What is Energy?
advertisement

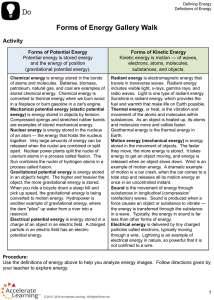
THE SCIENCE OF ENERGY \ 1. What is Energy? The ability to make things move or do work Can you make things move? Then you have energy! 2. The Law of Conservation of Energy-”energy is neither created or destroyed” The energy we use is stored in different forms. We do not use it up, it is just changed or transformed into other forms of energy. 3. Energy Efficiency The amount of useful energy obtained from a system Energy Transformation Demo Copy this Chart in your journal 0 Starting Temp Ending Temp Change in Temp 1/3 Full 0 F C Full 0 C 0 F Demo Energy Flow • Thermal energy from body in motion • Body got energy from chemical energy stored in food • Chemical energy in food came from transforming radiant energy from the Sun through photosynthesis • Radiant energy was created by nuclear energy of fission Ultimately all energy comes from nuclear energy *5 Main Things Energy can help us do……. 1. 2. 3. 4. make things move make heat make light make technology work (run electrical devices) 5. make things grow Can you think of an example of each? **2 Major forms of energy 1. Potential-stored energy; energy of position; energy at rest • • Depends on height and weight Can be calculated with the formula: PE= W x H 1a. Chemical Energy… (potential energy) • is the energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules. • Examples: Biomass, petroleum, natural gas, propane, and coal • Can be released by chemical reactions like burning wood 1b. Nuclear Energy (potential energy) • Holds protons and neutrons together in an atom’s nucleus • Powers the sun and nuclear power plants • The energy in the nucleus of a uranium atom is an example. 1c. STORED MECHANICAL ENERGY (potential energy) •is energy stored in objects by the application of force. •Examples: Compressed springs and stretched rubber bands 1d. Gravitational Energy (potential energy) •is the energy of place or position. •Water in a reservoir behind a hydropower dam is an example. 2. Kinetic-energy of motion (waves, atoms, molecules, substances) *can be affected by mass and speed * can be calculated: 2 KE=1/2mv 2a. Electrical Energy (kinetic) • The movement of electrons through matter • Electricity and lightning is a form of electrical energy 2b. Thermal/Heat Energy (kinetic) • The random motion, or vibration, of atoms in matter • Internal energy of substances • The faster the atoms vibrate the more heat energy they have • Example: geothermal 2c. Radiant/Light Energy • The energy carried by light in the form of electromagnetic (transverseside to side) waves • All lights and the rays of the Sun (Solar) are examples 2e. Mechanical/Motion Energy (kinetic) • The energy of moving things • When you ride a bike you use mechanical energy • Wind and hydropower are some other examples 2f. Sound Energy • Vibrates air molecules • The air molecules move tiny bones in your ear • The message of sound then moves to your brain • Can also vibrate objects in longitudinal waves Energy can be changed from one form to another • Chemical energy in gasoline is changed to heat energy and then to mechanical energy in a car