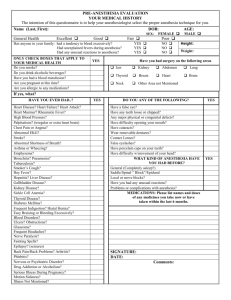
California Medical Bill Reviewer Certification
advertisement

California Medical Bill Reviewer Certification Unit 2: Official Medical Fee Schedule Module 4: Anesthesia Overview Hi! In this module, you Let’swill start by discussing about Then, learn you will learn general anesthesia anesthesia services, how anesthesia services how they arehow guidelines and are used for pain reimbursed, and the anesthesia services are management services. circumstances that can reimbursed... affect reimbursement. Part I: Anesthesia Anesthesia Guidelines Reimbursement of Anesthesia Services Modifiers: Basic Modifiers Physical Status Modifiers Qualifying Circumstances CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia What is Anesthesiology? Anesthesiology is the branch of medicine concerned with the control of acute or chronic pain. Anesthesia includes the use of: Sedative drugs Analgesic drugs Hypnotic drugs Anti-emetic drugs Respiratory drugs Cardiovascular drugs CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Anesthesia also involves: Preoperative assessment Intra-operative patient management Postoperative care Autonomic, neuromuscular, cardiac, and respiratory physiology Anesthesia Guidelines The anesthesia section in the OMFS ranges from 00100-01999. Anesthesia codes do not correspond one-to-one with surgery codes because multiple surgery codes may crosswalk to the same anesthesia code. For example, CPT 01382 is used for anesthesia services for any arthroscopic procedure on the knee joint. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Therefore, 17 surgery codes correspond to this single anesthesia service. Single anesthesia codes correspond to multiple surgical codes because the anesthesiologist performs the same tasks for any of the arthroscopic knee services and the only variation may be time. Anesthesia Services Anesthesiologists may bill for a variety of services and methods of anesthesia. Anesthesia Methods: General anesthesia Moderate sedation Regional anesthetic CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Anesthesia services include: Pre-operative visit with the patient. Ordering and giving medication. Monitoring the patient’s vital signs and level of sedation. Procedures not Separately Reimbursable Just like other procedures, some anesthesia procedures can be billed separately, while other procedures cannot be billed separately. Services not billed separately include: Pre and post-operative routine visits. Administration of fluids, including blood. Usual monitoring services such as: EKG, temperature, blood pressure, oximetry, capnography, and mass spectrometry. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia The system is automated to deny all non-invasive monitoring services billed with an anesthesia code. Separately Reimbursable Procedures In contrast, anesthesiologists can bill for invasive procedures. Some of these invasive procedures include: CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Insertion of a central venous catheter Esophageal catheter Swan-Ganz catheter Anesthesia Reimbursement Anesthesiologists are reimbursed per a base unit value assigned to each anesthesia code and by units of time. For up to 4 hours of service: 1 Time Unit = 15 minutes After 4 hours of service: 1 Time Unit = 10 minutes Five minutes or more is considered significant enough for the final unit. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Calculations are automated but may be required in a manual pricing situation. Anesthesia Reimbursement CPT 00630: Anesthesia for lumbar spine surgery Duration: 5 hours, 35 minutes Base Units: 8 TIME UNITS: First 4 hours: TIME UNITS: Remaining 1 hr, 35 minutes: = 16 units 335 – 240 = 95 minutes 95 minutes/10 minutes per unit = 9 units + 5 extra minutes What happens to 4 hours = 240 minutes the extra 5 minutes? 240 minutes/15 minutes per unit Base Units + Time Units = Total Units 8 + 16 + ? = ? CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Anesthesia Reimbursement Remember, 5 minutes or more is considered enough for a final unit. Therefore, we round the remaining 5 minutes of time up to count as 1 whole unit! TIME UNITS: Remaining time: 335 – 240 = 95 minutes 95 minutes/10 minutes per unit = 10 9 +units 5 extra minutes Base Units + Time Units = Total Units 8 + 16 + 10 = 34 CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Anesthesia Reimbursement CPT 01202: Anesthesia for hip arthroscopy Duration: 1 hours, 3 minutes Base Units: 4 TIME UNITS: 1 hour, 3 minutes: 1 hour, 3 minutes = 63 minutes 60 minutes/15 minutes per unit = 4 units Where did the last 3 minutes go? Remember, only 5 minutes or more can be reimbursed as a final unit. So, in this case, we round down to 60 minutes, or 4 units! Base Units + Time Units = Total Units 4+4=8 CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Modifiers Now that you are familiar with the basics will begin let’s by ofWe anesthesia, discuss how modifiers discussing a few basic and extreme anesthesia modifiers... circumstances can alter reimbursement. Part I: Anesthesia Anesthesia Guidelines Reimbursement of Anesthesia Services Modifiers: Basic Modifiers Physical Status Modifiers Qualifying Circumstances CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Modifiers As you know, each section of the OMFS has a list of modifiers that pertain to those services. We will discuss the following modifiers: Recall that modifiers indicate that a procedure was altered by additional circumstances, but was not changed from its standard definition. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Modifier 36 Modifier 47 Modifier 48 See the OMFS for a complete list of modifiers! Modifier 36 In some instances, special circumstances warrant an increase in the basic value of specific procedures. Procedures with a basic value of three or less base units which: Require endotracheal intubation for prone or other difficult positions Require surgical field avoidance Are performed for medical necessity ...may warrant an additional charge. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia 36 Anesthesia Procedures: This modifier increases the basic value for these procedures to four base units. Other applicable modifiers also apply. Modifier 47 In some instances, anesthesia is provided by a surgeon, rather than an anesthesiologist. 47 Anesthesia by Surgeon: regional anesthesia provided by a surgeon. No time units are applied. It is important to realize that Modifier 47 should only be billed with surgical codes, not anesthesia codes. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists (CRNA) also administer anesthesia, although they must be under the supervision of an anesthesiologist. Both the anesthesiologist and the CRNA are reimbursed. The anesthesiologist is paid for the base units and a reduced number of time units. The CRNA is paid the remainder of the total reimbursement of an anesthesiologist performing the service. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia To be eligible for reimbursement, the anesthesiologist must be within hearing and visual range, and cannot supervise more than 2 rooms, or administer anesthesia himself. Lastly, the anesthesiologist must be involved in the medical direction of the patient, including pre and post-operative care. Modifier 48 Modifier 48 indicates that a CRNA performed anesthesia services. 48 Reduced Anesthesia Value for Supervising Anesthesiologist: Reimbursement for the supervising physician shall be for the basic value of the procedure plus one unit per hour or fraction thereof for the duration of the anesthesia. Total reimbursement to the CRNA and supervising anesthesiologist shall not exceed the listed value of the service if performed by an anesthesiologist. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists Suppose Dr. Jones supervises two operating rooms with CRNAs giving anesthesia in each. He does not administer the anesthesia himself. Operating Room 1 CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Dr. Jones Operating Room 2 Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists Operating Room 1 Operating Room 2 Dr. Jones Duration: 1 hour, 15 minutes Base Value = 4 CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Duration: 45 minutes Base Value = 6 Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists Operating Room 1 Operating Room 2 Duration: 1 hour, 15 minutes Base Value = 4 75 minutes = 5 units Total Units = 9 Anesthesiologist: 1 unit/hour (or fraction thereof) = 2 time units Duration: 45 minutes Base Value = 6 45 minutes = 3 units Total Units =9 Now you try... Anesthesiologist Total = 2 + 4 = 6 CRNA: 9 – 6 = 3 Units CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Anesthesiologist: 1 time unit How many units can be reimbursed to the anesthesiologist and the CRNA? Anesthesiologist Total = 1 + 6 = 7 CRNA: 9 – 7 = 2 Units Physical Status Modifiers In addition to standard modifiers, there are other modifiers, known as physical status modifiers, which can affect the reimbursement of anesthesia services. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Physical Status Modifiers Anesthesia complicated by the patient’s condition may be additionally reimbursed if documentation supports the presence of significant disease. While hypertension and diabetes are These significant complications not considered significant enough to are indicated by physical warrant use of the higher level physical status modifiers. status modifiers, conditions such as: Congestive heart failure Emphysema Uncontrolled epilepsy ...are reimbursable. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Physical Status Modifiers The physical status modifiers and their values are: Modifier Description Unit P1 normal, healthy patient 0 P2 patient with mild systemic disease 0 P3 patient with severe systemic disease 1 P4 patient with severe systemic disease that is a constant threat to life 2 P5 moribund patient not expected to live without the surgery 3 P6 brain dead patient for harvesting 0 CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Anesthesia Reimbursement CPT 01402: Anesthesia for total knee replacement Duration: 3 hours, 25 minutes Complication: Patient has congestive heart failure (P3: 1 unit) Base Units: 7 TIME UNITS: 3 hours, 25 minutes: 3 hours, 25 minutes = 205 minutes 205 minutes/15 minutes per unit = 13 units + 10 extra minutes Remember, 195 minutes/15 min. per unit = 13 That leaves 10 minutes remaining. So, we round up to account for 1 extra unit, for a total of 14 time units! Base Units + Time Units + P3 Modifier Units= Total Units 7 + 14 + 1 = 22 CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Physical Status Modifiers Some providers will attach a physical status modifier to all anesthesia services, while others will only attach those with unit values greater than zero. Either method is acceptable and the system is automated to pay the modifier. It is the processor’s responsibility to verify that documentation justifies the addition of the payable modifiers. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Qualifying Circumstances As you know, physical status modifiers indicate significant complications. Similarly, there are special codes that indicate other extreme circumstances that can affect the reimbursement of anesthesia services. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Qualifying Circumstances You have probably realized that there are certain circumstances which make giving anesthesia much more difficult. If the patient is extremely old or extremely young, the reaction to the anesthetic medications may be very different and must be monitored more closely. Certain surgical procedures, such as cardiovascular or intracranial surgery, require lowering the blood pressure or body temperature significantly to reduce bleeding. These circumstances are known as qualifying circumstances, and are billed in addition to anesthesia services. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Qualifying Circumstances Qualifying circumstances are indicated by special codes, not modifiers. Qualifying Circumstance codes include: 99100 – Anesthesia for patient of extreme age, under one year or over seventy. 99116 – Anesthesia complicated by utilization of total body hypothermia. 99135 – Anesthesia complicated by utilization of controlled hypotension. 99140 – Anesthesia complicated by emergency conditions (specify). CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Qualifying Circumstances It is critical that documentation support the addition of qualifying circumstances. The age of a patient is easily verified to confirm an instance of “extreme age.” CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia In contrast, hypothermia can only be justified if, in the report, there is documentation stating that a hypothermia pad or blanket was placed under the patient and used to drop the body temperature. Qualifying Circumstances You probably realize that like other providers, anesthesiologists can incorrectly bill for certain codes. Qualifying circumstance code 99135 is often incorrectly billed by anesthesiologists who simply keep a patient’s hypertension under control or lower the blood pressure slightly to minimize bleeding. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia 99135 should only be reimbursed if documentation shows a significant reduction in the blood pressure—at least 20 points—for delicate surgery such as intracranial operations. Pain Management Now that you are familiar with how anesthesia is generally used, let’s discuss how it can be used for pain management. Part II: Pain Management Services Post-operative Pain Control Chronic Pain Control CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Pain Management Services Pain management occurs in two distinct circumstances: Post-operative Pain Control CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Chronic Pain Control Pain Management Services If a spinal, epidural, or regional anesthetic is used for anesthesia during a surgery instead of general anesthesia, the anesthesiologist should still bill with the correct anesthesia code associated with the procedure. This is because the service includes the anesthetic and all monitoring necessary to bring the patient safely through the surgery, regardless of the type of anesthetic. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Post-operative Pain Control Post-operative Pain Control CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia However, if a general anesthetic is given, making the patient unconscious, and the anesthesiologist gives an epidural or regional block for post-operative pain control in addition to the anesthesia given for the surgery, it can be billed separately. Post-operative Pain Control Example 1 Example 2 Bob Smith is having a meniscectomy performed in his right knee. Bob Smith is having a meniscectomy performed in his right knee. He and the anesthesiologist discuss the anesthetic options and decide he will be happiest with an epidural anesthetic, making him numb from the waist down, and some mild IV sedation for anxiety control. He and the anesthesiologist discuss the anesthetic options and decide he will be happiest with a general anesthetic because his anxiety level is so high. In addition, the anesthesiologist will insert an epidural catheter for pain control in the 24 hours following surgery. The anesthesiologist will code her services with 01382 for basic value and time but will not bill separately for the epidural insertion. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia The catheter insertion is separately reimbursed because it is not part of the anesthetic for the surgery. The anesthesiologist may not bill 01996 for pain control management on the day of surgery. Post-operative Pain Control Just like other procedures, the surgeon cannot bill separately for pain control services, such as inserting a pain pump catheter, if it is performed as part of the surgery. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia In this case, it is part of the global surgery package. Chronic Pain Control In chronic pain management, anesthesiologists that specialize in pain control may see the patient for a single or a series of injections, either into a joint or body area, or into the epidural space. They may also employ non-injection methods of pain control such as biofeedback, physical therapy, and counseling. However, the most common treatment is injection. Chronic Pain Control CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Chronic Pain Control In California, like any other specialty who performs these services, these injections are billed and reimbursed as Type of Service (TOS) 2, which is surgery. If these services are billed as TOS 7, which is anesthesia, the processor must change the TOS to reflect that this is a surgical service. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Chronic Pain Control Anesthesiologists often used the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) Relative Value Guide to bill for particular services. This reference guide lists the recommended base values for each procedure. Often, anesthesiologists will mistakenly indicate the anesthesia base value in the units field on the bill. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Remember, the bill review system already calculates the base value associated with a procedure. Chronic Pain Control As you can see, when reviewing bills, it is important to determine the type of units and verify that they coincide with the service provided. If multiple units are billed, the processor must determine if the provider has: performed multiple injections billed for time units indicated the anesthesia base value of the service in the unit field Unfortunately, all the above scenarios are viable possibilities. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Chronic Pain Control Example Suppose a provider bills CPT 20610: large joint injection, for 3 units. As a processor, you should ask, “Is he billing for 3 injections or 3 time units? Or, is this the base value?" Only documentation can verify if this represents injections of both hips and one knee, for a total of 3 injections... ...or a single injection took the anesthesiologist 45 minutes, for a total of 3 time units. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Chronic Pain Control 3 Joint Injections: left hip, right hip, & right knee 3 Injections The lines are separated, and the procedures are reimbursed at multiple procedure cascade. Left hip: 20610 x 100% of FS value Right hip: 20610 x 50% of FS value Right knee: 20610 x 25% of FS value CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Chronic Pain Control Single large joint injection representing time units or ASA base value 3 Time Units The processor will need to change the unit field to 1 and the TOS to 2 to represent the actual service performed. 1 injection Billed: 20610, TOS 7, Units: 3 Paid: 20610 x 100% of FS value TOS 2, Units: 1 CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Chronic Pain Control If multiple types of injections are performed, they are reimbursed at multiple procedure cascade. Example: 62278 lumbar epidural: 100% FS 64440 injection paravertebral nerve: 50% FS 20550 trigger point injection: 25% FS CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia If the provider appeals the recommendation, he is educated on multiple cascade logic, which avoids duplicating reimbursement for overhead, pre-operative, and post-operative care. Pain Management Services A common error in pain management occurs when providers bill for an E & M service each time the patient comes in for an injection. If a pattern, such as weekly visits is obvious, it is unlikely each visit was a significant, separately identifiable service and not just routine questioning about pain level. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Unless the provider is assessing the patient’s progress in detail, treating an additional condition, or teaching or counseling the patient extensively, the E/M service is included in the injection procedure payment. Summary Anesthesia: Services and Procedures How to calculate anesthesia reimbursements. Modifiers: How basic and physical status modifiers affect reimbursement. How post-operative pain control services are reimbursed. What constitutes qualifying circumstances. How chronic pain control services are reimbursed. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia Module Quiz It’s time to check your knowledge of the concepts presented in this module. This quiz is scored. You must achieve a score of 80% to pass. You may attempt this quiz as many times as needed to achieve a passing score. When finished, you may move on to the next module. CA Regulations Training - Anesthesia PROPERTIES On passing, 'Finish' button: On failing, 'Finish' button: Allow user to leave quiz: User may view slides after quiz: User may attempt quiz: Goes to Next Slide Goes to Next Slide After user has completed quiz At any time Unlimited times