Forecasting and Urban Planning: Introduction
advertisement

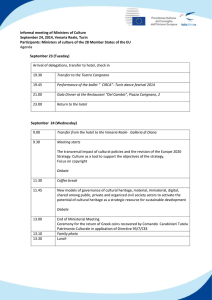
Growth and Development of Cities: Week 5. Urban Spatial Structure URBS 310 September 21, 2004 1 Urban Land Use Theory • Agricultural Land Use Theory (Von ThÜnen) – – September 21, 2004 Early 1800s. A particular type of production depends on three items: 1) distance to the market (perishable close to the market; more extensive crops farther from the market) 2) selling prices at the market 3) land rent Specialize in producing the ag. products yielding the highest land rent (economic rent) return at the particular location. 2 Urban Land Use Theory • Graphing Bid-Rent Curves – – Economic rent (monetary return from producing a particular good after all costs were deducted) Bid rent curve (relationship between economic rent and distance from the market) September 21, 2004 3 Agricultural Rent Gradients Economic Rent 75 50 25 0 0 5 10 15 Miles from the Market September 21, 2004 4 Agricultural Rent Gradients Economic Rent 75 Peas 50 25 Wheat 0 0 5 10 15 Miles from the Market September 21, 2004 5 Urban Rent Gradients 100 Economic Rent Commercial/Light Manufacturing 75 50 Residential 25 Industrial 0 0 5 10 15 Miles from the Market September 21, 2004 6 Population Density Gradient • Negative Exponential Model (Colin Clark) – di = doe-bx – ln di = ln do - bx September 21, 2004 7 Employment Density Gradient Employment Density (per square mile) 25000 22500 20000 17500 15000 12500 10000 7500 5000 2500 0 0 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 30 33 36 39 42 45 48 Distance from the CBD (in Miles) September 21, 2004 8 Population Density Gradient • Modified Negative Exponential (Bruce Newling) – di = doe+bx-cx(^2) – ln di = ln do + bx – cx2 September 21, 2004 9 Population Density Gradient Population Density (per square mile) 25000 22500 20000 17500 15000 12500 10000 7500 5000 2500 0 0 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 30 33 36 39 42 45 48 Distance from the CBD (in Miles) September 21, 2004 10 Population Density Gradient • • Crater Effect: depressed level of density in the center Density Rim: the peak September 21, 2004 11 Change in Population Density Gradient Patterns in North American Cities ln density Time Period 1 Time Period 2 Time Period 3 Miles from the CBD September 21, 2004 12 Three Models of Urban Land Use • Graphic prepared by Department of Geography and Earth Sciences, University of North Carolina at Charlotte. September 21, 2004 13 Concentric Zone Model • • • • • • • E.W. Burgess, a sociologist, a study of Chicago, 1925. A set of concentric circles. Zone 1: CBD Zone 2: Factory, slum, ethnic community (transition zone or gray zone) Zone 3: Lower income working people’s homes Zone 4: Middle income housng Zone 5: High income housing Zone 10: Commuting September 21, 2004 14 Sector Model • • • Homer Hoyt, a land economist, a study of patterns in over 100 cities, 1939 Once similar land uses emerge around the CBD, activities remain in the area and extend over time in the same direction (following rail, highway arteries, high or llow ground, clustering on the same side of the city). High income housing areas are dominant in urban growth. September 21, 2004 15 Mutilple Nuclei Model • • • Chauncy Harris and Edward Ullman, geographers, 1945. Land uses evolve at several nodes or focal points. Each node has a special function – commercial, industrial, residential. September 21, 2004 16 Urban Realms Model • • • James Vance, 1964. Peter Muller & Others Applied to LA Region & greater NY Pepperoni Pizza Emergence of large self-sufficient suburban sectors. September 21, 2004 17 Social Area Analysis • • • Eshref Shevky, Marily Williams,a nd Wendell Bell, sociologists, 1949. A theory of social differentiation. This theory shows how family characteristics, economic status, and ethnic patterns interrelate to produce distinct spatial patterns within the city. Use three constructs: social rank (economic status), urbanization (family status), and segregation (ethnic status). September 21, 2004 18 Optional Assignment 4 (Due on 10/5) 1. 2. • Draw a chart of population density gradients for 2000 and 2030 using xy scatter function in MS Excel. Determine whether the form of population density model is negative exponential or modified negative exponential. Interpret the change of the population density pattern between 2000 and 2030. Draw a chart of employment density gradients for 2000 and 2030 using xy scatter function in MS Excel. Determine whether the form of employment density model is negative exponential or modified negative exponential. Interpret the change of the employment density pattern between 2000 and 2030. The excel data for assignment 4 are available in the class webpage. Turn in 1 page answer in a MS Word format. September 21, 2004 19