An Earth Science teacher wants to see what affect homework has on
advertisement

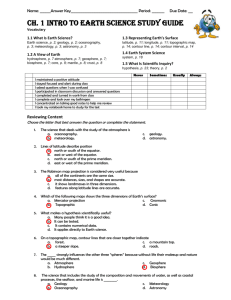
Earth Systems Scientific Method And Intro Terms Ch 1 Study Guide You will have mastered the content of this unit when you KNOW: the definitions and uses of the following terms 1. observation 10. 2. inference 11. 3. quantitative 12. 4. qualitative 13. 5. experiment 14. 6. control 15. 7. independent variable 16. 8. dependent variable 17. 9. data 18. x-axis y-axis hypothesis conclusion theory scientific method geology astronomy meteorology 19. environmental science 20. oceanography 21. biosphere 22. geosphere 23. atmosphere 24. hydrosphere 25. latitude 26. longitude UNDERSTAND: 1. 2. 3. 4. The various disciplines of science under the “earth sciences” umbrella. What each of the “–spheres” include (biosphere, etc) How to use latitude and longitude to locate positions on maps The various parts of a graph and how best to arrange the data points on a graph BE ABLE TO: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Differentiate between quantitative and qualitative data differentiate between observations and inferences Compare and contrast longitude and latitude and use them to locate positions on Earth Identify the various parts of a controlled experiment Identify the independent and dependent variables, given an experimental set-up Create a graph from a set of data Identify the independent and dependent variable for the following experiments. Also describe two possible controls or constants for the experiment. 1. A group of college students were given a short course in speed-reading. The instructor was curious if a monetary incentive would influence performance on a reading test taken at the end of the course. Half the students were offered $5 for obtaining a certain level of performance on the test, the other half were not offered money. 2. It is January and Haley, Sarah and Becky are tired of having cold feet while waiting for the school bus to come in the morning. They decide to design an experiment to test the effectiveness of wool, cotton and nylon as insulators. They fill identical bottles with 200 ml of water at 100oC and place inside each sock. They take the temperature of the water after 20 minutes. 3. A social psychologist thinks that people are more likely to conform to a large crowd than to a single person. To test this hypothesis, the social psychologist had either one person or five persons stand on a busy walking path on campus and look up. The psychologist stood nearby and counted the number of people passing by who also looked up. Complete the following crossword puzzle to check your knowledge of the unit vocabulary! Read the experiment below and use the data to answer the following questions: An Earth Science teacher wants to see what affect homework has on a student’s performance in class. The teacher makes homework worth different amount for five classes: 0%, 5%, 10%, 15% and 20%. The teacher than sees what the students’ average tests scores are at the end of 6 weeks. They collect the data below: Homework Percentage 0% 5% 10% 15% 20% 1. What are the independent and dependent variables? 2. Graph this data in the area to the right. 3. Draw a best-fit line for the data. Test Average 64% 68% 76% 81% 88% definitions for crossword puzzle observation information gathered by using any one of the senses inference based on observations and prior knowledge quantitative having to do with numbers, measurements qualitative descriptive, not numerical experiment A test of a hypothesis control The side of an experiment in which no factors are changed. Used for comparison. independent The variable that the scientist changes. It’s what is being tested. dependent The variable that is measured or observed to understand the outcome of the experiment. It changes as a result of the experiment. data information gathered and recorded during an experiment x-axis this is where the independent variable or time is usually plotted y-axis this is where the dependent variable is usually plotted hypothesis a testable prediction of outcome of an experiment conclusion Restates hypothesis and experiment’s outcome. May include analysis and experimental error. theory an explanation for a large body of evidence scientific method a logical series of steps for answering scientific questions geology the study of rocks, minerals, their formation and cycling, and the history of the earth astronomy the study of the universe and the objects outside of the earth’s atmosphere meteorology the study of the atmosphere, weather and climate environmental science the interaction of humans and the environment oceanography the study of salt water bodies, including their chemical and physical properties, such as tides, currents, salinity, temperature and biology biosphere all of the earth’s living organisms and the environment in which they live geosphere includes the core, magma and crust atmosphere the blanket of gases that surrounds the earth hydrosphere includes oceans, lakes, rivers, glaciers, polar ice caps and groundwater latitude run parallel to the Equator and give directions North and South longitude run parallel to the Prime Meridian and give directions East and West