Solutions Review
advertisement

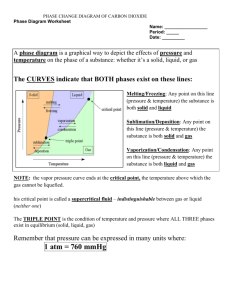
CDA #6 (KMT and Thermo) Review Phase Changes: Be familiar with phase change graphs and when kinetic and potential energy change. Know the parts of a phase diagram, including the 3 phases of matter, triple point, and critical point. Thermodynamics: Know the 3 laws of thermodynamics and how to calculate energy and specific heat. Calorimetry: Know how heat is transferred in a closed system and how to calculate specific heat of an unknown object. Phase Diagram Practice: 1. Consult the two phase diagrams below to answer the following questions. (Note: the graphs are not drawn to scale.) 218 Pressure (atm) 73 Solid Liquid Solid Liquid 5.1 1 atm Gas 0.006 Gas -78 -57 31 Temperature (C) Carbon Dioxide (CO2) 0 100 374 0.001 Water (H2O) a. At 1 atm of pressure and 55C, what phase is CO2 in? ________________________ And water? _________________________ b. What is the value of the triple point for CO2? _________C, _________ atm. And for water? _________C, _________ atm. c. What is the value of the critical point for CO2? _________C, _________ atm. And for water? _________C, _________ atm. d. What is the value of the melting point for water? _________C. And the boiling point? _________C. e. If the pressure on a block of ice is increased, the melting point of ice (increases, decreases, or stays the same). f. Pressure must be (increased / decreased) in order to liquefy water at 140ºC. g. What is the name of the process when CO2 is cooled at 1atm from 25ºC to -100ºC? h. Increased pressure will (lower / raise) the melting point of water. i. Solid water was heated to its critical temperature at a pressure of 1.00 atm. List the phases and phase changes in order as they occur. j. A sample of solid water is held at a constant pressure of 1.00 atm and is heated to 200 oC. List the phases and phase changes in order as they occur. k. A sample of CO2 is held at a constant temperature of 0C. The pressure is increased form 0.006 atm to 73 atm. List the phases and phase changes in order as they occur. l. List the phase change(s) for CO2 as temperature increases from -70ºC to 25 ºC at 1atm. Thermodynamics Problems: 2. How much heat is required to rasise the temperature of 19.68g of calcium from 18.00°C to 82.40°C? The specific heat for calcium is 0.647 J/g°C. 3. 150.0 J of heat are applied to a 35.73g sample of an unknown element. The sample’s temperature increases from 20.00°C to 49.99°C. What is the specific heat of the element? 4. 1000.0J of heat are applied to a 140.0g sample of water. If the sample’s temperature was originally 15.00°C, what will its final temperature be? The specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g°C. 5. A 4.5 g sample of a unknown metal at 100 °C is placed in 50g of water at 20 °C. The final temperature of the water and metal together is 23 °C. What is the specific heat of the unknown metal? 6. A 2.5 gram sample of an unknown metal at 11C is placed in 70 g of water at 62C. The final temperature of the water and metal together is 58C. What is the specific heat of the unknown metal? 7. A sample of nickel at 100C is placed in 50 g of water at 22C. The final temperature of the water and metal together is 26C. What was the mass of the piece of nickel? The specific heat of nickel is 0.540 J/g °C. Review Questions: 8. Draw a phase change graph for water (temperature vs. heat). Show where solid, liquid and gas exist as well as the relevant phase changes. Show where the kinetic and potential energy are increasing. 9. There are three laws concerning energy-explain and give an example of each. 10. What is entropy? Reactions always naturally occur to (increase / decrease) entropy. 11. Endo/Exothermic: define and give examples. What is the difference between them? 12. What is the difference between temperature and heat?