Animal cell
advertisement
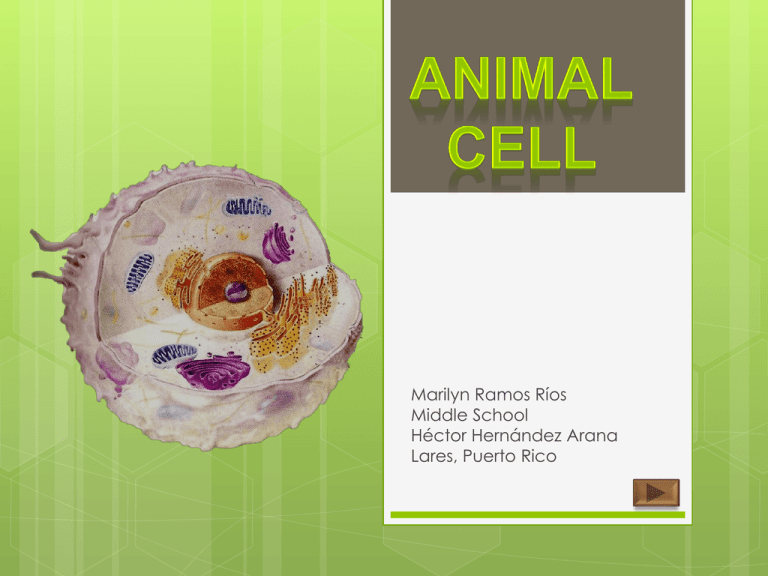
Marilyn Ramos Ríos Middle School Héctor Hernández Arana Lares, Puerto Rico Objective The student at the end of the lesson will recognize: Parts of the animal cell. Functions of the organelles in the animal cell. Click on each of the names for reading organelles features End Nucleolus Inside nucleus Contains RNA to build proteins Animal Cell End Nucleus Nucleus Directs cell activities Separated from cytoplasm by nuclear membrane Contains genetic material –DNA Nuclear membrane Surround nucleus Made of two layers Opening allow material enter and leave nucleus Chromosomes In nucleus Made of DNA Contains instruction for traits and characteristics Animal Cell End Ribosomes Each cell contains thousands Make proteins Found on ribosomes and floating thought the cell. Animal Cell End Endoplasmic Reticulum Moves material around in cell Smooth type: lacks ribosomes Rough type: ribosomes embedded in surface Rough Smooth Animal Cell End Golgi Apparatus Read more at Buzzle: http://www.buzzle.com/articles/golgiapparatus-function.html Golgi apparatus is one of the important organelles found in eukaryotic cells. Directing the carbohydrates and proteins, needed by the body, to their proper destination is the main function of this cell organelle. In the process of directing protein and carbohydrate molecules to their appropriate destinations, they are tagged with details about the destination and structural modifications. Animal Cell End Plasmatic Membrane Outer membrane of cell that controls movement in and out of the cell Double layer Animal Cell End Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton (also CSK) is a cellular scaffolding or skeleton contained within a cell's cytoplasm. The cytoskeleton is present in all cells; it was once thought to be unique to eukaryotes, but recent research has identified the prokaryotic cytoskeleton. It forms structures such asflagella, cilia and lamellipodia a nd plays important roles in both intracellular transport (the movement of vesicles and organelles, for example) and cellular division. Animal Cell End Mitochondrion Produce energy through chemical reactions – breaking down fats and carbohydrates Control level of water and other materials in cell Recycles and decomposes proteins, fats and carbohydrates Animal Cell End Cytoplasm Gel-like mixture Surrounded by cell membrane Contains hereditary material Animal Cell End Lysosome Lysosomes are the cell's waste disposal system and can digest some compounds Transport undisgested material to cell membrane for removal Cell breaks down if lysosome explodes Animal Cell End Centrioles A centriole is a cylinder shaped cell structure found in most eukaryotic cells, though it is absent in higher plants and most fungi. An associated pair of centrioles, arranged perpendicularly and surrounded by an amorphous mass of dense material, called the pericentriolar material, or PCM, makes up a compound structure called a centrosome. Centrioles are involved in the organization of the mitotic spindle and in the completion of cytokinesis Animal Cell End