but very slowly PERMEABILITY – ABILITY OF WATER TO FLOW
advertisement

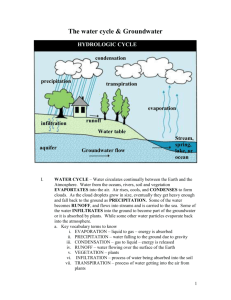
Objective : Agenda: Determine the porosity Ground water notes of soils and water flow with three different sized particles. Lab: Porosity of soils and water flow HYDROLOGIC CYCLE condensation precipitation transpiration evaporation infiltration runoff Water table aquifer Groundwater flow Stream, spring, lake, or ocean Groundwater is always moving --but very slowly PERMEABILITY – ABILITY OF WATER TO FLOW (IMPERMEABLE – NO WATER CAN FLOW THROUGH) POROSITY – PORE SPACES BETWEEN SEDIMENTS CAPILLARITY – THE ABILITY OF WATER TO MOVE UPWARD IN SOIL 1.Permeability – larger size = BETTER small – impermeable (cannot flow through) 2.Porosity – size has NO EFFECT a. Shape – round = best b. Packing – loosely packed or less dense c. Sorting – well sorted 3.Capillarity – smaller size sediment = BETTER GRAVEL Rapid drainage FINE SAND Moderate drainage CLAY Slow drainage Clay is impermeable – water will not flow through easily SMALLER SIZED PARTICLES INCREASE CAPILLARITY INFILTRATION Infiltration refers to water soaking into the ground: Infiltration rate Infiltration rate Permeability Porosity Infiltration rate Infiltration rate Slope Soil Storage Saturation 1. WATER INFILTRATES 2. STOPS AT IMPERMEABLE LAYER 3. RISES FROM BOTTOM UP – (LIKE FILLING A BATH TUB) THIS IS CALLED GROUNDWATER AKA – SATURATED ZONE AKA - AQUIFER 4. TOP OF SATURATED ZONE IS THE WATER TABLE 5. UNSATURATED ZONE – AIR AND WATER 6. CAPILLARY FRINGE – WATER RISES TO FEED ROOTS WATER TABLE RISES WITH RAINFALL FALLS WITH DROUGHT