Group 1 country presentation
advertisement

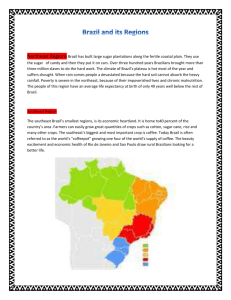
Team 1 Kent Copeland Population Birth – 201,103,330 (5th largest) rate – 18.11/1000 pop. (108th) • Niger – 51.08/1000 (224th) • Monaco – 7.03/1000 (1st) • United States – 13.83/1000 (151st) Death rate – 6.35/1000 pop. (155th) • Haiti – 32.31/1000 (226th) • UAE – 2.08/1000 (1st) • USA – 8.38/1000 (91st) Age Categories (0-14, 15-64, 65+) • Brazil – 26.7%, 66.8%, 6.4% • USA – 20.2%, 67%, 12.8% Gender Composition • Brazil – 0.98 male/female • USA – 0.97 male/female Very similar breakdowns across the different age categories. Brazil (6th) has a labor force of 101.7 million Median age – 28.9 (8 years younger than USA) Increased mobilization of women Urban pop. – 86% Urban growth – 1.8% Bauxite Gold Iron ore Manganese Platinum Tin Uranium Petroleum Hydropower Coal Coffee Cotton Brazil nut Timber Rubber GDP (PPP) • Brazil - $2.01 trillion (10th) • USA - $14.12 trillion (2nd) Inflation rate • Brazil – 4.9% • USA – (-0.3%) Unemployment • Brazil – 8.1% • USA – 9.3% Growth rate • Brazil – (-0.2%) • USA – (-2.6%) rate Currency Regulations • No restrictions on any currency up to BRL 10,000 (USD $5,820) • Higher than BRL 10,000 – must be declared Exchange rate – 1.7278 BRL per 1 USD on November 27, 2010. Financial System • Historically unstable • Increased reserve requirement • Ban on short selling • Credit Guarantee Fund (FGC) – provides capital funding to banks to preserve system Tax System • Overall rate – 34% • IOF tax – 4% Stock Market • BM&F Bovespa • Market capitalization of $1.338 trillion (10th) • 375 companies listed Key Products • Coffee, soybeans, wheat, rice, sugarcane • Textiles, chemicals, lumber, iron • Steel, aircraft and vehicle parts Business Segment (Ag, In, Ser) • Brazil – 20%, 14%, 66% • USA – 1%, 19%, 80% IMPORTS Machinery Electrical and transport equipment Chemical products Oil Automotive parts Electronics EXPORTS Transport Equipment Iron ore Soybeans Footwear Coffee Autos Standard of living and housing • Urban areas are expensive • Wealthy live in lavish houses • Middle class live in small apartments • Poor live in favelas, slums. 26% below poverty line Poor infrastructure, water, sewage Claimed by Pedro Alvares Cabral (Portugal) in April 1500. Slaves imported in the 1600s Portuguese Empire headed in Rio de Janeiro from 1808-1821 Declared independence on September 7, 1822. Slavery abolished in 1888. Old Republic – 1889 to 1930 Populism – 1930 to 1964 Military dictatorship – 1964 to 1985 Democracy – 1985 to present Dilma Rousseff elected President. Member of the Workers’ Party. Plans to continue social programs. Type of government • Federal republic • Constitution ratified on Oct. 5, 1988 • 26 states and 1 federal district • Bicameral legislature • Similar to the USA Key Issues and Controversies • Gay marriage • Privatization • Capital punishment • Drug liberalization • Improving social welfare programs State of Civil Liberties • Title II, Ch. I, Article 5 – free speech, religion, etc. • Bolsa Familia – Grants for education for poor • Torture and Afro-descendents rights • Manoel Mattos killed by gunmen Risk Factors • Political Instability Index Brazil – 5.4 USA – 5.3 • Brazil’s score should decrease after the successful transition of power in 2010 election. Derived from Portuguese civil law Based on Roman Codes Based on statutes Introduced a form of stare decisis No compulsory ICJ jurisdiction Effectiveness enforcement is determined by Fine individuals for criticism of candidates 3 months before an election ($90,000) Brief summary of Brazilian business law: http://www.lexmundi.com/images/lexmun di/PDF/guide_brazil.pdf) Eastern South America Borders Atlantic Ocean Borders all South American countries except Chile and Ecuador Total area – 8,514,877 sq. km. (5th) USA is third with over 9.8 million sq. km. Flat to rolling lowlands Plains, hills, and mountains Narrow coastal region Arable land – Brazil 6.93%, USA 18% Highest point • Brazil – Pico da Neblina 2,994 meters • USA – Mt. McKinley 6,194 meters Six regions: • Tropical rainforest • Tropical wet and dry • Tropical monsoon • Semiarid • Humid subtropical • Subtropical highland Temperatures • High along equator • Really high in Northeast • Cold in the South • Wide temp variations in Middle-West • Warm in Southeast Rainfall • Amazon – 80 in., long dry season • Northeast – little rainfall, long droughts • Middle-West – 60 to 80 in., smaller dry season • Southeast – parts receive up to 175 in., no dry season • South – no dry season Conditions • One of the most polluted countries in the world • 91 million tons of carbon emissions • About 1/10 the irrigated land of the USA • Shortage of freshwater due to improper mining techniques Key Challenges • Deforestation of Amazon Basin • Illegal wildlife trade • Air and water pollution • Oil spills Response • Increase law enforcement and land reform • • • • • policy Rehabilitate deforested areas Increased public transportation Rodoanel Mario Covas Cleaner vehicles Better monitoring and clean up One of the BRIC countries Increased mobilization of women Improvements in social welfare programs More citizens becoming highly educated Several ports, good infrastructure High GDP Adam Stone Kent Copeland Parental Roles Traditionally, women raised children, men earned income. Currently, more dual-worker households • Men take on more household chores • Some men become insecure • Women become stable force • More share approach Child rearing practices • Expected to contribute to family • Treated like adults • Taught value of interpersonal relationships • Nepotism is common Living arrangements • Nuclear families have close relationships with extended families. • Very common to have more than one generation under one roof. • Adult children expected to live at home until marriage. Categories and characteristics • Social classes historically divided • Workers’ Party been in power since 2002 • Bolsa Familia • Improve social welfare programs Presence of class barriers • Education and income • These two barriers are correlated • Whites and Asians are the highest class • Indians, pardos, and blacks are the lowest class Status of Ethnic Groups • The darker the skin the lower the status • Lower class are typically maids, bus drivers, or street beggars Ethnic Issues • Social apartheid • Blacks deprived of educational opportunities • Earn low wages • Live in low income neighborhoods • Spatial apartheid – separate building entrances • Youth gangs • Police violence Gender Status and Issues • 70% of women in the workforce are in the service sector • Wage disparity • More women than men attend universities • Dilma Rousseff elected President BRAZIL Roman Catholic – 73.6% Protestant – 15.4% Other – 3.6% None – 7.4% USA Roman Catholic – 23.9% Protestant – 51.3% None – 4% RITUALS Holy sacraments Baptism Confirmation Communion Penance Anointing the sick Matrimony Priesthood Seven Penitential Psalms Liturgy for the Faithful Departed Blessings Processions Exorcism Rites • Roman Rite • Latin Rite • Lent Taboos • Eating meat on the first day of Lent and Lent • • • • • Fridays Use of contraceptives Sex with unclean women Homosexuality Celibacy of priests Remarriage of divorcees Brazil White 53.7% Mulatto 38.5% Black 6.2 % Other 0.9% Unspecified 0.7% United States White 64.86% Hispanic 15.1% Black12.85 % Asian 4.43% Mix 1.61% North Region – Equatorial climate, almost all of this region is covered by rainforest and it has the lowest population density of the regions Northeast Region - Very Hot Climate, this was the first region discovered by the Portuguese. It is mainly coastal areas with tourism being the biggest economic factor. Central-West Region – Savanna Climate is very hot, most of the land here is used for grazing livestock Southeast Region – Tropical to Semi-arid climate, this region is the major powerhouse of the Brazilian economy. Heavily covered by highways, it is the most populous region and home to three of the largest cities in Brazil Handshakes are the most common form of greeting between business colleagues. It is polite to say ‘muito prazer’ (‘my pleasure’) Accept any food or coffee offered to you. Saying no can be seen as insulting Giving a gift is not required at a first business meeting; instead buy lunch or dinner New Years Day – January 1 Carnival – varies February or March Easter – same as U.S. Tiradentes’ Day – April 21 Labor Day – May 1 Corpus Christi – varies May or June Independence Day – September 7 Our Lady of Aparecida – October 12 All Souls Day – November 2 Republic Day – November 15 Christmas Day – December 25 Usually 10% Portuguese – Official language and spoken by 99% of Brazilians International business may also be conducted in English, French, German, etc. Good conversation topics include soccer, family, and children Do not bring up topics of conversation such as crime, corruption or deforestation as these are sensitive issues at the moment. Brazilians pride themselves on their ability to be in control, so acting in a similar fashion will improve your relationship and interactions with your Brazilian counterparts. Touching arms and elbows and backs very is common Brazilians tend to stand close together when they communicate and are not afraid to touch each other. Conflict Style - How do they handle conflict? • Arbitration • Mediation Negotiation Style • Person to person, not business to business • If you are invited to a Brazilian's house: – Arrive at least 30 minutes late if the invitation is for dinner. – Arrive up to an hour late for a party or large gathering. – Brazilians dress with a flair and judge others on their appearance. Casual dress is more formal than in many other countries. Always dress elegantly and err on the side of over-dressing rather than under- dressing. – If you did not bring a gift to the hostess, flowers the next day are always appreciated (Brazil Language, Culture, Customs and Etiquette, Website). Chase Luft Availability Population 174,500,000 Urban Households 83.7% GDP US$452.4 Billion Illiteracy Rate 12.3% Fixed Phone Lines and Cell Phone Lines 38.5% Personal Computers 6.3% Internet Level of Users Sophistication 14,000,000 Infrastructure Conditions • World Cup 2014 • Olympics 2016 Tariffs Country All Products Avg. Tariff* United States 4.3% Standard Deviation # 11.3 Agricultural Products Avg. Tariff* 8.5% Standard Deviation # 30.2 Industrial Products Avg. Tariff* 3.7% Standard Deviation # 5.1 Bribery Level of corruption Ethical Brazil or the use of influence considerations of doing business in Who why? does Brazil do Business with and Stereotype of Americans • Perceived as cold people Business Practices Chase Luft Private or Public Emphasis? Educational Attainment Levels Literacy Rate – 88.6% Resources Available for Govt. Funding Characteristics for High Education Systems Good Training? • Questions asked: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Are you required to take a certain amount of foreign language courses? Do you take any courses in English? If so, how many? Are your textbooks American textbooks or are they international versions, Brazilian texts or something different? Do you take any international business, management or any international based courses? If you were going to describe a day in your life at your school, how would you describe it? Would you say that there is bribery and corruption in Brazilian business? What country(ies) does Brazil do most of its business with? When comparing Brazil to what you know about the United States, what would you say are significant differences and similarities? In Brazil, do people look at business relationships or personal relationships as more important? Are women in upper management positions in Brazil? From what you know about the computer company Dell, how much power do you think they have in the Brazilian market and if you have any knowledge of how they operate in Brazil, please include that. Gustavo Alcimin Livia Mello Luiz Lamardo Alves Silva English required for University acceptance The english is very easy on the admissions test – you don’t have to really know it. We are required to take foreign language Never took English courses in Brazil I don’t have disciplines on english only research material My school doesn’t offer classes in english Textbook languages are usually in sync with topic related to We use all types, but it’s rare a mandatory textbook. Textbooks used are often in english, portuguese when authors are respected Yeah, a bunch We have management disciplines and international market, elective in my major I don’t take any international courses with that name in it Spent more time outside of class than inside The classes are four hours each, between classes we can do internships. Class in the morning, internship/work during afternoon, study during night 6 Yes, as in any other country in the world Unfortunately in some fields, yes. There is still some bribery and corruption 7 USA, China, and other BRIC countries. China, South America, US, Europe China, US, Latin America, Europe 8 Several, but a long discussion needed to answer that. Working and living similar, salary is lower. We have influenced American TV and music. Food is different and way of life 9 N/A Personal relationships even in business. Makes it easier. Personal relationships are more important 1 2 3 4 5 Brazillian elected president is a Eric Hamilton Employee/Employer Relations Importance of Personal Relationships at work Typical Management Style Typical Leadership Style Decision Making Practices View of Authority Primary Means of Motivating Employees Common Types of Organizational Structure Role/View of Women in Business Hiring Practices and Preferences Compensation Structure Minimum Wage Key Employment Laws Benefits for Employees Appropriate Business Dress Business Cards Work Schedule Measurement System Business Meeting Behavior After-Meeting Etiquette Do’s and Don’ts