Ch08
advertisement

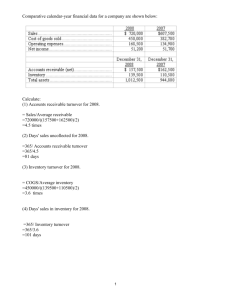
CHAPTER 8 Reporting and Analysing Receivables Types of Receivables • Amounts due from individuals and companies that are expected to be collected in cash • Frequently classified as – Accounts receivable – Notes receivable – Other receivables Accounts Receivable • Amounts owed by customers on account • From sale of goods/services (trade) • Normally expected to be collected within 30 days • Most significant type of claim held by company Notes Receivable • Claims for which formal instruments of credit are issued as evidence of debt • The credit instrument normally requires the debtor to pay interest and extends for time periods of 30 days or longer • Notes receivable can be current or long-term Other Receivables • Nontrade including: – Interest receivable – Loans to company officers – Advances to employees – Refundable income taxes – Recoverable sales taxes Accounts Receivable • Recorded when service is provided or at point of sale of merchandise on account Accounts Receivable Sales 100 100 Allowance Method • The matching principle dictates that the bad debt expense must be recorded in the period when the related revenue is earned • There are many acceptable methods to estimate uncollectible accounts The Percentage of Receivables Method • Management establishes a percentage relationship between amount of receivables and expected losses from uncollectible accounts – Apply percentage to total receivables – Apply percentage to receivables classified according to the length of time they have been outstanding (known as aging the accounts receivable) Recording Estimated Uncollectibles Abrams Furniture has credit sales of $1,200,000, of which $200,000 remains uncollected. The credit manager estimates $11,000 will prove uncollectible. The adjusting entry must take into consideration any opening balance in the allowance account to pick up amounts from prior years that are still outstanding. Bad Debts Expense Allowance for Doubtful Accounts xxxx xxxx Recording Estimated Uncollectibles Bad Debts Expense 10,000 Allowance for Doubtful Accounts The percentage of receivables method gives you the BALANCE in the Allowance account, not the amount of the adjustment. 10,000 Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Jan. 1 Bal. Adj. entry 1,000 10,000 Dec. 31 Bal. 11,000 HAMPTON FURNITURE Balance Sheet (partial) Current Assets Cash $ 14,800 Accounts receivable $200,000 Less: Allowance for doubtful accounts 11,000 Net realizable value 189,000 Net Realizable Value • Net amount expected to be collected in cash • Excludes amounts the company estimates it will not collect • Keeps receivables from being overstated on the balance sheet Write-Off of an Uncollectible Account The vice president of finance authorizes a write-off of $2,500 owed by T. O. Ebbet: Bad Debts Expense 10,000 Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Accounts Receivable Jan .1 Bal 227,500 Mar. 1 Bal 225,000 Mar. 1 2,500 10,000 Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Mar. 1 2,500 Jan .1 Bal 11,000 Mar. 1 Bal 8,500 Recovery of an Uncollectible Account Accounts Receivable—Ebbet Allowance for Doubtful Accounts 2,500 Cash Accounts Receivable 2,500 2,500 Record in two separate entries 2,500 Notes Receivable • Result from sale of goods and services (trade) • Stronger legal claim to assets than accounts receivable; written promise (promissory note) to repay • Negotiable instruments and may be transferred to another party by endorsement Notes Receivable • Credit instrument normally requires – Payment of interest – Extends for time periods of 60-90 days or longer • Often accepted from customers who need to extend payment of an account receivable • Often required from high risk customers Notes Receivable • Interest is charged as: Principal x Rate x Time • Interest is always quoted using annual rates – For example, a six-month $10,000 note at 4% means that the annual rate of interest is 4% – Interest would be $10,000 x 4% x 6/12 • To record note receivable: Dr. Note receivable (face value) Cr. Cash, A/R, or Sales Managing Receivables • • • • • Determine to whom to extend credit Establish a payment period Monitor collections Evaluate receivables balance Accelerate cash receipts from receivables when necessary Credit Risk • Risk of nonpayment of account concentrated by customer or geographically • Disclose concentration of credit risk Evaluating the Receivables Balance • Liquidity is measured by how quickly certain assets can be converted into cash – Receivables turnover – Average collection period Receivables Turnover • Is a measure of the liquidity of receivables Receivables Turnover = Net Credit Sales Average Gross Receivables Average Collection Period • Is the average amount of time that a receivable is outstanding 365 days Average Collection Period = Receivables Turnover Credit and Debit Card Sales • These sales have a cost to the business, which must be recorded at the times of sale • For example, the business may have to pay the credit card company 2% for each sale • A sale of $100 would be recorded as follows: Dr. A/R—Credit card (or Cash) Dr. Service Charge Expense Cr. Sales Revenue 98 2 100