Biology- inv. 1
advertisement

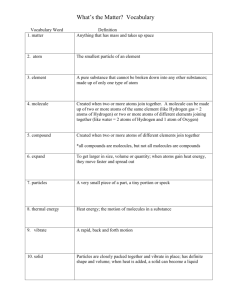
Uyanga Ganbold-Battulga Mr.Miller Biology 4 1 October 2010 MATTER AND ENERGY MY INITIAL QUESTIONS Main question: what is matter made up of and what kinds of energy exist? Minor questions: How does energy form? How are atoms structured? How does matter provide chemical building blocks to build an organism? How does energy assemble the pieces of organisms? What kinds of systems to living systems need? Where do living systems get their energy? MATTER AND ENERGY Matter is particles of atoms/molecules. It is anything that takes up space and has mass. All atoms/molecules are constantly in motion. The speed of the movement depends on the state of a substance (water , gas, solid) Energy comes in many different forms. However, they fall under two categories: -Potential energy -Kinetic energy There are many types of energy. However, All living systems need chemical energy, thermal energy, electrical energy, and mechanical energy. POTENTIAL ENERGY KINETIC ENERGY -chemical energy: energy that's stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules. -mechanical energy : energy stored in objects that create tension (rubber bands, springs) -Nuclear energy: Energy stored in the nucleus of an atom. It is what keeps the nucleus together. Large amounts of energy is released when the atoms are combined or split apart. Nuclear power plants split open the nuclei of uranium atoms in a process called * frission. The sun combines hydrogen atoms in a process called *fusion. -Gravitational energy: Energy stored in an object's height/weight. The heavier/higher an object is, the more gravitational energy it has. -Electrical energy: Electrons moving through a wire. It can operate things such as cell phones, kind of like a battery. Lightning is an example of -Radiant energy : Electromagnetic energy that travels in transverse waves. Light is an example of radiant energy(it is visible.) -Thermal energy: Also called, heat, thermal energy is the vibration/movement of the atoms/ molecules of substances. When a substance is heated up, the molecules move faster and collide faster(atoms too.) Geothermal energy is a example of thermal energy of the earth. -Motion energy: stored in movement in objects. The faster an object moves, more energy builds up and when it slows down, the energy is released. -Sound: Movement of energy in waves. When a force causes an object to vibrate. The vibration is the sound wave. ENERGY BUILDS UP EVERYTHING! Energy is a force. It helps build structures of an organism. Before structuring an organism, energy must first build an atom. In an atom, protons and neutrons circle around the nucleus, while the electrons circle around it. The Protons and neutrons are responsible for the atomic mass of an atom(believe or not, even a single atom has mass. Since an atom has mass, it is a matter. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space.) *Energy can be changed from one form into another OPPOSITES ATTRACT! When to atoms form a bond, it is called a “covalent bond” Atoms share electrons. When atoms bond, they are held there by a tight force, a magnetic force. When atoms come together, they create molecules. Molecules are made up of one or more atoms. MOLECULES TO CELLS As molecules start to form, they create single “elements” (Look at periodic table of the elements.) Molecules come together to create cells (which are the smallest form of an organism.) A cell is made up of trillions of atoms. Atoms are the units of cells, and cells are the units of life/systems/organisms. *Reminder: Matter is the particles of atoms/molecules. Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. Although atoms are extremely tiny, they still have mass. CELLS ARE THE BASIC UNIT OF LIFE Organisms that are made up of one cell is called a “unicellular organism” Most living things are made up of many cells and are called :multi cellular organisms Differentiation: Process in which cells of a multi cellular individual become specialized during development. (Ex: An organism transfers from a zygote into a complex form of tissues and cell types) Life on earth get their energy from the sun. Organisms capture energy from the sun and change it into another energy that can be used by living things. Organisms that obtain energy by making our own food (such as plants) are called “auto trophs” - Auto trophs use energy from the sun and change water and carbon dioxide from the environment into sugar and starches. Our bodies need sugar. It is where we get some of our energy. Question: What is in sugar that gives us energy? SUGAR Each sugar molecules contains of 12 carbon atoms, 22 hydrogen atoms, and 11 oxygen atoms (C12H22O11). Because sugar is made up of these three elements, it is another form of compound called “carbohydrate” ENERGY USE AND HOMEOSTASIS Living things go through a process called “metabolism” (which stores molecules for immediate use in another reaction) Living things must maintain stable internal conditions. For example, a plant has to have water. It can’t have too less water or too much or it will die!) With homeostasis, an organism has freedom to adapt to change in an environment. Homeostasis is the balance of an organism. MATTER AND ENERGY Matter and energy are extremely important to biology. There is a process of learning about biology and learning about atoms , molecules, energy, and matter are the first things you have to know to get started on an expedition to learning about the learn around us. Atoms, energy, etc. all create everything in the world today and it is crucial that we all know how that works to fully understand the concept of biology. SOURCES http://www.qrg.northwestern.edu/projects/vss/docs/thermal/3-where-does-energy-comefrom-and-go.html http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/NSC/2-matter.htm http://library.thinkquest.org/3659/energy/matterandenergy.html http://www.nyu.edu/pages/mathmol/textbook/atoms.html http://books.google.com/books?id=ANT8VB14oBUC&pg=PA7&lpg=PA7&dq=how+does+ene rgy+assemble+an+organism's+pieces%3F&source=bl&ots=cxVM5ySed9&sig=4SR5OVImADJtuOobMgpfyUrJvg&hl=en&ei=ww6iTLelE83wngei8uT1Ag&sa=X&oi=book_result &ct=result&resnum=3&ved=0CBsQ6AEwAg#v=onepage&q&f=false http://www.exploratorium.edu/cooking/candy/sugar.html http://www.eia.doe.gov/kids/energy.cfm?page=about_forms_of_energy-forms http://academic.brooklyn.cuny.edu/biology/bio4fv/page/covalenb.htm http://www.blurtit.com/q378098.html Owl book and blue book