Oct.29th - University of Maine System
advertisement

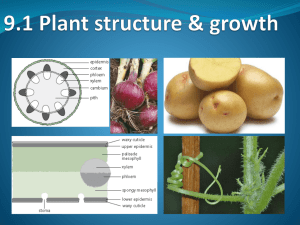
Day T Th T Th T Th T Date Reading Topic 10/15 no class – October Vacation 10/17 More plant development 10/22 Ch. 8 Mechanisms of morphogenesis 10/24 More morphogenesis 10/29 Ch. 10 Cell differentiation 10/31 Happy Halloween! Stem cells 11/5 quiz on Flowering video handout Ch. 11 Organogenesis Th T Th 11/7 11/12 11/14 T 11/19 Th More Organogenesis Ch. 12 Development of the nervous system EXAM 2 Chapters 2, 7, 8, 10 Drosophila, plants, cell biology, differentiation 11/21 Ch. 9 The saga of the germ cell T 11/26 More on reproduction term paper is due at the beginning of class on Tuesday, 11/19 Th 11/28 Your no class – Thanksgiving Break Also remember there are two, short writing assignments, each worth 20 points. Pick any topic in developmental biology (except your term paper topic) and learn more about it. Then write a two page paper and include all the sources you used (those can include any sources including web sites, newspapers, TV, etc). These are due anytime. Comparing animals and plants: Invented multicellularity independently Some differences: No germ line cells in plants (plants are easy to clone. No maternal factors???) No morphogenesis in plants (very simple fate maps) Plant cells contain plasmodesmata (a type of gap junction between cells) Comparing animals and plants: Invented multicellularity independently Some similarities: Totipotency (each cell retains the entire genome = genomic equivalence) Stem cells (called initials in plants) Stem cell niches (called meristems in plants) Homeotic genes BUT the genes are different in plants vs animals (they are not orthologs) Animal terms = totipotent, pluripotent Plant term = indeterminant 7.46 leaf shape Evolution of meristems: Pteridophytes, like ferns, have a single meristematic cell. Gymnosperms have a multicellular, but less defined organization (For example, they don’t have the organized layers cells of the tunica and corpus.) Angiosperms have the highest degree of organization. Several orthologs are found in the meristem cells of all plants. 7.10 stem/leaf pattern 7.21 root meristem 7.15 chimera 7.16 corn meristem fates 7.13 apical meristem 7.12 stem cell regulation STEM CELL NICHE 7.1 Arabidopsis thaliana 7.24 inflorescence meristem http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Florigen Thigmomorphogenesis = development affected by touch, breeze, etc. Examples of regulation of plant development by auxin 1.) patterning the early embryo (proteins pump auxin) 2.) patterning leaf primordia = phyllotaxy 3.) patterning lateral bud growth = apical dominance 6.18 leaf primordia phyllotaxy 7.19 leaf lateral inhibition (incorrect hypothesis) 7.20 auxin and leaf primordia