Statistics Chapter 1 Review Worksheet
advertisement

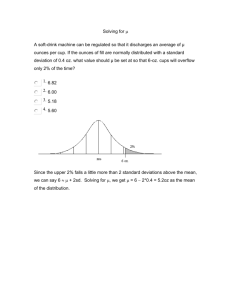
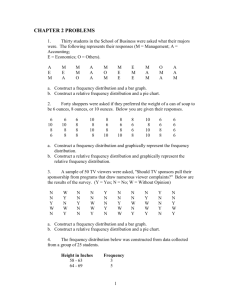
Name: ___________________________ Chapter 1 Review Part 1 – Whatever you do not finish is for homework 1. True or False a. Inferential statistics is based on probability b. Based on her electric bills from last year, Mrs. Smith expects she will be paying $75/month this year. This is an example of descriptive statistics. c. A person's hair color would be an example of a quantitative variable. d. The variable of height is an example of a quantitative variable. e. The number of birds in a tree is an example of a continuous variable. f. Quantitative data can be further classified as continuous or nonsequential. g. In a research study, it is always preferable for the researcher to carefully choose his participants rather than randomly select them from a suitable group. h. Questioning every 14th customer leaving a theatre about the movie they had seen, would be an example of systematic sampling. i. A dependent variable can also be referred to as an outcome variable. j. Probability is used as a basis for inferential statistics. k. The heights of the mountains in the state of Alaska are an example of a variable. l. The lowest level of measurement is the nominal level. m. When the population of college professors is divided into groups according to their rank (instructor, assistant professor, etc.) and then several are selected from each group to make up a sample, the sample is called a cluster sample. n. The variable temperature is an example of a quantitative variable. o. The height of basketball players is considered a continuous variable. p. The boundary of a value such a 6 inches would be 5.9-6.1 inches. q. When running an experimental study, the group that is manipulated can be called the treatment group. 2. Variables with values that are determined by chance are called _____________. A) B) specialized. erratic variables. C) D) random variables. inconsistent variables. 3. What level of measurement classifies data into mutually exclusive categories in which no order or ranking can be imposed on the data? A) nominal B) ordinal C) interval D) ratio 4. The number of ads on a one-hour television show is what type of data? a. Nominal b. Qualitative c. Discrete d. Continuous 5. What are the boundaries of 25.6 ounces? a. 25-26 ounces b. 25.55-25.65 ounces c. 25.5-25.7 ounces d. 25.5-25.7 ounces e. 20-49 ounces 6. A researcher divided subjects into two groups according to gender and then selected members from each group for her sample. What sampling method was the researcher using? a. Cluster b. Random c. Systematic d. Stratified 7. Explain the difference between qualitative, quantitative, discrete, and continuous variables. 8. Name and define the four basic sampling methods. 9. Give three examples each of nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio data.