The Economizing Problem
advertisement

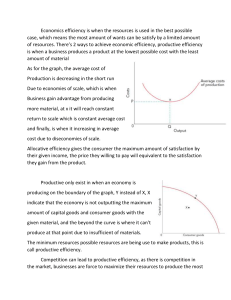
The Economizing Problem Chapter 2 Objectives Define the economizing problem, incorporating the relationship between limited resources and unlimited wants Differentiate between full employment and full production Explain the concepts of allocative and productive efficiency and how they differ Construct a production possibility curve when given appropriate data Illustrate economic growth, unemployment & underemployment of resources, allocative and productive efficiency and increasing costs using a PPC. Differentiate between product and resource (factor) markets Define and identify the terms and concepts listed at the end of the chapter The economizing problem: society’s material wants are unlimited while resources are limited or scarce. Fundamental Fact: Unlimited Wants Economic wants are desires of people to use goods & services that provide utility, which means more satisfaction Products are sometimes classified as luxuries or necessities, but division is subjective Businesses and gov’t also have wants Over time, wants change and multiply Fundamental fact: Scarce Resources Economic resources are limited relative to wants Economic resources are called the factors of production: land, labor, capital and entrepreneur 4 Factors of Production 1. land Must be natural & is limited 2. capital Must be used for production 3. labor The work force 4. Entrepreneurs Risk takers in search of a new business Phil Knight Nike Pierre Omidyar Ebay Chris DeWolfe & Tom Anderson My Space Mark Cuban Broadcast.com Mark Zuckerburg Facebook Warren Buffett--Berkshire Hathaway Sean Combs Bad Boy Records Economics: Employment and Efficiency Efficiency requires full employment of available resources and full production Full employment means all available resources should be used Full production means that employed resources are providing maximum satisfaction of our economic wants. Underemployment occurs if this is not so. Full production implies two types of efficiency ALLOCATIVE efficiency means that resources are used for producing the combination of goods and services most wanted by society PRODUCTIVE efficiency means that least costly production techniques are used to produce wanted goods and services In other words: Full production means producing the “right” goods (allocative efficiency) in the “right” way (productive efficiency) Circular Flow See document manager or board Write down the following list --goods & services --goods & services --business income --income from resources --land, labor, capital, entrepreneur --consumer spending --buy productive resources --payment for resources Production Possibilities Frontier or Curve Big Graph #1 See graph (document manager or board)