Assessment of Academic Achievement
advertisement

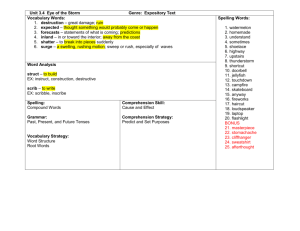
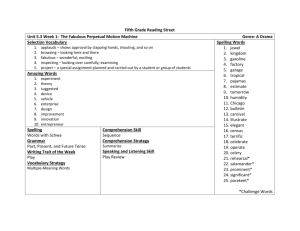
Assessment of Academic Achievement Chapter Eight CHAPTER OBJECTIVES Understand the purpose of achievement tests Understand why individually administered achievement tests are preferred rather than group achievement tests Discuss oral reading and miscues associated with it Understand the different types of reading comprehension Understand word recognition and word attack skills CHAPTER OBJECTIVES Thoroughly evaluate the various reading assessment measures Understand written composition and the tests associated with it Differentiate between mathematics and arithmetic Identify and thoroughly evaluate the various arithmetic tests Identify and thoroughly tests that measure spelling ability Identify and thoroughly evaluate the various comprehensive achievement tests ACHIEVEMENT TESTS • Tests designed to assess the academic progress of a student. • When doing an evaluation for identification and/or placement in special education, achievement tests will be individually administered. READING ORAL READING Common errors seen on oral reading tests… • • • • • • • Omissions Insertion Substitution Gross mispronunciation of a word Hesitation Inversion Disregard of punctuation Analyzing Oral Reading Miscues An oral reading error is often referred to as a miscue. Analysis of miscues can be of two types: 1. Quantitative miscues 2. Qualitative miscues Miscues are significant when… • The meaning of the sentence is altered and the student does not correct the miscue. • A nonword is used in place of a word • A partial word is substituted for the word or phrase • A word is pronounced for the student Miscues are not significant when… • The meaning of the sentences undergoes no change or minimal change • They are self-corrected by the student • They are applicable in the student’s dialect • They are later read correctly in the same passage READING COMPREHENSION Diagnostic testing often assess six kinds of reading comprehension skills: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Literal comprehension Inferential comprehension Listening comprehension Critical comprehension Affective comprehension Lexical comprehension Word Recognition Skills The purpose of word recognition tests are to explore the student’s ability with respect to sight vocabulary. Word Attack Skills Word attack skills are those used to derive meaning and/or pronunciation of a word through context clues, structural analysis, or phonics. READING ASSESSMENT MEASURES • Gates-MacGinitie Silent Reading Tests, 4th Edition • Gray Oral Reading Test- 3 (GORT-3) • Durrell Analysis or Reading Difficulty (DARD) • Gates-McKillop-Horowitz Reading Diagnostic Tests READING ASSESSMENT MEASURES • Gilmore Oral Reading Test • Slosson Oral Reading Test- Revised (SORT-R) • Spache Diagnostic Reading Scales (DRS) • Woodcock Reading Mastery Test- Revised (WRMT-R) • Test of Reading Comprehension, 3rd Edition (TORC-3) WRITTEN EXPRESSION Handwriting refers to the actual motor activity that is involved in writing. Most students are taught manuscript (printing) initially and then move to cursive writing (script) in later grades. Handwriting skills are usually measured through the use of informal assessment measures. The term writing refers to a variety of interrelated graphic skills including: • Composition • Spelling • Handwriting TESTS OF WRITTEN LANGUAGE • Test of Early Written Language- 2 (TEWL-2) • Test of Written Language- 3 (TOWL-3) • Test of Written Expression (TOWE) • Written Expression Scale (WES) • Writing Process Test (WPT) • Mather-Woodcock Group Writing Tests (MWGWT) MATH Mathematics refers to the study of numbers and their relationships to time, space, volume and geometry. Arithmetic refers to the operations or computations performed. Three types of classifications are involved in diagnostic math tests: • Content • Operations • Applications Analysis & Interpretation of Math Skills Four error types in computational analysis: 1. Incorrect operation 2. Incorrect number fact 3. Incorrect algorithm 4. Random error ASSESSMENT OF MATHEMATICAL ABILITIES • Key Math Diagnostic Arithmetic TestsRevised (Key Math-R) • Test of Early Mathematics Ability- 2 (TEMA-2) • Test of Mathematical Abilities- 2 (TOMA-2) • Diagnostic Mathematics Inventory/Mathematics Systems (DMI/MS) • Stanford Diagnostic Mathematical Test- 4 (SDMT-4) SPELLING Spelling is the ability to use letters to construct words in accordance with accepted usage. Analysis of Spelling Skills Several questions should be addressed before one begins to analyze the results of the spelling subtest: • Does the child have sufficient mental ability to learn to spell? • Are the child’s hearing, speech and vision adequate? • What are the child’s general level of spelling ability according to teacher comments, past evaluations, or standardized tests? Spelling Errors Primarily Due to Auditory or Visual Channel Deficits Certain spelling errors may be evident in students with certain auditory channel deficits: • Auditory discrimination problems or cultural problems • Auditory discrimination problems • Auditory acuity or discrimination problems • Auditory-visual association • Auditory-visual associative memory Certain spelling errors may be evident in students with certain visual channel deficits: • • • • Visual memory problems Visual memory sequence Visual discrimination problems Visual memory ASSESSMENT OF SPELLING • Diagnostic Word Patterns • Test of Written Spelling- 4 (TWS-4) • Spellmaster Assessment and Teaching Systems (SATS) COMPREHENSIVE TESTS • Brigance Diagnostic Inventory of Basic Skills • Kaufman Tests of Educational Achievement (KTEA) • Peabody Individual Achievement TestRevised (PIAT-R) • Wechsler Individual Achievement Test-2 (WIAT-2) COMPREHENSIVE TESTS • Wide Range Achievement Test-3 (WRAT-3) • Woodcock-Johnson Achievement TestIII (WJ-III) • Test of Academic Achievement SkillsRevised (TAAS-R) CHAPTER OBJECTIVES Understand the purpose of achievement tests Understand why individually administered achievement tests are preferred rather than group achievement tests Discuss oral reading and miscues associated with it Understand the different types of reading comprehension Understand word recognition and word attack skills CHAPTER OBJECTIVES Thoroughly evaluate the various reading assessment measures Understand written composition and the tests associated with it Differentiate between mathematics and arithmetic Identify and thoroughly evaluate the various arithmetic tests Identify and thoroughly tests that measure spelling ability Identify and thoroughly evaluate the various comprehensive achievement tests THE END