2nd-Med-immunol-Feighery
advertisement

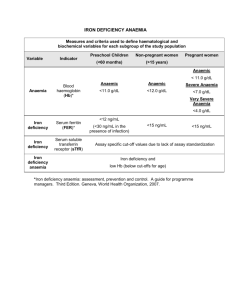
Clinical immunology Conleth Feighery John Jackson Niall Conlon Case histories • Clinical medicine - learning through a series of cases • How knowledge of immunology can help • Types of diseases • Types of tests Inflammatory diseases Specialisation • Respiratory - asthma, lung infections • Bowel - peptic ulcer, Crohn’s disease • Brain - neurology - multiple sclerosis • Joints - rheumatology, RA, SLE • Allergy - immunology Immune deficiency disorders • Primary immunodeficiency - rare, immunology • Secondary - common, e.g. HIV, infectious disease specialty Making a diagnosis! • • • • • Analysis of patient’s story - “the history” The clinical findings Which lab tests? Which radiology tests? Where to go from there ……. Patient does not wear a label ! How doctors think In-built biases in our thinking about likely diagnosis Jerome Groopman A case history 1 • • • • Female, 48 years Tiredness, “slowing down” Weight gain, 5kg Noticing the cold - cold peripheries Case history 1. • Questions you would ask ? • On examination - what you might look for in particular ? • Tests you might initially perform ? Case history 1. • • • • Patients often use non-specific terms Slowing down = breathlessness Dyspnoea on exertion ? “Systems review” - all the main body systems - respiratory, cardiac etc. • Past history ? Specific terms • • • • • • Time to learn these and use them! Impress?? Dyspnoea Ankle oedema Tachycardia Bradycardia Case history 1. • • • • • • Examination Pale conjunctiva, palmar creases Mild swelling of ankles - oedema Cold hands, white fingers Pulse 55 beats/min DIAGNOSIS ? Case history 1. • • • • • Pale conjunctiva - anaemia ? Oedema - possible cardiac failure Cold hands - vascular disease ? Pulse 55 beats/min - cardiac disease ?? DIAGNOSIS ? Case history 1. Diagnosis - Hypothyroidism • Common disorder ~ 4% pop. affected • Need high index of suspicion • Test - thyroxine and TSH levels • Autoantibody - to “thyroid peroxidase” • Previous hyperthyroidism ! Clinical hypothyroidism but often the signs are not noticeable ……. Hypothyroidism • Inflammatory damage to thyroid • Impaired synthesis of thyroid hormone • “Hashimoto’s thyroiditis” Hyperthyroidism • Common cause - Graves’ disease • Caused by auto-antibody to TSH receptor • Antibody can transfer across placenta neonatal hyperthyroidism • Test - anti-TSH receptor antibody • Diagnosis - raised T4 (thyroxine) and low TSH level Graves’ disease • Autoantibody binds to cell receptor • Excessive thyroid hormones produced Goitre Graves’ disease Auto-immune thyroid disease Patient 1 has anaemia • • • • What is the cause ? Does hypothyroidism cause anaemia ? Chronic disease - some cause anaemia Is it due to deficiency of haematinic ? Anaemia in a 48 yr old female Possible causes • Iron deficiency • Folic acid deficiency • Vit. B12 deficiency • Causes of deficiency ?? • Haemolytic anaemia Anaemia in a 48 yr old female Iron deficiency • Blood loss ? From where ? • Dietary ? • Malabsorbtion ? Anaemia in a 48 yr old female Folic acid, B12 deficiency ? Causes • Malabsorption ! • Dietary ? • Increased folic acid requirements - pregnancy Case 2 • • • • • Male, 73 years Numbness, pins and needles in feet Unsteady gait Breathless on exercise QUESTIONS ? Case 2 • • • • • Very pale Red tongue – glossitis Decreased sensation in lower limbs* Unsteady gait Otherwise appears well * proprioception B12 malabsorbtion Pernicious anaemia • Auto-immune gastritis Auto-antibodies to • Parietal cells • Intrinsic factor Thomas Addison • Often subtle, sub-clinical presentation Pernicious anaemia - autoimmune gastritis Diagnosis – Vitamin B12 level Pernicious anaemia • Red cells enlarged = macrocytic • Atypical nuclei = megaloblastic * • Raised bilirubin – yellow pigmentation * seen only in bone marrow Text books • Case studies in Immunology – Fred Rosen, Raif Geha • Essentials of Clinical Immunology – Helen Chapel, Mansel Haeney et al. • Concise Clinical Immunology for Healthcare professionals – Mary Keogan, Eleanor Wallace, Paula O’Leary Case 3 • • • • • Female, 33 years of age flatulence abdominal distension Alternating diarrhoea, constipation Given diagnosis “irritable bowel synd.” Case 3 • More questions ? • Examination - what features might you look for ? Case 3 • • • • Hgb – 10g/dl MCV – 73 Ferritin – 8ug/L (low) Folic acid – 3ug/L (low) • DIAGNOSIS ? Iron, folic acid deficiency • Malabsorption ! • Coeliac disease Iron, folic acid deficiency • Malabsorption ! • Coeliac disease Coeliac disease Destruction of villi - “atrophy” Coeliac disease • Common ~ 1% of population Subtle symptoms • Often asymptomatic • Bowel - dyspepsia, diarrhoea, bloating • Deficiency - anaemia, osteoporosis Cause - eating gluten ! Gluten - essential for disease Coeliac disease An auto-immune disease ? • Strong association with MHC class II allotypes - HLA-DQ2, HLA-DQ8 • MHC genes ~ 40% of genetic component • Auto-antibodies - very specific ! Essential genetic factors Endomysial auto-antibody IgA class antibody Highly specific - only found in coeliac disease Very sensitive + in 85% of patients Auto-antibody detection Immunofluorescence - tissue sections with relevant antigen patient serum aby * subjective, specific Endomysial auto-antibody Antigen in tissue – enzyme called tissue transglutaminase – tTG Modifies gluten Tissue transglutaminase auto-antibody - ELISA anti-IgA patient antibody tissue transglutaminase IgA class antibody Tissue transglutaminase is the antigen found in monkey oesophagus Tissue transglutaminase auto-antibody anti-IgA patient antibody tissue transglutaminase IgA class antibody Very specific - in 95% patient has CD Very sensitive + in 95% of CD patients MOLECULAR MECHANISMS UNRAVELLED Tissue transglutaminase Gluten HLA-DQ2/8 T-cells Frits Koning, Leiden 20003 Deamidation of gliadin peptides by tTG increases their affinity for DQ2 tTG Gliadin peptide APC DQ2 TCR H2O T Cell Inflammation Greg Byrne, PhD 2006 Auto-immune diseases • Co-associate • Thyroid disease, pernicious anaemia, coeliac disease co-exist • Also diabetes mellitus • More common in females • Auto-antibody - often diagnostic • Linked to MHC class II genes Endocrine auto-immunity Case history 4 23 year old female Joint pain, stiffness Rash on sun exposed areas Cold peripheries Tiredness DIAGNOSIS ? Case history 4 Questions Swelling of joints ? Stiffness - when during day, how long ? Rash - permanent, comes and goes ? Cold - Raynaud’s phenomenon ? Tiredness - sleep pattern, concentration? Case history 4 Diagnosis “Connective tissue disease” Possibilities include Rheumatoid arthritis Systemic lupus erythematosus Case history 4 Investigations Blood tests FBC Hgb 9 g/l low 9 WCC 3.2 x 10 /L - low Lymphocytes - 0.7 x 109 /L - low Platelets – 100 x 109 /L - low Case history 4 More tests ESR - 55mm/hr high C-reactive protein – 5 mg/L - normal Rheumatoid factor - negative Anti-nuclear antibody - positive, 1280 titre Anti-nuclear antibody positive staining Hep2 cells used Will stain nucleus in any cell Not specific for systemic lupus !!! SLE Systemic disease - multiple areas of damage possible Red, white cells and platelets often affected Case history 4 Diagnosis Findings suggestive of systemic lupus erythematosus Additional tests ? Antibody to double stranded DNA ? Anti-dsDNA Crithidia lucilea ds DNA antibodies SLE - synovial inflammation SLE synovial inflammation “butterfly” rash on “malar’” region of face photo-sensitive SLE - classic butterfly rash Rheumatoid arthritis • Commonest form of connective tissue disease • No diagnostic blood test !! Rheumatoid arthritis Joint deformity in established disease Rheumatoid arthritis • X-ray findings very helpful in diagnosis Lytic lesions on X-ray Rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis • • • • • • Common - 1-2% of population Female > male Older age group - 50s + Chronic, destructive arthritis in some pts Reduced life expectancy Anti-TNF drugs beneficial Rheumatoid arthritis • • • • Rheumatoid factor positive = “RF” RF = IgM antibody to IgG NOT specific for RA New antibody test – antibody to “cyclic citrullinated peptide” – more specific for RA Other connective tissue diseases • • • • Some have features similar to lupus Commonly ANA positive but …… Also have antibodies to other specific antigens These are antibodies to so-called “extractable nuclear antigens” = ENA Sjogren’s syndrome • Dry eyes, dry mouth • Inflammation in salivary, lacrimal glands • ENA antibodies – anti-Ro, anti-La* • Ro and La named after patients Scleroderma • Condition in which skin thickening develops • Caused by deposition of collagen in skin and internal organs • ENA antibody – anti-Scl-70 Tightening of skin in some types of CTD “Scleroderma” End of lecture 1