Macromolecules Test Answers
advertisement

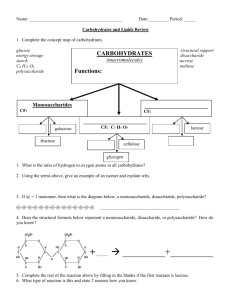
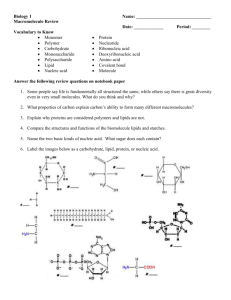
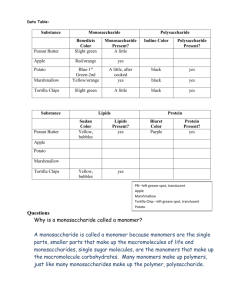
Macromolecules Quest Name:___________________ Period:__________ 1. Which of the following is true of monomers? a) Monomer is another word for macromolecule b) Monomers make up polymers c) Polymers make up monomers d) Monomers are large molecules made by smaller subunits 2. The process in which smaller units join up to make bigger units is called: a) Monomerization b) Monosaccharide c) Polymerization d) Lysis reaction 3. A carbohydrate is: a) a sugar b) a fat c) a protein d) easily and quickly used for energy in any form 4. The simplest form of a carbohydrate is called a(n): a) monosaccharide b) polysaccharide c) monose d) amino acid 5. Which of the following is a polysaccharide? a) glucose b) starch c) lactose d) sucrose 6. Animals store sugar in glycogen. Glycogen is a: a) monosaccharide b) polysaccharide c) lipid d) protein 7. A characteristic of lipids is that they: a) are insoluble b) need to be broken down before they can be used c) contain genetic information d) need to be a specific shape to work 8. The monomers of lipids are: a) glycerol and amino acids b) amino acids c) nucleotides d) glycerol and fatty acids 9. Which of the following is true? a) saturated lipids are often liquid, unsaturated lipids are solid b) saturated lipids are often solid, unsaturated lipids are liquid c) both saturated lipids and unsaturated lipids are solid d) both saturated lipids and unsaturated lipids are liquid 10. What happens to the melting point of a fatty acid as the number of double bonds increases? a) it increases b) it decreases c) it does not change d) there is no correlation between melting point and double bonds 11. What type of macromolecule is a hormone or a steroid? a) carbohydrate b) lipid c) nucleic acid d) protein 12. What is the monomer of a nucleic acid? a) fatty acid b) amino acid c) nucleus d) nucleotide 13. What is an example of a nucleic acid? a) pasta b) vinegar c) DNA, RNA d) meat 14. What is the monomer of a protein? a) fatty acid b) amino acid c) monosaccharide d) nucleotide 15. What is the most important characteristic of a protein? a) shape b) solubility c) size d) color 16. A biological catalyst is called: a) a carbohydrate b) a nucleic acid c) a lipid d) an enzyme 17. Which of the following is a sugar? a) lactase b) amylase c) ribose d) fatty acid 18. Which of the following is an enzyme? a) fructose b) polymerase c) ribose d) monosaccharide 19. What is the minimum amount of energy required to undergo a chemical reaction? a) activation energy b) minimum state c) catalyst d) substrate 20. Which of the following is true of enzymes? a) they raise the activation energy b) they keep the activation energy constant c) they lower the activation energy d) none of the above 21. Enzymes convert starting molecules into different molecules. What are those starting molecules called? a) products b) substrates c) catalysts d) proteins 22-23 (2 pts) Explain why we did not detect glucose when lactase was added to the sucrose solution. Lactase, an enzyme, is a specific shape to a single substrate (lactose) which means it can only break down lactose (into glucose and galactose). Lactase does not match up with sucrose, which is why we did not detect glucose (lactase cannot break down sucrose, it can only break down lactose) 24. Describe one way you could denature a protein. To denature a protein (change a protein’s shape), you can change the pH or the temperature. 25-26 (2 pts) Explain the different characteristics between a saturated and an unsaturated lipid and the reason for them. Saturated lipids = typically solid, single-bonded carbons (saturated with hydrogen atoms), more stiff bonds Unsaturated lipids = typically liquid, double-bonded carbons, more fluid/flexible bonds 27-29 (3 pts) What are the 3 categories of lipids? ____fats_______, ______oils____, ______waxes_ 30-31 (2 pts) The evening before a cross country race, should you eat a loaf of bread or drink a bottle of Gatorade? For credit, explain why and how you know. A whole day before a big athletic event, you should eat starch which is a polysaccharide. The human body can only use carbohydrates (sugars) in their simplest form (monosaccharides), which means polysaccharides need to break down first, which takes time. If you eat a starch the night before, it will have time to break down and be ready the next morning for energy use. If you were to drink Gatorade (still a carbohydrate but it contains monosaccharides), the sugars would not need to break down and would be used up instantly, and it would not be available the next day during the race. 32-33 (2 pts) In terms of activation energy, why are enzymes considered biological catalysts? Also, what do enzymes do? Explain. Enzymes are biological catalysts which means they speed up chemical reactions without being consumed in the reaction. They lower the activation energy which is the energy required for a chemical reaction to happen (they make reactions happen faster and more easily).