TPJ3M VITAL SIGNS

TPJ3M
VITAL SIGNS
Vital Signs
These signs may be observed, measured, and monitored to assess an individual's level of functioning.
physical
Taking Vitals:
Procedure
1. Welcome patient and introduce yourself
2. Ask patient to assume a sitting position
3. Prior to measuring vitals, the patient should have had the opportunity to sit and relax for approximately
5 minutes
Taking Vitals:
Procedure
4. Take a minute or so to look at the patient in their entirety
5. Observe
- Does the patient seem anxious?
- In pain? - Upset?
**REMEMBER! The exam begins the minute you lay eyes on the patient
VITAL #1
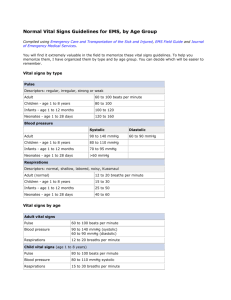
HEART RATE (HR)
Wavelike sensations felt by fingertips as blood passes through a peripheral artery (away from the heart) each time the heart contracts
11 sites to palpate (touch with fingers to feel for pulse) or osculate (using stethoscope to listen)
These sites are also called “pressure points” because you can provide pressure in these areas to stop bleeding
VITAL #1
HEART RATE (HR)
Units:
HR is measured in beats per minute (BPM)
Normal HR Ranges:
Infant = 110 - 180 BPM
Child = 70 - 110 BPM
Adult = 60 - 100 BPM
VITAL #1
HEART RATE (HR)
Documenting HR:
(A) Site: Radial
(B) Rate: 72 BPM
(C) Rhythm: Regular or Irregular
(D) Depth: Normal,
Strong, weak, bounding, thready
Text
1. Temporal Artery
2. Carotid Artery
3. Apical Artery
4. Brachial Artery
5. Radial Artery
6. Femoral Artery
7. Popliteal Artery
8. Dorsalis Pedis Artery
VITAL #2
RESPIRATIONS
-BREATHING RATE!
-The number of breaths a person takes in one minute
-1 Respiration = 1 inhalation, 1 exhalation
VITAL #2
RESPIRATIONS
Units:
Respirations are measured in respirations per minute (RPM)
Normal RPM Ranges:
Infant: Up to 40 RPM
Child: 20 - 25 RPM
Adult: 12 - 20 RPM
VITAL #2
RESPIRATIONS
Documenting RR :
(A) Rate : RPM
(B) Rhythm : Regular or Irregular
(C) Depth : Quiet or Laboured
VITAL #3
Driving force is the contraction
BLOOD PRESSURE
Relaxation force created by your heart “pump
Pressure of blood inside your blood vessels
Systole
When the heart contracts
Diastole
When the heart relaxes
VITAL #3
BLOOD PRESSURE
Tools
Sphygmomanometer (BP Cuff
-
Different sizes and stethoscope
VITAL #3
BLOOD PRESSURE
120 mmHg
80
Systolic Pressure:
Pressure in the arteries when the heart contracts
Diastolic Pressure:
Pressure in the arteries when the heart relaxes
VITAL #3
BLOOD PRESSURE
Units: mmHg
Normal BP Ranges:
Baby/infant = 90/55 mmHg
Child = 110/58 mmHg
Teenager/Adult = 120/80 mmHg
Important to note!
•
Hypertension – high blood pressure 140/90 mmHg +. High risk for blood clots, stroke or heart attack, arteries lined with fat
•
Hypotension – low blood pressure 90/60 mmHg and below. May stop blood flow through kidneys, may cause shock or hemorrhaging.
ONLY a concern if it cause signs or symptoms such as dizziness, virtigo and syncope (fainting)
VITAL #4
BODY TEMPERATURE
4 Sites
1. Oral “O” (mouth)
2. Tympanic “T” (ear)
3. Axillary “A” (armpit)
4. Rectal “R” (rectum)
VITAL #4
BODY TEMPERATURE
Normal Range
36.5 - 37.5
°C
Documentation
Site: O, T, R, A
Temperature in degrees Celcius
Important to Note!
Hypothermia – low body temperature below 35 degrees Celsius
Hyperthermia – high body temperature above
40 degrees Celsius (can lead to stroke, heart attach, death)