Factors Affecting Infiltration
advertisement

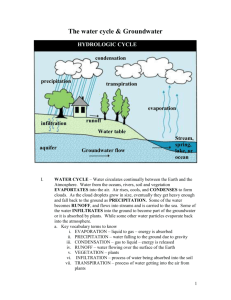
Topic 8: Water Cycle and Climate What is the water cycle? ~The water cycle is also called the hydrologic cycle. It is a model used to illustrate the movement and the phase changes of water at and near the Earth's surface. ~It is fueled by the sun. What happens when precipitation falls on the ground? ~It can be stored or retained on the surface as ice or snow (water retention). ~It can infiltrate or seep (sink into) the Earth’s surface. ~It can flow over the Earth’s surface as runoff. ~It can be evaporated or transpired (both of these together is called evapotranspiration). Factors Affecting Infiltration ** Remember: Infiltration means to sink into. ** Ex: Watering a plant • Slope of the Land • Sorting • Degree of Saturation • Shape • Porosity • Capillarity • • Permeability Packing • • Vegetation Land Use Slope of the Land The steeper the slope (gradient), the less the infiltration or seepage --- inverse or indirect relationship Degree of Saturation The more saturated the loose Earth materials are, the less the infiltration --- inverse or indirect relationship Water infiltrates into the ground until it meets the interface between the zone of saturation and the zone of aeration This interface is the WATER TABLE The depth of the water table below the surface varies with the amount of infiltration Subsurface water below the water table is called GROUND WATER Porosity Porosity is the percentage of open space (pores and cracks) in a material compared to its total volume Generally: the greater the porosity, the greater the amount of infiltration that can occur ---Direct Relationship Dependent upon shape Shape Well rounded particles have a greater porosity. Round particles = more pore space, higher porosity, and more infiltration Angular particles = less pore space, less porosity, and less infiltration Packing The closer the particles are packed together, the lower the porosity Therefore if you have a lower porosity, infiltration will also be lower. Sorting If all the particles in a material are about the same size, they are said to be sorted If the particles are of mixed sizes, they are said to be unsorted Sorted = higher porosity or pore space Unsorted = lower porosity because the smaller particles fill in the pore space Permeability The ability of a material to allow fluids such as water to pass through it. Larger particles will increase permeability, because pore space is larger. **Impermeability may be due to tight packing or cementing of particles, which seals off the pores from one another. ex: ice in the winter Capillarity The process by which water is drawn into openings due to the attractive force between water molecules and the surrounding earth materials. As the particles decrease, capillarity increases. When water moves upward against gravity, it is called capillary action. ex: How plants take water from the soil Vegetation Grasses, trees and other plant types capture falling precipitation on leaves and branches, keeping that water from being absorbed into the Earth If any water gets through the vegetation, the velocity of the water will be reduced and this will give the ground more time to absorb the water Ground without vegetation usually has high runoff and low infiltration rates Land Use Roads, parking lots, and buildings create surfaces that are not longer permeable. These impermeable surfaces often channel runoff. Farming, cutting down trees and grazing animals will reduce vegetation and therefore decrease permeability. Factors Affecting Runoff and Stream Discharge Runoff can occur when: 1) The rate of precipitation exceeds the permeability rate 2) The pore space of loose material or rock is saturated with water 3) The slope of the surface is too great to allow infiltration 4) The water on the surface has not evaporated **The greater the runoff, the greater the amount of stream discharge (volume of water flowing past a certain spot in a stream in a specific amount of time.)** UNITS FOR STREAM DISCHARGE = meters/sec **Flooding occurs when a stream overflows its normal channel**