Measurement and Converting Units PowerPoint
advertisement

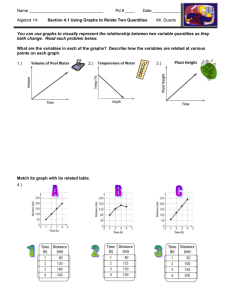
Objective: We will review measurement with a lab investigation. Homework: • Complete Measurements Lab! Objective: We will review measurement with a lab investigation. Homework: • Complete “1. Stop and think: a. and b.” on Measurements Lab if not already finished. • Measurement : – a determination of the amount of something. What are the two parts to measurement? : Value (a number) Unit • English System – Most familiar to us in U.S. – What units are common? • Miles, yards, feet, pounds, pints, quarts, gallons, cups, teaspoons • SI – International System of Units – Used by most countries and by the scientific community. – Metric system based on factors of 10. – Common Units? • Meters, liters, grams, celsius • Would you say the person who shot this arrow was accurate or precise? • Accuracy – how close a measurement is to the accepted value. • Would you say these arrows are accurate or precise? • Precision – how close together repeated measurements are to one another. • The smallest interval that can be measured. – The “sharpness” of a measurement. ~ Write Your Name ~ Objective: We will briefly discuss conversions and finish our lab investigation of measurement. Homework: • Complete “Measurements” lab and answer HW questions on pg. 5 of lab. ~ Write Your Name ~ Objective: We will briefly discuss conversions and finish our lab investigation of measurement. Homework: • Complete “Measurements” lab and answer HW questions on pg. 5 of lab. • Have you ever had to convert something? Can you give an example? – Conversions help us to relate quantities. – Conversion Factor – a ratio that is used when setting up a unit conversion problem. It is often used when you want to convert SI units to English units. • Ex. - Convert 4.5 ft to cm (there are 30.48 cm in 1 foot) • Use the Decimal Point Rule and conversion chains! King Henry Died By Drinking Chocolate Milk • Given: How many decimeters in 0.0025 kilometers? King Henry Died By Drinking Chocolate Milk • Visual Representations of data that are used to show how variables are related. • What are some ways that graphs are used in our daily lives or in the scientific community? • Various Types of graphs: – Scatterplot graph ( XY graph) – used to visualize 2 variables thought to be related – Bar graph – compares data grouped by a name or category. – Pie graph – Shows the amount each part makes up to form the whole (100%) – Line graph – often shows how data changes over time. • Interpreting graphs: – With scatter plot graphs, you have 2 variables • Independent Variable – might influence another variable (ex. – water depth) • Dependent Variable – is influenced by the independent variable (ex. – water pressure) • Interpreting graphs: – With scatterplot graphs and line graphs, you have direct and indirect relationships • Direct relationship – one variable increases with an increase in another variable. – Ex? – Depth vs. Pressure scatterplot graph • Indirect relationship – one variable decreases when another variable increases • MIXES TUCS: – Trick to remember how to make a graph – – – – – – M: IX: ES: T: U: CS: Maximize your graph Independent variable on x-axis Equally spaced scale increments Title (includes axis names) Units and labels on both axes Continuous smooth curve connects data • How to read a graph: • When measuring time you can answer two types of questions. What are they? – 1) What time does the game begin? – 2) How long does the game last? (also known as a time interval) • Name some familiar units of measuring time: – Seconds – Hours – Minutes – Years – Centuries • Distance – the amount of space between two points. – The meter stick is a common tool used for measuring length – Do you know the distance you travel to school each day? – What units do we use to measure distance? • Meters, kilometers, light years (1 ly = 9.46 x 1012 km), parsec (equals about 3.26 ly), miles, feet