Econ_Chap2 - joshuabryant
advertisement

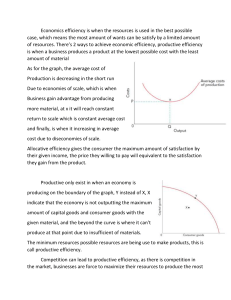
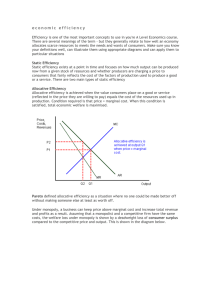
Chapter 2: The Economizing Problem 1. The foundations of Economics a. Society has virtually unlimited wants but limited or scarce productive resources b. Goods and services provide utility i. Luxuries vs. Necessities 2. Scarce Resources a. Economic Resources are limited relative to wants b. Sometimes called factors of productions and include four categories: i. Land or natural resources ii. Capital or investment goods 1. Manufactured aids, goods, or services iii. Investment Goods 1. Real capital (MONEY!!!) 2. Financial Capital iv. Human Resources 1. Labor or human resources which include physical and mental abilities used in production v. And Entrepreneurial Ability 1. Special kind of human resources that combines resources for production, makes basic business economic policy decisions, innovator for services and goods 2. Takes initiative and combines resources 3. Resource Payments a. Property Resources i. Land: Rental income ii. Capital: Interest income b. Human Resources i. Labor: Wages ii. Entrepreneur: Profits and Losses 4. Economics and Efficiency a. Full Employment: all available resources should be employed b. Full Production: employed resources are providing full satisfaction of our economic wants i. Implies two kinds of efficiency: Productive and Allocative ii. Underemployed if full production is not occurring c. Productive Efficiency: the least costly production techniques are used to produce wanted goods or services i. You produce things as cheaply as possible d. Allocative Efficiency: resources are used to produce the combination of goods and services most wanted by society 5. Production Possibilities a. Production possibilites tables and curves are devices used to clarify the economizing problem i. Assumes economy is operating efficiently 1. Means full production and full employment ii. Fixed Resources: the available supply of resources is fixed in quality and quantity at this time iii. Fixed Technology: technology hasn’t increased or improved iv. The Economy only produces two products b. Limited resources means limited output i. At any point in time, a full-employment, full-production economy must sacrifice some of product X to obtain more product of Y. c. Law of Increasing Opportunity Costs: The amount of other products that must be forgone or sacrificed to obtain one unit of a specific product is called the opportunity cost of that good. i. Economic resources are not completely adaptable for other uses d. Allocative Efficiency: MB = MC i. Marginal Benefits = Marginal Costs e. Economic Growth: The ability to produce a larger total output- a rightward shift of the production possibilities curve caused by: i. Increase in resources ii. Better resource quality iii. Technological advances 6. Economic systems a. The Market System i. Pure Capitalism ii. Laissez-faire b. The Command System i. Socialism ii. Communism