Revision Worksheet 1 (2015)
advertisement
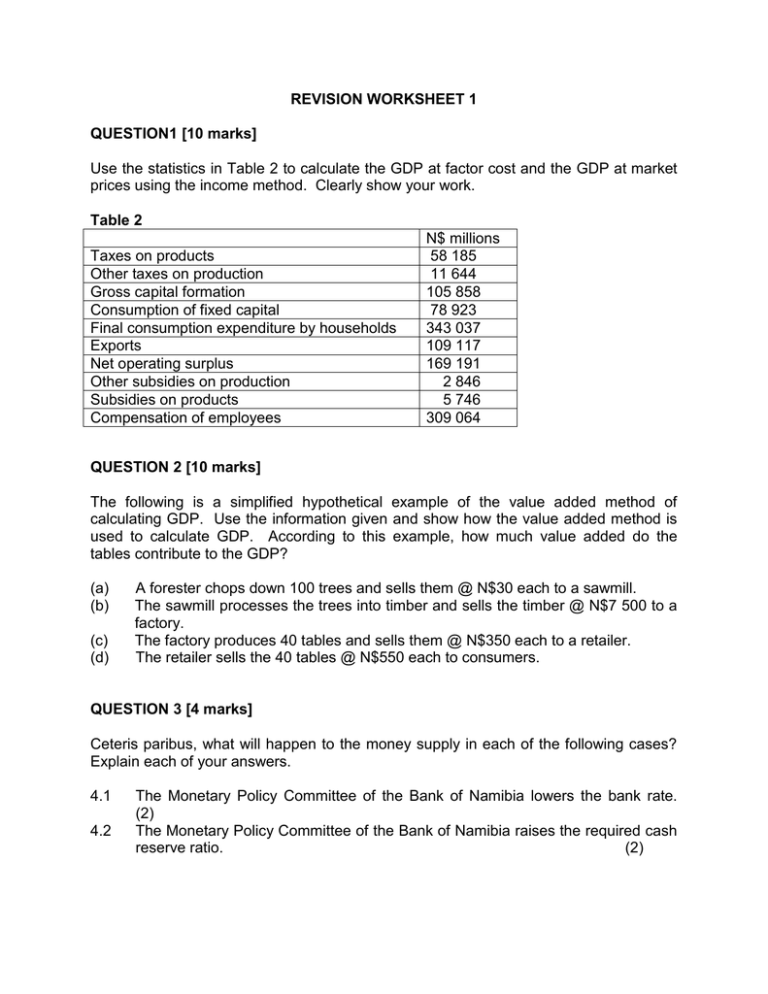
REVISION WORKSHEET 1 QUESTION1 [10 marks] Use the statistics in Table 2 to calculate the GDP at factor cost and the GDP at market prices using the income method. Clearly show your work. Table 2 Taxes on products Other taxes on production Gross capital formation Consumption of fixed capital Final consumption expenditure by households Exports Net operating surplus Other subsidies on production Subsidies on products Compensation of employees N$ millions 58 185 11 644 105 858 78 923 343 037 109 117 169 191 2 846 5 746 309 064 QUESTION 2 [10 marks] The following is a simplified hypothetical example of the value added method of calculating GDP. Use the information given and show how the value added method is used to calculate GDP. According to this example, how much value added do the tables contribute to the GDP? (a) (b) (c) (d) A forester chops down 100 trees and sells them @ N$30 each to a sawmill. The sawmill processes the trees into timber and sells the timber @ N$7 500 to a factory. The factory produces 40 tables and sells them @ N$350 each to a retailer. The retailer sells the 40 tables @ N$550 each to consumers. QUESTION 3 [4 marks] Ceteris paribus, what will happen to the money supply in each of the following cases? Explain each of your answers. 4.1 4.2 The Monetary Policy Committee of the Bank of Namibia lowers the bank rate. (2) The Monetary Policy Committee of the Bank of Namibia raises the required cash reserve ratio. (2) QUESTION 4 [6 marks] Table 1 shows the amount of tax paid by individuals in three different income categories. Calculate the percentage of income tax paid and for each of the three taxes A, B and C indicate whether the tax is progressive, proportional or regressive. Table 1 Amount of Tax Paid by Income Level Income Percentage Income Percentage N$1 000 of income N$10 000 of income Income N$100 000 Tax A N$200 N$3 000 N$40 000 Tax B N$80 N$600 N$4 000 Tax C N$100 N$1 000 N$10 000 Percentage of income Tax A is _____________ Tax B is _____________ Tax C is _____________ (12 x 0.5 = 6)