Economic Choices: Production, Opportunity Cost, & Consumer Rights
advertisement

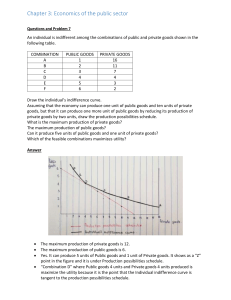
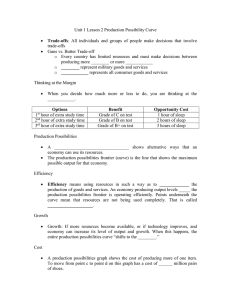
Our Economic Choices Choices Consumers Make • 2 major groups: Producers & Consumers • All producers use Factors of Production: – Land – Capital – Labor – Entrepreneurs Land • Gifts of nature, or natural resources not created by people. • Finite amount available at any given time. • World events affect availability & price. Capital • Tools, equipment, machinery, and factories used in the production of goods & services. • Unique because they are the result of production. Labor • People with all their efforts, abilities, and skill. • Includes all people except entrepreneurs. • Quantity & quality affected by birthrate, immigration, famine, war, & disease. Entrepreneurs • Risk takers in search of profits who do something new with existing resources. • Driving force in economy – Start new businesses and introduce new products. Production Possibilities • Production Possibilities Curve – Diagram representing all possible combinations of goods &/or services an economy can produce when all productive resources are fully employed. Fully Employed Resources • Points located on the curve represent maximum combinations of output with all resources being used. Opportunity Cost • Value of next best alternative given up. • Cannot always be measured in monetary terms. Opportunity Cost of Idle Resources • If some resources are not being used it is impossible to reach maximum output. Trade-Offs • Alternative choices given up in favor of the choice we select. • Making best decision requires a plan. Require More Last a Long Money Time Used Motorcycle Go to Prom Spring Break Trip New Computer Impress Your Friends Requires Parental Approval Used Multiple Times Opportunity Cost for Consumers • Previous table shows opportunity cost of buying one of the goods. • Trade-offs are all the other options that were not chosen. Consumer Rights 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Right to Safety Right to be Informed Right to Choose Right to be Heard Right to Redress Consumer Responsibilities 1. Include important details & copies of receipts, guarantees, & contracts to support your case. 2. Report the problem immediately. Don’t try to fix a product yourself, it may void the warranty. 3. If you contact the manufacturer type a letter or send an e-mail directly. Keep a copy. 4. Keep cool. Person you’re talking to probably isn’t responsible for causing the problem. 5. Keep accurate record of your efforts to get the problem solved. Quick Write • Write 1 paragraph explaining how scarcity effects Deer Park High School.