Tutors: Who Needs them? - the Enhancement Themes website
advertisement

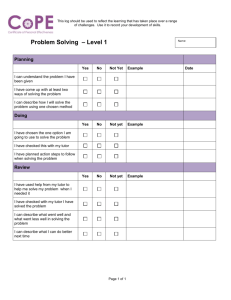
Tutors: Who Needs them? Self assessment using Grade Related Criteria http://www.rgu.ac.uk/celt/learning/page. cfm?pge=7347#Tutor Aims of this Session To Review the literature on Self assessment To outline the research design of an “experiment” with final honours year students To review the results To discuss the implications of the research for assessment Aims of Assessment Assessment has traditionally four main roles: Formative, to provide support for future learning; Summative, to provide information about performance at the end of a course; Certification, selecting by means of qualification and Evaluative, a means by which stakeholders can judge the effectiveness of the system as a whole. Role of Assessment Assessment as an aid to learning? Assessment as a means of identifying ways of improving? Assessment as a skill to be acquired by students? Aims of Self assessment An aid to student learning To help students understand more clearly the basis on which they are assessed To develop self assessment skills To encourage students to be more self critical about their work To give students more effective feedback To improve the efficiency of the assessment process The Context Module Economics of Taxation and Corporate Taxes (BS4214) Part of Accounting Module on taxation Accounting students used to assessments which involve a known or correct answer How do you assess an economics answer? Session 2002/3 48 final year accounting honours students Using the Common Grading scheme with grade related criteria If GRC Scheme is as transparent as it claims then students should be able to use it to assess themselves accurately Literature Review How Reliable is Self Assessment? What factors influence Self Assessment? Literature Review Mabe and West (1982) Review of 55 studies from 1942-1977 involving 267 correlations Findings: Poor relationship between students and tutor ratings R= 0.29 SD 0.25 (high degree of variability) Literature Review Boud and Falchikov (1995) Total of 68 studies from 1932 -1994 Do students over-rate themselves? ( 17 studies) Good students better at rating themselves than bad students? (11 studies) Advanced PG students better than “freshmen” (7 studies found PG better at self assessment) More practice made self assessment better? (7 studies found that it did not!) Gender differences? (6 studies – 3 showed women more accurate than men; the rest no evidence) Literature Review Larres, Ballantine and Whittington (2003) Self Assessment with Accounting Students Computer Literacy in two UK universities with sample of accounting students “Vast majority” over-estimated their computer knowledge Conclusion: “Self Assessment is not an appropriate means of determining computer literacy” But it did provide: “a useful adjunct into students’ attitudes to computing and stimulated reflection on their abilities.” Literature Review Self Assessment Fitzgerald as an aid to learning (1997) Found significant improvements in learning amongst medical students when self assessment introduced Literature Review Self Assessment as an aid to learning Rust (2003) Developed the use of grade related criteria with a group of 290 second year undergraduate students 140 attended a workshop in which they used the criteria to assess work by students from previous years; 150 did not attend: Experimental v control; Performance monitored and samples controlled for ability Results: significant gains both short run and long-run Methodology Set three topics for students to choose Set up iNET discussion forum using Salmons Five stage model Salmon (2003) Gave out the criteria and ran a one hour workshop on what was meant be each of the criteria Conducted an online Q & A session Students handed in coursework and completed a Self assessment proforma using the same criteria as the tutor. Students completed an evaluation of the work. Ways in which it could be improved. Analysis of self evaluation feedback + comments on iNET(the qualitative data) Proformas submitted but not read by tutor-assessor Coursework assessed internally, double marked Comparisons made student v tutors assessment Criteria Presentation Research Knowledge Analysis Evaluation Overall and Understanding 10% 10% 20% 30% 30% Grade obtained by “averaging” + profile of grade Accuracy of Self Assessment Actual Grades Degree of Match Combinations of both Tests used Correlations Kruskall Wallis, Mann Whitney Pearson Chi Square Results Variable Min Max Mean Median St Dev Presentation 4 6 5.84 6 0.426 Research 2 6 5.31 6 1.045 Knowledge and Understanding 3 6 5.37 6 0.883 Analysis 3 6 4.96 5 0.841 Evaluation 2 6 4.10 4 0.984 Overall grade 3 6 4.94 5 0.827 Presentation 4 6 5.45 6 0.709 Research 3 6 5.04 5 0.865 Knowledge and Understanding 3 6 4.71 5 0.645 Analysis 3 6 4.41 4 0.674 Evaluation 3 6 4.37 4 0.636 Overall grade 3 6 4.61 5 0.571 TUTOR Grades STUDENT Grades Results Dimension Correlation between tutor grade and student grade Presentation 0.179 ns Research 0.470 *** Knowledge 0.444 *** Analysis 0.471 *** Evaluation 0.438 *** OVERALL GRADE 0.611 *** (Whole integer data) Results Element Same One Grade Grade Variance Presentation 59.2 Research Two Grade Variance Students Grade Exceeds the Tutor Grade 30.6 10.2 6.1 42.9 46.9 10.2 16.3 Knowledge and Understanding 20.4 69.4 10.2 12.2 Analysis 38.8 51.0 10.2 8.2 Evaluation 36.7 55.1 8.2 42.8 Overall 53.1 44.9 2.0 8.2 Hypotheses H1: There will be no statistically significant differences in the degree of match in grade tutor v student H2: There will be no statistically significant gender differences in the degree of match between tutor and students assessments. H3 There will be no statistically significant differences in the degree of match made by good and poor students and the tutor Three definitions of a good student 1. Grade 5 and above (Broad) 2. Grade 6 only (Narrow) 3. First (Honours Narrow) 4. First + 2:1 (Honours Broad) Hypothesis 1 Element Kruskall-Wallis Mann-Whitney Presentation 10.087*** 3.176*** Research 3.859*** 1.964*** Knowledge & Understanding 20.528*** 4.531*** Analysis 12.343*** 3.513*** Evaluation 1.611 1.269 Overall 6.013*** 2.452** Hypothesis 2 Gender (Pearson Chi Square ) Presentation Research 1.584 6.756 *** Knowledge and Understanding Analysis 1.197 Evaluation Overall 0.023 0.000 0.063 Hypothesis 3 (1) Student (2) Student (3) Student (4) Student Ability Ability Ability Ability (Pearson Chi (Pearson Chi (Pearson Chi (Pearson Chi Square) Square) Square) Square) Presentation 2.019 2.069 0.005 3.679 * 0.152 1.838 1.642 9.317*** Knowledge and Understanding 0.206 1.426 0.057 0.611 Analysis Evaluation 2.561 0.942 6.204 *** 0.166 0.348 0.330 0.987 0.234 Overall 1.181 12.765 *** 0.016 0.023 Research Conclusions on Quantitative Data There were statistically significant differences between the grades by the tutor and grades by students. Students rated themselves significantly below the tutor on all dimensions except “Evaluation” There were no significant gender differences on any of the dimensions with the exception of “Research” where female students underscored themselves on this in comparison to male students No strong evidence that the “best” students rated themselves better than weaker students Qualitative Evidence Used quotes from the self evaluation form + iNET discussion forums to ascertain whether students were more aware of the criteria against which they were assessed Did a content analysis of responses Qualitative Evidence “ I feel I have enhanced my ability to perform research and critical analysis through this assignment” Female student Grade 4 “ I feel the strengths of this report was (sic) the research conducted as well as the knowledge and understanding I gained from this” Female student overall grade 5 “As a result of this work I have learned that tax can be interesting!. The strengths of this work is (sic) in its presentation, application of knowledge and analysis of the issues identified” Male student overall grade 4 Feedback on the exercise “ Thank you! I cant believe I got that mark ( I’m still shaking!) I honestly did think this was one of my poorer pieces of coursework, but I’m very glad you didn’t agree! Thanks also for such a detailed feedback, it’s not often we get this and I found it very useful” Female student Grade 6 Quote from Paper Biggest mismatches on Research and Evaluation Conclusions Using a university–wide grade related criteria scheme improves the accuracy of self assessment Self Assessment: helps students “unpack” the criteria by which they are assessed improves feedback that tutors can give to students identifies criteria that need to be made clearer in the future with more detailed briefings (or giving students actual coursework from previous years to practice assessing) has the potential to change the role of tutor from “front-line” assessor to “ moderator” of the assessment process. has the potential to improve both effectiveness and efficiency in assessment