Multiple Intelligences
advertisement

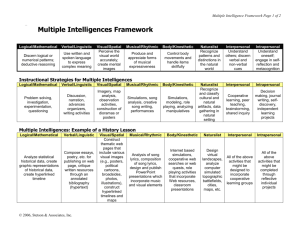
Multiple Intelligences College Preparatory General Vocational Special Education Adapt instruction to the child rather than having the child adapt to the instruction. Howard Gardner The theory of Multiple Intelligences serves as a template for constructing strategies for student success. Theory of Multiple Intelligences The question is not, “How smart are you?” Rather, it is, “How are you smart?” Why Multiple Intelligences? Increased variety (students/ teachers) Higher level skills Potential for all students Why Multiple Intelligences positive learning tone increased student participation greater student achievement How can I determine the learning styles of my students? teacher observation self-report instruments analysis of students’ work Theory of Multiple Intelligences VERBAL/LINGUISTIC LOGICAL/MATHEMATICAL VISUAL/SPATIAL RHYTHMIC/MUSICAL KINESTHETIC INTERPERSONAL INTRAPERSONAL NATURALIST Learning and Emotion The best teachers know that kids learn more readily when they are emotionally involved in the lesson because emotion drives attention, which drives learning and memory. Robert Sylwester, Ed. Leadership, March 1997 Interpersonal and intrapersonal intelligences are the integrators and synthesizers of the other intelligences. Intrapersonal Characteristics Intrapersonal intelligence involved knowledge Has a deep awareness of inner feelings, strengths, of internal aspects of the self such as feelings, weaknesses the Displays sense of independence, strong will, selfrangea of emotional responses, thinking direction processes, self-reflection, and a sense of or Reacts with strong opinions intuition about spiritual realities. Intrapersonal Prefers own, private inner world intelligence allows you to be conscious of your Motivates self consciousness. Self-image and the ability to Marches to the beat of a different drummer transcend theintuitive self are part of the functioning of Is strongly intrapersonal Prefers individual interests,intelligence. hobbies, or projects Intrapersonal Ideas Grapple with the moral issues raised by Spanish conquest of the Aztecs by acting as jurors in a hypothetical trial of Hernan Cortez Experience the sting of discrimination during a simulation of a “separate but equal” classroom in the American south in the 1950s Examine personal convictions of right and wrong during a recreation of the hysteria surrounding McCarthyism Create their own Student Bill of Rights as they struggle to define their individual rights in a society governed by the rule of law. Interpersonal Characteristics Interpersonal intelligence involves the ability to Enjoys with people workinteracting cooperatively in a group and the ability Socializes at schools, home, or nonverbally, work to communicate, verbally and with other People. It builds on the capacity to notice Has many friends moods, temperament, motivations, contrasts Organizes,in communicates, sometimes manipulates intentions amongand other people. Those with and Learns best by relating cooperating developed interpersonal intelligence highly Serves as the “Family Mediator” during disputes can have genuine for another’s Displays empathyempathy for the feelings of othersfeelings, fears, anticipations, and beliefs. Counselors, teachers, Responds to the moods and temperaments of others therapists, politicians, salespeople, and religious leaders usually have strong interpersonal intelligence Interpersonal Ideas: Working in groups, students are given key passages from the writings of Marco Polo and Ibn-Batuta to incorporate into travel brochures designed to encourage traders to use the Silk Road between Europe and China A group of student assume the perspective of some societal group – feminists, fashion models, advertising executives, university sociologists – and meet for a panel discussion with other groups about the changing image of women in the American media from the 1950s to the present. Assume the roles of historical figures to recreate a 1776 town meeting to determine whether or not the colonists should declare independence. Interpersonal importance “...unless people enjoy, in the main, good human relationships, they can neither be educated nor educate themselves.” – Everett Reimer, 1972 – School Is Dead Bodily-Kinesthetic Characteristics Body-kinesthetic intelligence is the ability or toacting use the body Learns best by moving around, touching, things out emotion (as in dance and body language), to to express Processes knowledge through bodily sensations play a game (as in sports), or to create a new product Moves, taps, an twitches, or fidgets while sitting (as in devising invention). Learning by doing has long recognized an important part of education. been Engages in physicalasactivities; can become accomplished Our bodies know things our motor mindstasks don’t and can’t know in Performs fine and gross skillfully anyother People such as talking actors,toclowns Likesway. to touch people when them and mimes demonstrate the endless forthe using Demonstrates skill inpossibilities a craft that uses handsthe body to know, understand, and communicate ways that touch the Enjoys “hands-on”, manipulatives,in role-playing, simulations, competitive humansports, spirit.and action stories Bodily/Kinesthetic Ideas: Students create a “living statute” commemorating some aspect of daily life in Constantinople Recreate life on the assembly line by drawing a small part of a picture over and over against until they feel the fatigue, stress, and boredom of factory production Act out what they see in a picture Estimation Line-UP Students estimate the answer to a problem Line up - lowest to highest Fold line in half Discuss and record strategies Partners report each other’s strategies List strategies Walking Tour Activator Post quotes, problems, concepts, pictures around the room Tour groups of 3-4 review posters for 2-5 minutes Respond to reaction prompts: this means... this reminds us of... we are confused by...advantages/disadvantages of this are... this may cause... Discuss responses...then read, solve, etc. Musical/Rhythmic Characteristics Musical-rhythmic intelligence includes such capacities as Sensitive to a and variety sounds in the and environment the recognition useofof rhythmic tonal patterns, sensitivity Plays a musical instrument and/or enjoys music the human and to sounds in the environment, voice, Remembers melodies of songs and musical instruments. Of all forms of Can tell when a musical note is off key intelligence has intelligence identified, musical-rhythmic Can relax“consciousness with music on or altering” when studying or on working the greatest effect the brain. Collects tapes,you CDsare stressed, stimulates you Music calmsrecords, you when Sings songs when you are bored, and helps you attain a steady rhythm Keeps time rhythmically to and musicexercising. It has been during such tasks as typing used to inspire religious to intensify national Hums or whistles tunes tobeliefs, him/herself loyalties, and the express great loss or intense joy. Musical/Rhythmic Ideas: Listen to West African songs to understand how music is used to commemorate an event and express emotion, and then create commemorative music of their own Analyze the lyrics and music of Civil War songs to discover different perspectives held by Northerners, Southerners and African Americans View slides of immigrants on the transatlantic voyage to the United States, they make sounds as the creaking of a boat, the clanging of a steering mechanism, and the howling of wind and waves. Visual/Spatial Characteristics Visual-Spatial intelligence deals with such things as Thinks in images and pictures the visual arts (including painting, drawing, and Likes to draw, paint, sculpt, participate in arts activities sculpture), navigation, map-making, and architecture, Reports clear visual images when thinking about all ofsomething which involve the use of space and knowing how to get around. Games such as chess and marbles, Easily reads maps, charts, and diagrams which require the ability to visualize objects from Draws accurate representations of people or things different perspectives and angles, are also included. Likes to see movies, slides, or photographs The key sensory base of this intelligence is the sense of Can do jigsaw puzzles and mazes sight, but the ability to form images and pictures in the Engages in daydreaming mind is also involved. Visual/Spatial Ideas: Create a physiographic map of Latin America showing key bodies of water, rivers, mountains, flatlands and canyons Create visual metaphors representing the relationship between the US and the USSR during the Cold War Analyze a series of Allied and Central Power propaganda posters from World War I by looking for political distortion Graphic Organizers Venn Diagram Matrix Attribute Web T-Chart Cluster Charts 5 W article organizer Logical/Mathematical Characteristics Logical/Mathematical intelligence is most often associated Explores categories, patterns, andscientific relationships with what is called thinking or Computes problems quicklyto observe and deductivearithmetic reasoning: the ability Enjoys using computers, especially datapattern. base and Inductive understand details as part of a general spreadsheet thought processes are also involved, such as the ability Able to group, order, analyze, andand, interpret tomake objective observations, fromdata the observed Solves problems through logical reasoning data, to draw conclusions, to make judgments, and to Plays checkers and strategy games to win formulate hypothesis. Logical-mathematical intelligence Enjoys working on logical puzzles patterns, to work with involves the capacity to recognize Devises experiments out things that aren’t easily abstract symbols, andtototest discern relationships and see understood connections. Logical/Mathematical Ideas: Given geographic data about a particular location in the United States, student are told to create a city on that site Place the date key inventions were created in Chinese history along a time line Graph and analyze various indicators of the United States’ rise to industrial prominence Linguistic/Verbal Intelligence Characteristics Linguistic intelligence is responsible for the production Likes to read of language and all the complex possibilities that Has highly developed auditory skills follow including poetry, humor, storytelling, grammar, Tells tales, jokes, stories metaphors, similes, abstract reasoning, symbolic Has a good memory for names, places, dates, trivia thinking, impromptu speaking, verbal debate, Enjoys writing conceptual patterning, and the written word. Enjoys speaking to groups Linguistic intelligence is awakened by the spoken Readily uses a word processor word, by reading someone’s ideas about poetry, by Spells accurately and easily writing one’s own ideas, thoughts or poetry, and by Likes crossword puzzles, word games listening to a speech, lecture or group discussion. Linguistic/Verbal Ideas: Write a dialogue between Patriots and Loyalists detailing the tensions between the American colonies and Great Britain Read haiku about the experiences of JapaneseAmericans interned during World War II Discuss Islamic contributions to the world in the fields of medicine, engineering and astronomy Word Splash Activator Teacher creates word splash prior to book, movie, speaker, lecture, field trip. Students (individual or group) make predictions for each item. Read, listen, watch, visit. Share predictions. Revise predictions for accuracy. When planning a lesson, ask the right questions. Linguistic: How can I use the spoken or written word? Logical-Mathematical: How can I bring in numbers, calculations, logic, classifications, or critical thinking? Spatial: How can I use visual aids, visualization, color, art, metaphor, or graphic organizers? Musical: How can I bring in music or environmental sounds, or set key points in a rhythm or melody? Asking the right questions Bodily-Kinesthetic: How can I involve the whole body, or hands-on experiences? Interpersonal: How can I engage students in peer or cross-age sharing, cooperative learning, or large-group simulation? Intrapersonal:How can I evoke personal feelings or memories, or give students choices? A Private Universe Principles of Learning Learning is not necessarily an outcome of teaching What students learn is influenced by their existing ideas Progression in learning is usually from the concrete to the abstract Principles of Learning People learn to do well only what they practice doing Effective learning by students requires feedback Expectations affect performance