The Civilization of the Greeks - Loudoun County Public Schools
advertisement

The Civilization of the Greeks
{
431 BCE: Period of Warring States in China and
beginning of Peloponnesian War between
Athens and Sparta
Pericles Funeral Oration: democracy and
importance of the individual
Greeks questioned the world around them and
created system of logical, analytical thought to
examine
8th c BCE city-state (polis) emerged
Classical era= 5th c. BCE
Ultimately defeated by Philip II of Macedonia,
but Greek culture continued to spread by
Alexander the Great
(Hellenic “Greek” vs. Hellenistic “Greek-like”
culture)
{
Mountainous terrain/ limited arable land: couldn’t unifyrise of independent city-states
Mediterranean Sea was Key
Sparta on Peloponnesus
Athens on Attica Peninsula
Early Greece
earliest civilization in Aegean region on island of
Crete around 2800 BCE
Palace at Knossos- sea empire
Contact with Egypt: evidence in trade
Height between 2000 and 1450 BCE
Palace had bathrooms with drains!
Bull-vaulting
Around 1450BCE sudden and catastrophic collapsecause still debated: perhaps an invasion by the
Mycenaeans?
Minoan Crete
Greek civilization that flourished between 1600 and
1100BCE
Key city= Thebes
Epic poetry of Homer- did Mycenaean Greeks, led by
Agamemnon, King of Mycenae, sack the city of Troy c.
1250BCE?
Was Troy a vassal of the Hittites?
Decline due to invasion
First GREEK State- Mycenae
Declining population and failing food
production
Large number of Greeks migrated to
other places, including SW shore of
Asia Minor “Ionia”
Iron replaced bronze in weapons=
more affordable and prevalent
8th c. BCE: Greeks adopted
Phoenecian alphabet
Homer – Iliad and Odyssey
The Greeks in a Dark Age (c.
1100-750BCE)
Homer and Homeric Greece
Iliad and Odyssey based on oral tradition
Gave Greeks an idealized past
Iliad: poem of Trjoan War- sparked by
Paris, a prince of Troy, kidnapping Helen,
wife of King of Sparta. Spartan king’s
brother, Agamemnon of Mycenae Greeks
attacked Troy
Helen was “The Face which launched a
thousand ships.”
Tale of Greek hero Achilles “Achilles heel”
Odyssey: Epic Romance- journeys of
Greek hero, Odysseus, from fall of Troy
until reunited with his wife Penelope, 20
years later
Values of aristocratic heroes
Homer’s Enduring
Importance
Gave Greeks a common and
idealized past
Arete: excellence befitting a
hero…won in a struggle or a
contest
Popularity of Homer’s epics as
educational tools:
memorization
Homer’s Ideal of Excellence:
The Iliad “Fate is a thing that
no man born of woman,
coward, or hero can escape.”
The Greek City States
(c. 750-c. 500 BCE)
What were the chief features of the polis, or city –
state, and how did Athens and Sparta differ?
Plural poleis
Small, autonomous political
unity…consisted of city and its
surrounding countryside
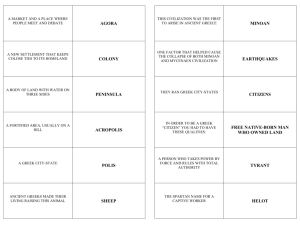
Acropolis: fortified hill
Agora: open marketplace
(agoraphobia: fear of crowds)
Polis: community of citizens in which all
political, economic, social, cultural, and
religious activities were focused.
Citizens with political rights (free adult
males), citizens with no political rights
(women and children, and noncitizens
(slaves and resident aliens)
The Polis
Greek Way of War
New military order based on
hoplites: heavily armed
infantrymen who wore
bronze or leather helmets,
breastplates, and greaves
(shin guards)…round shield,
short sward, and thrusting
spear about 9 feet long
Battle formation=
phalanx…safety of which
depended on the solidarity
and discipline of its
members
War was an integral part of
the Greek way of life
Excellent weapons and body
armor, wide number of
citizen-soldiers (rather than
mercenaries), use of heavy
infantry
Colonization
and Trade
Between 750 to 550BCE large
numbers of Greeks left to
settle in distant lands due to
the growing gulf between rich
and poor, overpopulation,
and the development of
trade.
New Greek settlements:
coastline of southern Italy,
southern France, eastern
Spain, and northern Africa,
west of Egypt…city of
Byzantium in the
north…fostered greater sense
of Greek identity
Colonization also led to
increased trade and
industry…new wealthy class
to compete with aristocrats
Tyranny in the Greek Polis
Greek tyrants came to power in an unconstitutional way (usurpers of
power)…support for tyrants mostly came from new rich and poor
Oligarchies “rule by small group of wealthy people”
Common transition of power in Athens: monarchy-oligarchy-tyrannydemocracy
{
S
P
A
R
T
A
located in the southeastern
Peloponnesus
Spartans conquered the Laconians
and Messenians and reduced them
to serfdom…known as HELOTSforced to work for
Spartans…created military state to
control the helots
The New Sparta 800-600BCE
Lycurgan Reforms: in Sparta to maintain control over the conquered
Messenians
Spartan’s lives were rigidly organized and controlled
Spartan= highly self-disciplined (ex: Spartan lifestyle)
Boys moved to military barracks at 7…could marry at 20…could live at
home at 30…could visit home, but not get caught
Military life: “come back with your shield, or on top of it…”
Spartan women had greater rights/freedom…marry later, exercise
The Spartan State
Government organized as an oligarchy
2 kings, led army, shared power with the gerousia, (council of elders)
apella= assembly of all male citizens
Isolationist
Philosophy discouraged, focus on war
By 500 BCE: Sparta dominated the Peloponnesian League
A
t
h
e
n
s
Government in Athens: Monarchy to Oligarchy to
Tyranny to Democracy
Disparity between rich and poor, some Athenian
farmers were being sold into slavery if they couldn’t
pay debts by their aristocratic neighbors
The Reforms of Solon
Solon= reform-minded aristocrat
as sole archon in 594BCE w/ full
power to make changes…Solon
canceled all land debts, no human
collateral, and freed slaves from
debts…did not redistribute the
land
Pisistratus seized power in
560BCE as a tyrant (usurper of
power)
solon
{
The Reforms of Cleisthenes
Created the Council of 500, chosen
by lot by the ten tribes in which all
citizens had been
enrolled…administration of both
foreign and financial affairs
Assembly of all male citizens had
final say
Reforms of Cleisthenes created the
foundation for Athenian democracy
Democracy= demos, “people”, kratia,
“power”
{
The Birth of Democracy
Foreign Influence on Early Greek Culture
Cultural diffusion between the Greeks and the older
civilizations of the Near East and Egypt
Ex: multiple gods and goddesses and the story of a flood
from Mesopotamia
Kouros statues= example of diffusion between Egypt and
Greece
Greeks adopted the Phoenician alphabet, but added
vowels…Greek was a truly phonetic alphabet, easier to
read and use
Persians…
Greeks versus Persians, Greeks saw the struggle
with the Persians was a contest between freedom
and slavery
Ionian Greek cities in Asia Minor were subjects of
the Persians
Unsuccessful Ionian revolt, aided by Athenian
navy, led to Persian ruler Darius to seek revenge
by attacking mainland Greeks
490BCE Persians defeated by Athenians at
Marathon
Xerxes succeeded Darius
Greek Trireme= standard warship of ancient
Greece…especially effective at ramming enemy
ships
Xerxes led an invasion of Greece…Greeks tried to
delay the Persians at the pass of
Thermopylae…Greek force led by Spartan King
Leonidas and 300 Spartans held pass for 2
days…then a traitor showed the Persians a pass to
outflank the Greeks…Spartans fought to the last
man
Athenians abandoned their city and Persians
burned it
Defeat of the Persians with use of the navy at
Salamis
The Growth of an Athenian Empire in the
Age of Pericles
Formation of the Delian League, led by
Athens…city-states had to pay tribute,
Athens controlled the treasury
Age of Pericles, 461-431 BCE, height of
Athenian power and the culmination of its
brilliance as a civilization
Magistrates chosen by lot, many male
citizens got the chance to serve during their
lifetime
Strategoi: board of 10 officials elected by
public vote to guide affairs of the state
Lower-class citizens were now eligible for
public offices with state pay for
officeholders
However, aristocrats still held most
important offices
Pericles used the treasury money of the
Delian League to rebuild Athens, for
example: the Parthenon
Sparta accused Athens of mismanaging
Delian League funds
Athenian
Empire in
the age of
Pericles
The Great Peloponnesian
War and the Decline of the
Greek States
Sparta vs. Athens
431BCE outbreak of war
Athenians wanted to rely on their
walls and their navy, Spartans
wanted to rely on their army
Plague broke out in Athens, losing
1/3 of population, including Pericles
404BCE Athens was defeated by
Sparta, and was forced to tear down
the walls of their city
Ultimately weakened the Greek Citystates, next 70 years Athens, Sparta,
and Thebes jockeyed for position,
oblivious to growing threat of
Macedonia to the north.
{
{ Greek Culture
Athens was the center of culture
The Writing of History
Herodotus – Persian Wars
Thucydides- Peloponnesian War
Drama
First Greek dramas were tragedies
with all parts played by men.
Aeschylus: first tragedia
Sophocles: most famous work=
Oedipus Rex (or Oedipus the
King)…man is destined to kill his father
and marry his mother
Euripedes: questioned traditional
moral and religious values
Common theme: humans are free but
can only operate within limitations
imposed by the gods
Comedies came later: Aristophanes=
famous comedian with Lysistrata and
The Clouds
{ The Arts
Classical style- reason, moderation,
symmetry, balance, and harmony in all things
Parthenon: ideal classical style
Wisdom
Philosophy= Greek word meaning “Love of
Wisdom”
Sophists: group of philosophers in the 5th
century BCE – believed in relative truth and
that understanding the universe was beyond
the reach of the human mind…importance of
rhetoric…”true wisdom consisted of being
able to perceive and pursue one’s own good”
Socrates: believed in absolute truth…Socratic
Method…believed all knowledge is within
each person, only critical examination was
needed to call it forth…sentenced to death
for corrupting the youth
3 orders of columns: Doric, Ionic, and
Corinthian
Plato: student of Socrates…how do we
know what is real? The objects that we
perceive with our senses are simply
reflections of the ideal Forms.
Plato’s government ideas- book: The
Republic…rule by “philosopherkings”…established school in Athens
called The Academy…believed men and
women should have the same education
and equal access to all positions
Aristotle: student of Plato, teacher to
Alexander the Great. Analyzing and
classifying things based on thorough
research and investigation
Aristotle’s book on government:
Politics…3 good forms of government:
monarchy, aristocracy, and constitutional
government…believed women were
biologically inferior to men
Aristotle
Socrates
Plato
Religion was integral to Greek society
Public festivals important…civic cult
necessary for the well-being of the
state…multiple gods/ goddesses
Axial Age: between 700 and 300 BCE:
development of ideas or “axes” that
remained the basis for religions and
philosophies for hundreds of years:
Socrates, Plato, Aristotle, Zoroaster,
Hebrews, Confucianism, Daoism, Hinduism,
Buddhism
Polytheistic, 12 chief gods who lived on Mt.
Olympus
Zeus, Hera, Athena, Apollo, Aphrodite,
Poseidon
Rituals and sacrifice
Olympic games originated to honor Zeus
Oracles as interpreters of the gods
Religion
{
Life in Classical Athens
Polis was a male community, women, slaves, and foreign
residents of Athens were excluded (about 85% of total
pop.)
Slavery was pervasive
Economy and Lifestyle
Athenian economy was based on agriculture and trade
Lack of arable land…Athens had to import 50 to 80% of
its grain, therefore trade was very important
Olive oil
Family and Relationships
Family was central institution in ancient Athens
Women’s primary role was to bear children, especially
boys
Athenian women married at 14 or 15…Spartan women
later 18 to 20
Male homosexuality was a prominent feature of Athenian
life.
Life…
{
http://www.youtube.com/watc
h?v=0LsrkWDCvxg#t=32
{
http://www.youtube.com/watc
h?v=xvRWUCfAPs0
{
Alexander the Great
{