Photosynthesis - Cloudfront.net
advertisement

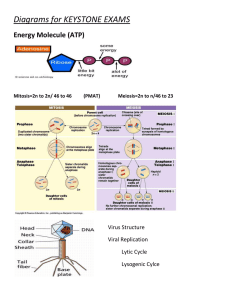
Cellular Respiration What we do with our energy Root Words Mito Cyto Di Aero Ana Thread Cell Two Air Back Mitochondria Cytoplasm Dioxide Aerobic Anaerobic Anaerobic vs. aerobic Uses no oxygen Makes a little energy Uses oxygen Makes a lot of energy Overview Of Cellular Respiration Cellular respiration is the process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other molecules in the presence of oxygen. Mitochondria (mainly) Purpose of cellular respiration? To release energy from food molecules and make ATP! Why do we need ATP? To run chemical reactions that keep us alive and functioning. Summary equation for Respiration The pathways Stage 1- Glycolysis (Anaerobic) Glycolysis- Breakdown of glucose in the cytoplasm Breaks glucose into 2 pyruvate Pyruvate enters into Kreb’s Cycle Glycolysis uses 2ATP but produces 4ATP, so there is a net gain of 2 molecules Cooking food Requires Energy Anaerobic respiration Not enough oxygen for aerobic respiration Fermentation-releases energy from food by producing ATP in the absence of oxygen. (Anaerobic = no oxygen) Two types: alcoholic fermentation, lactic acid fermentation Lactic acid No oxygen Occurs in muscles Occurs so muscles can continue making ATP Get lactate build up in muscles Causes soreness Alcoholic No oxygen Seen in yeast and fungus Used to make beverages, food, makes dough rise Stage 2: Krebs Cycle Krebs cycle (aerobic) Takes place in mitochondria Pyruvate is broken down into carbon dioxide for energy Creates more ATP than Glycolysis Overall Cellular Respiration breaks down C6H12O6. It produces H2O and CO2 It produces 36 ATPs! Comparing Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Function Energy capture Energy Release Location Chloroplasts Mitochondria Reactants CO2 & H2O C6H12O6 & O2 Products C6H12O6 & O2 CO2 & H2O Equation 6CO2 + 6H2O -> C6H12O6 + 6O2 C6H12O6 + 6O2 > > > 6CO2 + 6H2O