Ch 1
advertisement

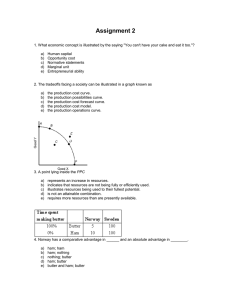
Chapter 1.2 Opportunity Costs WARM-UP • Tell me 5 vacation destinations you would like to go to...(place them in order of which you prefer) • What are you giving up by choosing your top choice? Trade - Offs alternatives • All of the ___________that we give up whenever we choose one course of action over another. • Tell me 3 Trade-offs that you made in order to come to school today… Guns v. Butter Goods • Military v. Consumer ______________ ALWAYS – RESOURCES ARE ________LIMITED tank – now can not be used – Steel to make a _____ to build dairy ________equipment to make butter. Opportunity Cost MOST • The _______ desirable alternative given up as a result of a decision – If I buy a computer, then I can not use that money to go on a vacation… – Should I sleep late or wake up early for a ski trip? – Sleep late or wake up early to take a test? – Sleep late or wake up early to go to practice? Global Connections The same decision made in two different countries can have vastly different opportunity costs. Malaysia bought two warships in 1992, paying a price equal to the cost of providing safe drinking water for the 5 million Malaysians lacking it. In other words, the opportunity cost of the warships was safe drinking water. The opportunity cost of building warships in wealthier countries is not nearly so high. However, there are still costs to consider. In the US, the number of people employed by the military decreased dramatically following the end of the cold war. In response, the Pentagon developed a new program, “troops to teachers,’ to help former soldiers get jobs teaching in schools. The switch from army duty to teaching reminds us that the opportunity cost of a soldier may be a teacher and vice versa. Ch 1.3 Production Possibilities Curves Production Possibilities graph • A production possibilities curve, or______, shows alternative __________ ways to use an economy’s resources. • The axis of the graph can show categories goods and services of ___________________, such as farm goods and factory goods or capital and consumer goods. Drawing a PP Curve • First an economist decides which goods or services _____________________ to examine. two goods and the • The line drawn for the ____ combinations of those goods is the ___________ frontier production possibilities_________. This line represents a point at which the maximum ___________ combination of two products/resource is being produced. Watermelons v. Shoes Food v. Computers Lets Graph • Butter 0 80K 100K 120K 130K • Guns 80K 60K 40K 20K 0K • Fish • Coconuts 4 0 3 2 2 4 1 6 0 8 Efficiency, Growth, and Cost • PP graphs can show how efficient an economy is, whether ________ an economy has grown or shrunk, and the opportunity cost _________________of a decision. • Efficiency means using resources in such a way as to maximize the production or output of goods and services. • Any point inside the line indicates an underutilization of resources than the economy is capable of using. • A production possibilities curve reflects the current country’s _________production possibilities as if frozen the country’s resources were ________in time. However, quantity of resources a country has constantly changing is__________________. If the quantity or quality of available land, labor, or capital move changes, then the pp curve will______. New inventions ___________, immigration can help with growth. grows economists say that When the economy ______ the entire production possibilities curve has “_______to the right.” And if a country’s shifted population ages, becomes __________ unhealthy or less educated, then the curve would shift to the____. left Resources and Technology • A country’s resources ________include its land and natural resources, its work _____ force, and its physical and human capital. Both human technology and physical capital reflect a vital _______ ingredient – technology. Countries have different ways to produce items, each using different technology, or know-how. Economist asses each country’s level of technology, and resources which ppc determine its _______. rain forests are areas of thick vegetation • Tropical ____ found in equatorial altitudes around the world. These forests contain an enormous diversity of plant and animal life. Most rain forest areas, _____ such as the Amazon Basin, are part of _________ Developing countries. In many cases these nations hope to exploit the land for economic growth. Groups ______ that want to protect and preserve the environment, however, point to the ecological hazards of clearing this land and developing it for settlement commercial or for _________uses, such as mining. • Illustrate the impact of each event on a PPC – The computer is invented – 1 million farm workers remain unemployed for 6 months – A drought Buying a car Safety at any cost • When you buy a car there are trade-offs. Economists urge consumers to consider the trade-offs and opportunity costs of each of their purchase decisions. For cars they fall into: • Safety vs. cost and convenience • Pollution v. size • Safety v. personal freedom Choose the right car for your group…chart out the 3 opportunity costs & trade-offs for each vehicle.