3-23_Genetics
advertisement

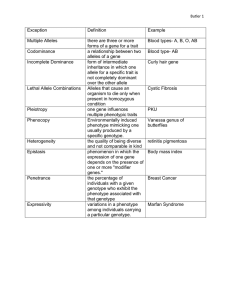
Warm Up – put homework on desk to be checked Question: 1.Draw T chart and categorize the following traits: eye color, sun tan, ear piercing, height, purple hair, shaved head, naturally curly hair Acquired Sun tan Ear piercing Purple hair Shaved Head Inherited Eye color Height Naturally curly hair Notebook Info Table of Content March 7th Genetics Day 2 Notes Page March 7th Genetics Day 2 What is an allele? What is the main difference between genotype and phenotype? Homework Review Inherited Eye Color Hair Color Height Face Shape Foot Size Acquired Colored Contacts Nail Polish Tattoo Sun Tan Playing Drums Speaking Spanish Dyed Hair Pierced Ears 2. C. Heredity E. Genetics F. Trait B. Inherited Trait D. Acquired Trait A. Gregor Mendel 3. Three inherited traits 4. Four acquired traits 5. Gregor Mendel was an Austrian Monk. He studied pea plants to discover how traits are passed from generation to generation Venn Diagram Inherited In DNA From Parents Eye Color Height both a type of trait skin color Acquired learned/changed dyed hair learning to read Trait Detached Earlobes Dyed Hair Freckles Naturally Curly Hair Dimples Hitchhikers Thumb Ears Pierced Asthma Widow’s Peak Curl / Straighten Hair See Color Not Colorblind Cleft Chin Yes No Acquired or Inherited Inherited Acquired Acquired Inherited Inherited Inherited Acquired Inherited Inherited Acquired Inherited Inherited What, How, & Where of Genes • What are Genes? – Genes are the “code” that determine our inherited traits. • How do we get genes? – We get our genes from our parents. • Where are genes found? – All humans, animals, and plants have genes! – Genes are found in your DNA. The DNA is inside your chromosomes. Genes are found in your DNA! 23 + 23 = 46 (mom) (dad) chromosomes How many possible combinations of 1 pair of JEANS and 1 pair of SHOES? 1 2 3 4 FRAYER DIAGRAM: ALLELE DEFINITION: EXAMPLE: CHARACTERISTICS: ALLELE PICTURE: FRAYER DIAGRAM: ALLELE DEFINITION: CHARACTERISTICS: Different versions of the same trait/gene EXAMPLE: ALLELE PICTURE: TRAIT/GENE: EYE COLOR ALLELES: Blue, Brown, Green, Hazel… TRAIT/GENE: HAIR COLOR ALLELES: Brown, Red, Black, Blonde… MOM DAD f R f r B B a a H h Q q D d J j GENES Chromatid 1 ALLELES Alleles are different versions of the same trait/gene Chromatid 2 FRAYER DIAGRAM: ALLELE DEFINITION: CHARACTERISTICS: Alleles are Different versions represented using of the same CAPITAL & lowercase trait/gene letters. EXAMPLE: ALLELE PICTURE: MOM DAD f R f r B B a a H h Q q D d J j GENES Chromatid 1 ALLELES Chromatid 2 FRAYER DIAGRAM: ALLELE DEFINITION: CHARACTERISTICS: Alleles are Different versions represented using of the same CAPITAL & lowercase trait/gene letters. EXAMPLE: ALLELE B = Brown Eyes b = Blue Eyes PICTURE: FRAYER DIAGRAM: ALLELE DEFINITION: CHARACTERISTICS: Alleles are Different versions represented using of the same CAPITAL & lowercase trait/gene letters. EXAMPLE: ALLELE B = Brown Eyes b = Blue Eyes PICTURE: Let’s Review… 1.What are these two things? 2. Where did you inherit these from? 3. What do the colored squares represent? 4. Why do we use capital and lowercase letters? ALLELES: Where do YOU stand? 1. What is an allele? 2. What do we use to represent alleles? 3. Draw a picture of two small chromatids. Then, draw 3 different alleles on them (DON’T FORGET THE LETTERS!). ALLELES: Where do YOU stand? 1. Alleles are different versions of the same trait/gene. 2. CAPITAL and lowercase letters! 3. Genotype vs. Phenotype Definition Example Memory Trick GENOTYPE PHENOTYPE combinations of alleles in our genes physical characteristics that can be observed Bb G is your genes! brown hair P you can see! Take a look at the following example… Are they genotypes or phenotypes? BB Brown Eyes Genotype Rr Genotype RR Phenotype Tall Genotype Phenotype Alleles can be DOMINANT or RECESSIVE What is an allele? Different versions of one gene! What do we use to represent alleles? CAPITAL and lowercase letters! Make a prediction: What type of letter do you think represents a DOMINANT allele? UPPERCASE LETTERS! What type of letter do you think represents a RECESSIVE allele? lowercase LETTERS! 2 Types of Alleles DOMINANT - The allele that is always shown. -Represented by CAPITAL letters - BB or Bb TT = tall Tt = tall tt = short Which allele is DOMINANT? 2 Types of Alleles DOMINANT - An allele that always shows up in the phenotype -Represented by CAPITAL letters - BB or Bb RECESSIVE - An allele that only shows up if there is NO DOMINANT ALLELE - Represented by lowercase letters TT = tall Tt = tall tt = short Which allele is RECESSIVE? Homozygous or Heterozygous • HOMOZYGOUS having identical alleles for the same trait ( 2 capitals or 2 lowercases) – Homo = same – Also called PURE • HETEROZYGOUS having different alleles for the same trait (1 capital and 1 lower case) – Hetero = different – Also called HYBRID Homozygous or Heterozygous? • BB • Homozygous • bb • Homozygous • Bb • Heterozygous • FF • Homozygous • Ff • Heterozygous Yellow body color is dominant to blue Y = Yellow y = Blue YY = Yellow Yellow body color is dominant to blue Y = Yellow y = Blue Y y= Yellow Yellow body color is dominant to blue Y = Yellow yy= y = Blue Blue Square shape is dominant to round S = Square SS = s = Round Square Square shape is dominant to round S = Square Ss = s = Round Square Square shape is dominant to round S = Square ss = s = Round Round TT – HO Bb – HT DD – HO Ff – HT tt – HO dd – HO Dd – HT ff - HO Tt – HT bb – HO BB – HO FF – HO Purebred = all HO Hydrid = all HT YY – Yellow Yy – Yellow yy – Blue SS – Square Ss – Square ss – round Tall = TT or Tt Short = tt Pink = PP or Pp Yellow = pp 1. A 2. C 3. B 4. A 5. B 6. C 7. C 8. B 9. D 10. C 11. A 12. C 13. C 14. A. Anaphase B. Prophase C. Metaphase D. Telophase 15. B, C, A, D 16. Prophase = Nuclear membrane disappears Metaphase = Spinal Fibers attach, chromosomes move to center of cell Anaphase = Spindal fibers pull chromosomes to opposite sides of the cell Telophase = nuclear membrane develops and cell divides 17. Cytokinesis 18. Telophase II/ Cytokinesis II – because there are about to be 4 cells 19. The three forms of asexual reproduction are budding, binary fission and regeneratioin. Budding happens when an organism grows a bud off of itself. The bud eventually becomes its own organism. In binary fission, a cell splits in 2. In regeneration lost or broken body parts are regrown. Asexual reproduction involves 1 parents, while sexual requires 2. 20. Meiosis occurs in sexual reproductive organs. It is necessary to create egg and sperm cells. Exit 1. Is BROWN HAIR a genotype or phenotype? 2. Give an example of a heterozygous genotype 3. In palm trees, the allele for dark green leaves (D) is dominant. The allele for light green leaves (d) is recessive. If a palm tree has light green leaves, what GENOTYPE must it have? THE END Bikini Bottom Genotypes and Phenotypes! EXAMPLE (SpongeBob) Trait: Pants Shape Possible phenotypes: _______: represented by “____” _______: represented by “____” Possible genotypes: __, ___, and ___ Possible outcomes: ___ ___ = _______________ ___ ___ = _______________ ___ ___ = _______________ Which phenotype is expressed? ____________ Which genotype do you predict he has? ___ ___ EXAMPLE (SpongeBob) Trait: Pants Shape Possible phenotypes: _Square Pants_: represented by “__S___” _Round Pants_: represented by “__s___” Possible genotypes: __, ___, and ___ Possible outcomes: ___ ___ = _______________ ___ ___ = _______________ ___ ___ = _______________ Which phenotype is expressed? ____________ Which genotype do you predict he has? ___ ___ EXAMPLE (SpongeBob) Trait: Pants Shape Possible phenotypes: _Square Pants_: represented by “__S___” _Round Pants_: represented by “__s___” Possible genotypes: _SS_, _Ss__, and _ss__ Possible outcomes: ___ ___ = _______________ ___ ___ = _______________ ___ ___ = _______________ Which phenotype is expressed? ____________ Which genotype do you predict he has? ___ ___ EXAMPLE (SpongeBob) Trait: Pants Shape Possible phenotypes: _Square Pants_: represented by “__S___” _Round Pants_: represented by “__s___” Possible genotypes: _SS_, _Ss__, and _ss__ Possible outcomes: S S = Square Pants S s = Square Pants s s = Round Pants Which phenotype is expressed? ____________ Which genotype do you predict he has? ___ ___ EXAMPLE (SpongeBob) Trait: Pants Shape Possible phenotypes: _Square Pants_: represented by “__S___” _Round Pants_: represented by “__s___” Possible genotypes: _SS_, _Ss__, and _ss__ Possible outcomes: S S = Square Pants S s = Square Pants s s = Round Pants Which phenotype is expressed? __Square Pants___ Which genotype do you predict he has? __S S__ Bikini Bottom Genotypes and Phenotypes! QUIZ #17: REVIEW In palm trees, the allele for dark green leaves (D) is dominant. The allele for light green leaves (d) is recessive. If a palm tree has light green leaves, what GENOTYPE must it have? dd REVIEW In giraffes, the allele for brown spots (S) is dominant. The allele for black spots (s) is recessive. If a giraffe has black spots, what GENOTYPE must it have? ss QUIZ #17: REVIEW In butterflies, the allele for long antennae (A) is dominant. The allele for short antennae (a) is recessive. If a butterfly has long antennae, what GENOTYPE must it have? AA or Aa QUIZ #17: REVIEW In butterflies, the allele for long antennae (A) is dominant. The allele for short antennae (a) is recessive. If a butterfly has the genotype aa, what would be the butterfly’s PHENOTYPE? Short antennae QUIZ #17: REVIEW In Labrador retrievers, the allele for yellow fur (Y) is dominant. The allele for black fur (y) is recessive. If a Lab has the genotype Yy, what would be the PHENOTYPE of the lab’s fur? Yellow fur QUIZ #17: REVIEW In tomato plants, the allele for tall plants (T) is dominant. The allele for short plants (t) is recessive. If a tomato plant has the genotype tt, what would be the plant’s height PHENOTYPE? Short QUIZ #17: REVIEW INHERITED and ACQUIRED traits – what’s the difference? EXAMPLE? Inherited traits are determined by your genes (Example: height). Acquired traits must be LEARNED (Example: math). QUIZ #17: REVIEW • • • • • Eye shape Intelligence Hair color Hair length Accent (the way you speak) • Attitude • Smile • Tattoos • Broken leg • Face shape • Diseases like HIV/AIDS or cancer • Disorders like albinism or colorblindness • Hair texture • Cheek size trade & grade QUIZ #17: REVIEW What is an ALLELE? What do we use to represent alleles? Alleles are different versions of the same gene/trait. We use CAPITAL and lowercase letters to represent them! QUIZ #17: REVIEW GENOTYPES and PHENOTYPES – What’s the difference? EXAMPLES? Genotypes are combinations of your alleles (Example: Bb). Phenotypes are your physical characteristics (Example: blue eyes). QUIZ #17: REVIEW DOMINANT and RECESSIVE alleles – What’s the difference? EXAMPLES? Dominant alleles always show up (Example: B=brown eyes). Recessive alleles only show up if there is NO dominant allele (Example: b=blue eyes). QUIZ #17: REVIEW In apple trees, the allele for green apples (G) is dominant. The allele for red apples (g) is recessive. If an apple tree produces red apples, what GENOTYPE must it have? gg QUIZ #17: REVIEW In apple trees, the allele for green apples (G) is dominant. The allele for red apples (g) is recessive. If an apple tree has the genotype GG, what would be the PHENOTYPE of the apples produced? Green NEMO DORY WALL-E EVE BUZZ WOODY QUIZ #17 – PART 4 MIKE SULLY How many possible combinations of 1 pair of JEANS and 1 pair of SHOES? These baby girls are also TWINS and these are their BIOLOGICAL parents! How is that possible?! Skin color is controlled by 6 different genes! This is called a PUNNETT SQUARE! Y B R R Y RB P PY PB B b B BB Bb b Bb bb Invent-An-Alien! Possible Phenotypes: S/s: Square head (S) or Round (s) E/e: Three eyes (E) or Five eyes (e) H/h: Horns (H) or No horns (h) G/g: Circle nose (G) or Triangle nose (g) A/a: Two antennae (A) or Three antennae (a) Y/y: Two eyebrows (Y) or Four eyebrows (y) T/t: Sharp teeth (T) or Flat teeth (t) 1. Use these seven characteristics to invent and draw your alien. 2. Trade aliens with a partner. 3. On the back of your partner’s paper, draw two chromosomes, each with seven alleles. Label each chromosome with the alien’s alleles!