Formative Guide 1 Answers
advertisement

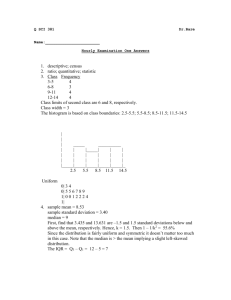
Elementary Statistics Unit 1 Formative Guide Match the word to the definition. (problems 1-17) a. b. c. d. e. f. population Statistics (the course) descriptive statistics inferential statistics sample parameters g. h. i. j. k. l. qualitative quantitative cluster systematic discrete statistics m. n. o. p. q. stratified random right skewed left skewed continuous _____b____ 1) is a collection of methods for planning experiments, obtaining data, and then organizing, summarizing, presenting, analyzing, interpreting, and drawing conclusions based on the data. _____a____ 2) is the complete collection of elements to be studied. _____e____ 3) is a sub-collection of elements drawn from a population. _____c____ 4) are things that describe a sample’s contents. _____d____ 5) is making inferences about what sample data may indicate about a population _____g____ 6) data can be separated into different categories distinguished by some non-numerical characteristic. _____h____ 7) data consists of numbers representing counts or measurements. _____k____ 8) data result from either a finite number of possible values or a countable number of possible values. _____q____ 9) numerical data results from infinitely many possible values that can be associated with measurement error. _____n____ 10) sampling is when members of the population are selected in such a way that each has an equal chance of being selected. _____m___ 11) sampling is when you subdivide the population into at least two different subpopulations that share the same characteristics and then draw a sample from each subgroup. _____f____ 12) are numbers that describe a population. _____l____ 13) are numbers that describe a sample. 1 Elementary Statistics Unit 1 Formative Guide _____i____ 14) sampling is when you divide the population into sections and randomly select some of those sections, and then choose all the members from the selected sections. _____j____ 15) sampling is when you choose some starting point and then select every kth element in the population. _____p____ 16) is when the mean is significantly less than the median. _____o____ 17) is when the mean is significantly greater than the median. List the level of measurement that best fits the following variables. __nominal _18) asking people their political affiliation __interval _ 19) measuring the temperature in Fahrenheit ___ratio __ 20) measuring the time it takes to run a race __ordinal _ 21) rating how good a movie is by awarding it one, two, three or four stars Use the following set of data values for problem numbers 20 - 25. 2, 5, 7, l2, 7, 4, 9, 5, 0, 7 Compute the Following. ___ 5.8____ 22) mean ____12____ 23) range ____6_____ 24) median ___11.76__ 25) variance ____7_____ 26) mode ____3.43__ 27) standard deviation 2 Elementary Statistics Unit 1 Formative Guide Answer true or false to the following statements. ____T_____ 28) A histogram can be used at any level of measurement. ____F_____ 29) The range is not effected by outliers. ____F_____ 30) The 50th percentile is equal to the mode. ____T_____ 31) The lowest level of measurement the mean can be computed at is interval. ____T_____ 32) A percentile is a value that shows what percentage of scores in a given data set are at or below a given value. ____F_____ 33) The mean is the most appropriate measure of central tendency when the data set contains outliers. ____T_____ 34) A frequency polygon is sometimes referred to as a line graph. ____T_____ 35) A box plot would be preferred over a histogram for multiple comparisons. ____F_____ 36) The median is not appropriate at the ordinal level of measurement. ____T_____ 37) The standard deviation is the square root of the variance. ____F_____ 38) A convenience sample is a statistically random method of data collection ____F_____ 39) Pie charts should be used at the Ratio level of measurement. ____F_____ 40) The range is always the most appropriate measure of variability at the ratio level. ____F_____ 41) Cluster sampling is used to provide each group input into the study. ____T_____42) A line graph can be used for multiple comparisons. 3