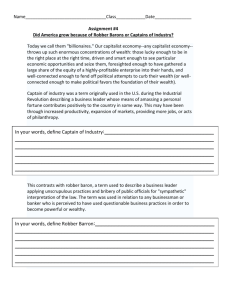
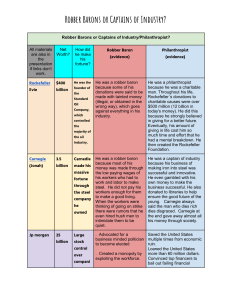
Immigration
advertisement

Technology, Robber Barons and immigrants, OH MY! Review: Pacific Railway Act Morrill Land-Grant Act Homestead Act 1862 Exodusters Sand Creek 1864 Red Cloud War’s Battle of the Little Big Horn Ghost Dance Battle of Wounded Knee Assimilation Dawes Act The Master of Invention! Thomas Edison Light Bulb Phonograph Motion Picture 1093 patents Edison's Lab Advances in communications TelegraphPerfected the telegraph Morse Code Western Union (1870) 1900- 900,000 miles of wire 63 million messages Advances in technology Telephone Alexander Graham Bell (Scottish immigrant) Earliest line only connected two lines Created switchboards 1900 1.5 million telephones in use Transcontinental Railroad At first, no standard rail gauge, short lines, no signals, costly delays Expanded after Civil War Transcontinental Railroad started in 1862 funded by government grants. (Central Pacific and Union Pacific) Most workers were immigrants Two lines met in in Utah on May10,1869 (Promontory Summit) Drive the golden spike Dirty, noisy but continued to expanded and develop Developed schedules and standard time Impact of the Rails Faster and more practical transportation Lower costs of production Creation of a nation market Model for big business Stimulation of other industries The Haves Robber Barons/Captains of Industry Robber Baron Robber baron - term revived in the 19th century as a reference to businessmen and bankers who dominated their industries and amassed huge personal fortunes, by pursuing various anti-competitive or unfair business practices. Captains of Industry Captains of Industry- Term originally used in the U.S. during the Industrial Revolution describing a business leader whose means of amassing a personal fortune contributes positively to the country in some way. Why is this Era so important? Changed from a society based on agriculture to a society based on industry Captains of Industry vs Robber Baron J.P. Morgan Andrew Carnegie John D. Rockefeller J.P. Morgan (April 17, 1837 – March 31, 1913) John Pierpont Morgan financier, banker, philanthropist, and art collector Dominated corporate finance Arranged merger to form General Electric. Financed the creation of the Federal Steel Company he merged several other steel and iron businesses to form the United States Steel Corporation By 1901, he was one of the wealthiest men in the world Andrew Carnegie (November 25, 1835 – August 11, 1919) Widely respected philanthropist, and the founder of the Carnegie Steel Company which later became U.S. Steel. Built one of the most powerful corporations in United States history Gave away most of his riches to build libraries, schools, and universities and worldwide John Rockefeller, Sr. (July 8, 1839 – May 23, 1937) American industrialist and philanthropist. Revolutionized the oil industry Believed his purpose in life was to make as much money as possible, and then use it wisely to improve the lot of mankind. Rockefeller founded the Standard Oil He became the world's richest man and first billionaire. Standard Oil was convicted in the Federal Court of monopolistic practices and broken up in 1911. The Box Scores Year 1904 The Times of London $21 M 1910 The New York American $179 M 1913 The New York Herald $332 M Newspaper Carnegie Rockefeller $10 M $134 M $175 M Sherman Anti-trust Act Was the first United States federal government action to limit monopolies, and is the oldest of all U.S. antitrust laws The have-nots Immigration/labor Immigration Came to the US in steamships, often in steerage 10 million between 1865-1890 German, Irish, British 10 Million between 1890 – 1920 Italians, Greeks, Slavs Immigration 70% came through NYC- Ellis Island Had to pass physical exams Could be quarantined (TB) Literacy exams Immigrants Chinese Exclusion Act- Chinese labor used to build rail but Act prevented entry to establish residence in US Nativism- favoring native born Americans over immigrants Child Labor As young as six years old worked up to 19 hours a day, with a one-hour total break. Horrible conditions. Large, heavy, and dangerous equipment was very common for children to be using Children were paid only a fraction of what an adult Orphans were the ones subject to this slave-like labor. Reformers Reformers – built Settlement Houses (Hull house – Jane Adams) Reporters/Photographers- wrote books like The Jungle which exposed the meat industry and published photos Social reformers- preached temperance, staying away from vice Tenements – low cost housing built to hold as many people as possible Turned area into slums