Ecosystems
advertisement

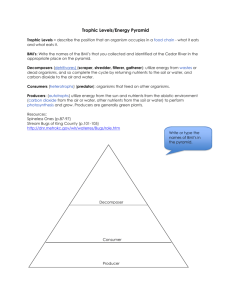
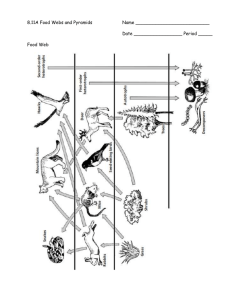
Ecosystems The flow of energy in an Ecosystem. Movement of Energy in an Ecosystem How does energy and nutrients flow or move through a community? How is the flow or movement of energy or nutrients essential to a community? How does the movement of energy and nutrients bind together a community and its environment – how are they interconnected? Life depends on energy from the sun. PHOTOSYNTHESIS 6CO2 + 6H2O -> C6H12O6 + 6O2 Others use inorganic chemical compounds - hot springs, deep ocean trenches – chemosynthesis http://www.jamstec.go.jp/jamstec-e/30th/part5/image/p74_3.jpg Trophic Levels of Energy Flow Producers – make their own food (ex. Plants, algae and phytoplankton (autotrophs)) Consumers – can not make their own food, relies on other organisms for energy (heterotroph) Decomposer- breaks down organic matter and absorbs nutrients (ex. fungi and bacteria (heterotrophs)) Scavenger – feed on dead/dying animals (ex. Hyena) Types of Consumers Herbivore – eats plants, 1° Consumer Carnivore – eats meat, 1° Consumer, 2° or 3° Consumer, Omnivore – eats plants AND/OR meat 1°, 2° or 3°Consumer Autotrophs – make their own food – producer Heterotrophs – eat other things – consumers bp2.blogger.com/ Heterotroph – herbivores eat plants Heterotrophs carnivores – eat animals Heterotrophs omnivores – eat plants and animals http://animals.nationalgeographic.com/staticfiles/NGS/Shared/StaticFiles/anim /images/primary/grizzly-bear.jpg Heterotrophs detritivores – eat dead things http://life.bio.sunysb.edu/marinebio/fc.rhithro.lind.jpg http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=4505683808705904903&ei=LqIFSprHJZKurgLftKSFCg&q=crab+eating+google&hl=en&client=firefox-a Heterotrophs decomposers – break down organic matter http://lc.k12.mn.us/HighSchool/KenSchmidt/Images/bacteria. jpg http://photo.joedlh.net/Images/LittlePond06/Crepidotus_applanatus.jpg Heterotrophs scavengers – feed on dead/dying animals What Type of Consumer am I? Which do you think there would be the most of in an ecosystem: Producers, 1° Consumers or 2 ° Consumers and why How many rabbits would it take to feed one fox? How many plants would it take to feed hundreds of rabbits? 1,000’s Food Chain -linear diagram -sequence of organisms through which energy moves in a community Producer 1° Consumer 2° Consumer 3° Consumer Is a food chain an accurate representation of what REALLY happens in an ecosystem? •A food chain is a very simple way to show what is happening in an ecosystem. •In reality, organisms eat more than one thing in an ecosystem. Food chains and food webs do not show how many organisms live in the ecosystem at each level. Food web *combination of many food chains *starts with producers and ends with consumers http://www.abe.ufl.edu/~owens/age2062/lect/lect_28/40_07.GIF Food Web in a Marsh Ecological Pyramid – flow of energy 1. Each Consumer can not process 100% of the Biomass. 2. At each trophic level of the pyramid, 10% of the energy is transferred to the next trophic level (90% lost). 3. Energy is stored in the organism or lost as heat into the atmosphere (once lost is can not be replaced). As we move up a food chain, there are less and less numbers of organisms at each level. Ecological Pyramids Energy Pyramid Shows the relative amount of energy available at each trophic level. Organisms use about 10 percent of this energy for life processes. The rest is lost as heat. Biomass Pyramid Represents the amount of living organic matter at each trophic level. Typically, the greatest biomass is at the base of the pyramid. Pyramid of Numbers Shows the relative number of individual organisms at each trophic level. Ecological Pyramid – represents the flow of energy Diagram showing how much energy/biomass there is at different trophic levels Energy Pyramid shows the amount of energy through a food chain only about 10 % of the energy goes to the next level What happens to the rest? Biomass Pyramid shows the total mass through a food chain Pyramid of Numbers show the number of organisms through a food chain Biotic and Abiotic Factors Abiotic Factors Biotic Factors ECOSYSTEM Cycles of Matter Matter is recycled within and between ecosystems. The Water Cycle Condensation Precipitation Evaporation Transpiration Runoff Seepage Root Uptake The Carbon Cycle CO2 in Atmosphere CO2 in Ocean The Nitrogen Cycle N2 in Atmosphere NH3 NO3and NO2- Cape May Warbler Feeds at the tips of branches near the top of the tree Bay-Breasted Warbler Feeds in the middle part of the tree Spruce tree Yellow-Rumped Warbler Feeds in the lower part of the tree and at the bases of the middle branches