Energy transfer
advertisement
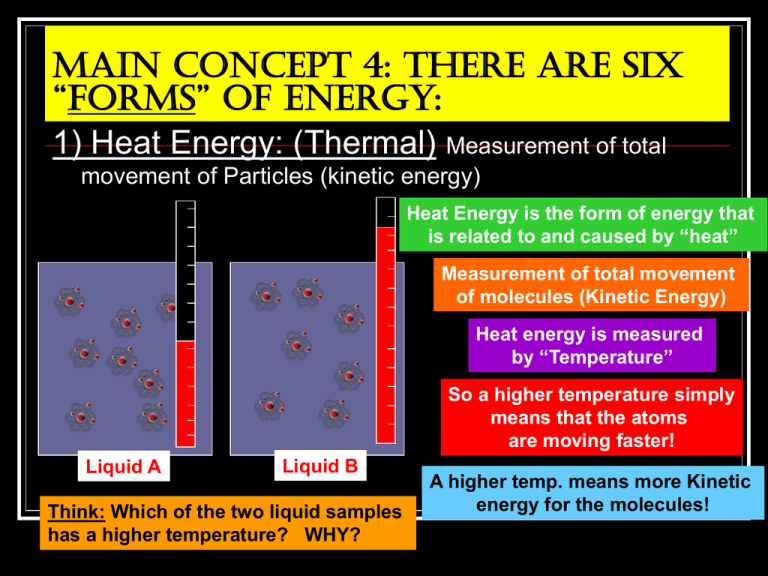
Main Concept 4: There are six “forms” of energy: 1) Heat Energy: (Thermal) Measurement of total movement of Particles (kinetic energy) Heat Energy is the form of energy that is related to and caused by “heat” Measurement of total movement of molecules (Kinetic Energy) Heat energy is measured by “Temperature” So a higher temperature simply means that the atoms are moving faster! Liquid A Liquid B Think: Which of the two liquid samples has a higher temperature? WHY? A higher temp. means more Kinetic energy for the molecules! 2) Mechanical Energy: Energy which deals with the motion of physical both large and small. Likeobjects a ball bouncing… Ball A person running… Oh! And don’t forget music! A rocket launching… Important: All motion will create heat! Rub your hands together, what do you feel? Run a mile, what happens to your core temp? Drive a car then feel the hood, what does it feel like? Mechanical Energy The little squares represent individual Sound = Oscillations or vibrations of just Molecules of a “medium”. Notice they molecules compressional Move back anddue forthtoas he energy passes through! disturbances The wave lines represent the movement of energy! Not the movement of the molecules themselves! 3) Electric Energy: = Movement of electric charges in FLOW These charges can be made to move through a wire Electric energy “flows” through wires to our houses where we plug stuff in! Electricity is electric energy Lightning is Electric energy 4) Light Energy: Energy from the wave motion of a moving charged particle in the that disturbs the electromagnetic field, the result is the light we see. +/- Color is simply a form of light that our eyes can see. All forms of light are from a wave motion of particles 5) Chemical Energy: = Energy holding atoms to other atoms (“bonds”) Batteries use atomic bonds for energy Food=People Fuel! 2 Oxygen atoms being held together by chemical energy! Plants make sugar from sunlight Fire is a result of chemical energy Gasoline=Car Fuel! 6) Nuclear energy: Energy holding the nucleus (center) of an atom together. Nuclear energy holds P+ and N0 of the nucleus together If we split an atoms nucleus, we release TONS of energy!!! Nuclear Energy The most classic example of Nuclear Energy is the Sun! We normally think of Nuclear Energy like a nuclear bomb! The idea of this energy being let canAtoms be scary Insideloose the sun, of Hydrogen are being broken apart and remade into new elements (like: Helium and Carbon) In fact, all the energy for every solar system starts out as Nuclear Energy in a star! But humans have figured out that we can control this energy enough to use it for electricity! Main Principal # 5 Energy Transfer One of the most important concepts is: All types and forms of energy can be changed into any other type or form. Example: Potential changes into Kinetic Video: “Elasta-Girl!” Stop once you reach this slide!!! Wait for the teacher to show you the video. How “Elasta-Girl” shows Energy transfer: As she gets pulled back the bungee cords gain more elastic potential energy Wait a minute! Why did we get A change in the graphs at the end? When she is released, all that Elastic Potential changes into Kinetic as the cords snap back Potential Kinetic Remember the roller coaster? The Gravitational Potential Energy of the roller coaster transfers into Kinetic Energy when it rolls down the hill! Watch the graphs while the coaster falls! Potential Kinetic What about the rocket? Watch the graphs while the rocket takes off: Potential Kinetic But it isn’t as simple as that! There isthe more energy here Think: so why are heights ofinvolved each graph different? than just Potential and Kinetic: The total amount of the Potential energy we started with equals the amount of energy we ended up with! Chemical Potential Kinetic Gravitational Potential Heat Energy Form Transfer: All energy can be transferred from one form to another. For example: Mechanical Heat Stop here and wait for the teacher to do a demo: Ex: “Burrell’s Energy Spheres of FUN!” Main Concept 5: Any Form of energy can change into pretty much any other form of energy including a change into more than one at a time! Heat Nuclear Electromagnetic Heat Chemical Chemical Mechanical Heat Heat Electric AllDid energy also make heat! Thisenergy” heat is usually lost to space.. Think: you changes notice how many times “heat showed up? What might explain this? Three main facts of energy transfer: Main Concept 6: There is only so much total energy in the universe. All forms of energy are interchangeable “Law of Conservation of Energy” Says: Energy cannot be created or destroyed it is always conserved somewhere/somehow. Energy can only be moved or changed into something else. (changed from one type or form into another) Stop here and wait for your teacher to do a demonstration: Conservation of Energy: Ex: “The Pendulum of Fear!” The pendulum will NOT gain or lose energy when it swings! It only swings with as much energy as it is given! Application of Energy Conservation: But we realize that pendulums WILL eventually slow down and stop swinging! This seems to contradict the Law of C.E. BUT IT DOESN’T! Can you explain why the pendulum does slow down? (hint: think about forces!) Friction from air resistance Both forces act to slow down and eventually stop the pendulum. Gravity is constantly pulling down We can draw a “flow chart” to show energy changes: Gravitational Potential Mechanical Electric Light and Heat Moving water turns a “generator” to make electricity that comes to our house and we use for lots of things



