use of integrated technologies in foundation and enrichment curricular content. Demonstrates knowledge and application of strategies for searching (e.g., keyword, Boolean, natural, language), locating, and acquiring information from electronic resources (e.g., collaborative software, the Internet, intranets). Knows how to organize, store, and retrieve electronic information found in various formats (e.g., text, graphic, video, audio). The Master Technology Teacher: Knows how to identify and evaluate information acquired from primary and secondary sources for accuracy, relevancy, and content validity by accessing, researching, and comparing data from multiple sources (e.g., the Internet, encyclopedias, databases). 10. Demonstrates knowledge of the acceptable use of electronic information and products while in an individual classroom, lab, or on the Internet or an intranet. 11. Demonstrates knowledge of copyright laws and violations and of ethical issues (e.g., fair use, patents, and trademarks; computer hacking; computer piracy; computer vandalism; intentional virus setting; invasion of privacy) when using, manipulating, and/or editing electronic data. 9. The Master Technology Teacher: Knows how to obtain and cite the source of print and digital information from a variety of resources (e.g., the Internet; encyclopedias; databases; libraries of images in a variety of formats including text, audio, video, and graphics). 13. Demonstrates respect for intellectual property and understands the ethical acquisition and use of digital information (e.g., citing sources using established methods). 12. Terminology Terminology Experience counts. Broad & shallow. Operating System (OS) Terminology Digital Operating System (DOS) Graphic User Interface (GUI) WYSIWYG (whizzgy) QWERTY Windows Terminology Start Menu System Tray (Sys tray) Quick Launch Task Bar Task Manager OOPS! Now What? Control + Alt + Delete Assistive Technology-Accessibility Making a Windows computer more usable to students with special needs. Accessibility- Control Panel Accessibility Panel Magnifier Magnifies selected portions of desk top. Magnifier Magnified area can be moved to a different part of the screen. Other features can be modified, too. Magnified Area Menu Magnifier Further Review http://computer.howstuffworks.com/ http://www.wikipedia.org/ Education & Microsoft Software Tutorials http://www.microsoft.com/education/Tutorials.mspx Microsoft Accessibility Tutorials http://www.microsoft.com/enable/training/default.as px Applications Hardware Applications Can you operate: A printer on a network? A scanner? A digital camera? A projector? Software Applications Can you use: Photo editing software? (Photoshop) Video editing software? (Windows Movie Maker) Word processor? (MS Word) Presentation Software? (Power Point) Spreadsheet (Excel) Applications- File Manipulation & Conversion Copy, move, delete files safely Recover files accidentally deleted Find files on a computer system Convert file types Doc- TXT Doc- PDF Gif- JPEG Review & Evaluation Should We Buy It? Quality Appropriateness Effectiveness Efficiency Tech Integration Tech Integration Supports Curricular Goals Four key components of learning: Active engagement Participation in groups Frequent interaction Feedback, and connection to real-world experts. Further Review http://www.edutopia.org/tech-integration http://www.remc11.k12.mi.us/bstpract/ Search Strategies for Searching Keyword Boolean Natural Language Further Review http://www.searchengineshowdown.com/strat/ http://www.google.com/support/bin/static.py?page= searchguides.html&ctx=advanced&hl=en Formats File Extensions *.exe *.doc *.ppt *.txt Visual Media Terminology Pixels *.jpg *.gif Thumbnail Research Sources Know Your Sources Primary Sources Original work Secondary Sources Cite other sources Encyclopedia Reviews Accuracy Relevancy Content validity Copyright & Fair Use Public Domain Fair game for all. It mainly depends on when the item was written. Before Jan. 1, 1923 Public Domain 1923-1978 Works published between Jan. 1, 1923 and Dec. 31, 1978 Registered copyright was not renewed. If the original copyright has been renewed, the published works may be protected for a total of 95 years from date of first publication. Before 1978, but Never Published 70 years after the death of the author. If the author died over 70 years ago, the copyright in an unpublished work lasted until December 31, 2002. If such a work was published before December 31, 2002, the copyright will last until December 31, 2047. After 1978 Public domain 70 years after the author dies. If the work is a work for hire (that is, the work is done in the course of employment or has been specifically commissioned) Or is published anonymously or under a pseudonym The copyright lasts between 95 and 120 years, depending on the date the work is published. Fair Use- a Definition Allows public to use a minimum amount of a copyrighted item for a reasonably limited amount of time until permission can be obtained. Examples Reserve copy of a single article from a journal for one semester- YES Copied class set of a book used year after year.NO Fair Use Is it copyrighted? yes/no Fair Use- A defense in copyright violation case Education is not a blanket excuse. Basic Rule: When in doubt, get permission. If you don’t have permission, don’t use it. Fair Use- Four Tests 1. 2. 3. 4. Each one has equal weight. Judged on case by case basis Character of Use Nature of the Work How Will Work be Used Effect on Potential Market Value or Value of the Work Character of Use Fair Use Nonprofit Educational Personal Support for Fair Use Criticism Commentary News reporting Parody Transformation Copyright Owner Commercial Nature of the Work Fair Use Fact Published Support for Fair Use A mixture of fact and imagination Copyright Owner Imaginative Unpublished How Will Work be Used Fair Use Small amount Copyright Owner More than a small amount Effect on Potential Market Value or Value of the Work Fair Use Support for Fair Copyright Use Owner Factors 1-3 favor fair use Original is out of publication There is no ready market Copyright owner is unidentifiable Competes with sales of original Avoids payment of royalty Sources for Permission Copyright Clearance Center www.copyright.com Swank Motion Pictures, Inc. www.swank.com/college/main.html Further Review Review & test for copyright & Fair Use. http://www.utsystem.edu/ogc/intellectualproperty/co pypol2.htm#test Guidelines for Education Multimedia http://www.utsystem.edu/ogc/intellectualproperty/cc mcguid.htm Guidelines for Digital Images http://www.utsystem.edu/ogc/intellectualproperty/im agguid.htm Citations Why Cite? It’s a pain in the rear! Recognition of the work of others. Keeps authors honest Pre-digital Age Link Plagiarism The outright copying of the work of another person Using a direct quote without quotation marks Paraphrasing that does not depart substantially from the original text A statement that represents the opinion of another who is not identified Inclusion of not commonly known facts or unique information Reproduction of statistics, charts, or tables without giving credit Basic Format (APA) Print Journal Author(s), (Year of Publication). Title of article. Journal name, Volume (Issue), Pages. Web Article Author(s), (Year of Publication). Title of article. Journal name, Volume (Issue), Pages. Retrieved from Link Further Review http://lib.radford.edu/tutorial/VII/comp.asp http://lib.radford.edu/resources/handouts/styleguide s-apa.asp © Copyright 2008 R. W. Young, Jr. Ojalá Concepts Copyright Policy Materials published by Ojalá Concepts may be duplicated in hard copy format if unchanged in format and content for educational, non-profit school district use only. All other uses, transmissions and duplications are prohibited unless permission is granted expressly. Showing these pages remotely through frames on a website is not permitted.