Chapter 8, Lesson 4 The Ming Dynasty
advertisement

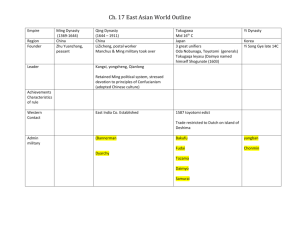
The Ming Dynasty SPI 7.26- I can draw evidence from the informational text to analyze the contributions made during the Ming dynasty such as building projects, the reconstruction of the Great wall, isolationism, and sea voyages. I. The Rise of the Ming A. In 1294, Kublai Khan died, Yuan Dynasty quickly lost people’s support – The Yuan Dynasty was overthrown by a peasant uprising B. In 1368, military officer Zhu Yuanzhang became emperor 1. Founded the Ming (“brilliant”) Dynasty a. Ming Dynasty lasted 300 years 2. Zhu took the name Hong Wu (“Military Emperor”) a. was a harsh leader b. died, 1398 C. Hong Wu succeeded by son, Yong Le 1. moved capital to Beijing 2. built the Forbidden City, where only the emperor’s family & top officials could enter 3. China’s emperors lived in Forbidden City for 500 years D. Like Pax Romana, peace in China led to economic & artistic rebirth 1. Roads, canals, farms rebuilt 2. New crops & farming techniques led to population growth 3. Newly wealthy merchants & artisans led revival of literature & theater of literature & theater II. Architecture A. Era of large civil engineering projects B. The Great Wall – The Great Wall was almost completely rebuilt by the Ming Dynasty 1. The tall, wide bricks that are still standing today were built by the Ming Dynasty C. The Forbidden City – This was the emperor’s palace and was located inside the capital city of Beijing 1. Had almost 1000 building and covered over 185 acres of land D. The Grand Canal – Was rebuilt during the Ming Dynasty 1. Had a significant impact on trade and helped the economy flourish III. Government A. Strong Ming government provided peace & security B. Ming emperors conducted a yearly census 1. Census - count of number of people in a place 2. Helped empire collect taxes C. Government ran by the Civil Service Organization 1. Men studied for years to take the civil service exam 2. Top scoring men were given the best jobs 3. Exam covered many subjects, but a large majority of the test was over the studies of Confucius IV. Chinese Exploration A. Ming emperors built fleets of ships for trade & war B. Zheng He led large trade voyages 1. 28,000 men 2. >300 ships 3. Largest ship was 5 times as large as Santa Maria C. Zheng He traveled to SE Asian islands, India, E. Africa 1. Returned with exotic animals from Africa D. Later emperors ended voyages, fearing outside influence in China V. European Arrival A. In 1514, Portuguese ships made first contact with China since Marco Polo 1. Portuguese wanted to trade & convert Chinese to Christianity 2. China was powerful & saw Europeans as uncivilized VI. The Fall of the Ming A. Ming Dynasty declined for reasons similar to Rome 1. Corrupt government officials 2. Heavy taxes on citizens 3. Decay of law & order B. Northern barbarians known as Manchus invaded 1. Captured Beijing, 1644 2. Ended Ming Dynasty, founded Qing Dynasty The Ming Dynasty It Matters Because: The Ming Dynasty’s early emperors wanted to spread China’s influence. By the late 1500s, however, China had limited its contact with the rest of the world. \ Standards and Objectives I can analyze the contributions of the Ming Dynasty SPI 7.26- I can draw evidence from the informational text to analyze the contributions made during the Ming dynasty such as building projects, the reconstruction of the Great wall, isolationism, and sea voyages. I. The Rise of the Ming A. In 1294, Kublai Khan died, Yuan Dynasty quickly lost people’s support – The Yuan Dynasty was overthrown by a peasant uprising B. In 1368, military officer Zhu Yuanzhang became emperor 1. Founded the Ming (“brilliant”) Dynasty a. Ming Dynasty lasted 300 years 2. Zhu took the name Hong Wu (“Military Emperor”) a. was a harsh leader b. died, 1398 I. The Rise of the Ming C. Hong Wu succeeded by son, Yong Le 1. moved capital to Beijing 2. built the Forbidden City, where only the emperor’s family & officials could enter 3. China’s emperors lived in Forbidden City for 500 years D. Like Pax Romana, peace in China led to economic & artistic rebirth 1. Roads, canals, farms rebuilt 2. New crops & farming techniques led to population growth 3. Newly wealthy merchants & artisans led revival of literature & theater top II. Architecture A. Era of large civil engineering projects B. The Great Wall – The Great Wall was almost completely rebuilt by the Ming Dynasty 1. The tall, wide bricks that are still standing today were built by the Ming Dynasty C. The Forbidden City – This was the emperor’s palace and was located inside the capital city of Beijing 1. Had almost 1000 buildings and covered over 185 acres of land D. The Grand Canal – Was rebuilt during the Ming Dynasty 1. Had a significant impact on trade and helped the economy flourish III. Government A. Strong Ming government provided peace & security B. Ming emperors conducted a yearly census 1. Census - count of number of people in a place 2. Helped empire collect taxes C. Government ran by the Civil Service Organization 1. Men studied for years to take the civil service exam 2. Top scoring men were given the best jobs 3. Exam covered many subjects, but a large majority of the test was over the teachings of Confucius IV. Chinese Exploration A. Ming emperors built fleets of ships for trade & war B. Zheng He led large trade voyages 1. 28,000 men 2. >300 ships 3. Largest ship was 5 times as large as Santa Maria C. Zheng He traveled to SE Asian islands, India, E. Africa 1. Returned with exotic animals from Africa D. Later emperors ended voyages, fearing outside influence in China V. European Arrival A. In 1514, Portuguese ships made first contact with China since Marco Polo 1. Portuguese wanted to trade & convert Chinese to Christianity 2. China was powerful & saw Europeans as uncivilized VI. The Fall of the Ming A. Ming Dynasty declined for reasons similar to Rome 1. Corrupt government officials 2. Heavy taxes on citizens 3. Decay of law & order B. Northern barbarians known as Manchus invaded 1. Captured Beijing, 1644 2. Ended Ming Dynasty, founded Qing Dynasty Table Top Twitter You will be reading 4 articles on the following topics: • Sea Voyages • Isolationism • Forbidden City • Reconstruction of the Great Wall Table Top Twitter Reading Activity 1. Read the article in front of you in the time allotted. 2. Comment below the article by writing a 1 sentence tweet that summarizes the article. 3. Use 1 or more hashtags after your tweet that summarizes the article. Be creative! 4. Pass the articles when instructed Create a Question • With your group, write a test question for each of the articles. • Write the test question on the back of the article. • Be sure to write the answer to the questions whether it Question Review • Now that we have created questions about the articles, let’s see if we can answer them as a class. • Each group will read their question out loud and challenge the rest of the