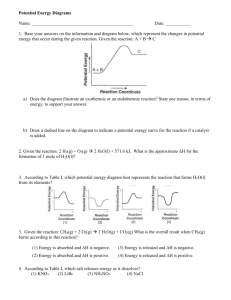
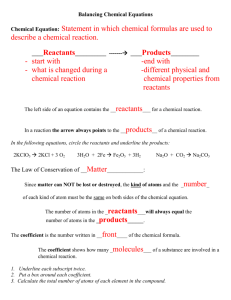
Chemical Reactions 2
advertisement

Warm-up: 11/15 *formula review* Write formulas for the following: 1. trisulfur tetroxide 2. sulfuric acid 3. lead (IV) phosphate Dihydrogen monoxide • Is present in cases of excessive sweating and vomiting • A major component of acid rain • Can cause severe burns in the gaseous state • Accidental inhalation can kill you • Primary contributor to erosion • Decreases effectiveness of automobile brakes • Is associated with major cyclonic events • May dissolve metal ions especially in the presence of road salt • Reacts violently with certain metals, such as sodium and potassium **HAVE YOU EVER COME IN CONTACT WITH THIS CHEMICAL COMPOUND?? **WRITE THE FORMULA FOR THE COMPOUND. **Are there ANY benefits to this compound? Chemical Reactions What is a chemical reaction? • A chemical reaction is the process by which the atoms of one or more substances are rearranged to form different substances. Chemical Reaction Indicators • Some ways to tell that a chemical reaction have occurred include: 1. Color change – a fast change indicates the particles have changed. 2. Heat content change – did the temperature go up or down. 3. Gas is produced – if it bubbles (without being heated) it’s a gas! 4. Precipitate forms – a precipitate is a solid produced during a chemical reaction between solutions. Chemical Equations • Chemical equations are used to represent chemical reactions. Fe (s) + Cl2 (g) Reactants FeCl3 (s) Products Symbols Used in Equations + (s) Used to separate two reactants or products “Yields” separates reactants from products Identifies solid state (l) Identifies liquid state (g) Identifies gaseous state (aq) Identifies aqueous state – a substance dissolved in water Ticket Out Choose the correct equation for the following: 1. B. Calcium reacts with water to yield calcium hydroxide and hydrogen. C. a. Ca2 + H2O → CaOH + H B. b. Ca + HO2 → CaOH2 + H2 E. c. Ca + H2O → Ca(OH)2 + H2 2. Iron reacts with Bromine to produce Iron(II)bromide. a. Fe2 + Br → Fe2Br b. Fe + Br2 → FeBr2 c. Fe2 + Br2 → Fe2Br2 Warm-Up • Which of the following is a chemical change? A. Water is decomposed into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. B. Water droplets collect on the outside of a glass filled with ice. C. A boiling pot of water produces steam. D. Water is frozen into ice. • As Cyndie mixed two liquids together, she observed the resulting mixture was hotter than either of the two liquids before they were mixed. What had caused this increase in temperature? A. Electricity had been generated. B. A physical change had occurred. C. A chemical reaction had occurred. D. Hydrogen bonds in the water had been broken. Balanced equations • Chemical equations MUST be balanced to show that the number of atoms in the reactants is the same as the number in the products. What goes in MUST come out!!! *Law of Conservation of Mass/Matter* Rules for Balancing • The only place you can change any number is the coefficient. • A coefficient is a number written in front of a chemical formula. • Don’t forget diatomic molecules. • Use the smallest ratio of coefficients possible. How to Balance • If you are starting with words, write the equation using formulas. Example: hydrogen and oxygen gases react to form water. (Hint: diatomics!) H2 + O2 H2O Things To Do: • Draw boxes around each formula: you can NEVER change anything in the boxes (including subscripts)!!! • Inventory your individual atoms for both reactant side and product side • Write numbers in front of the boxes (coefficients) until inventory of reactants matches inventory of products Problems and How to try to fix them: • Try lowest common denominators • If you think you want to use a fraction/decimal—DON’T!! Instead try sticking a 2 in front of the largest molecule in the equation and start again. • Keep you Inventories CURRENT! Practice Problems • _NaCl + _BeF2 → _NaF + _BeCl2 • _ AgNO3 + _ LiOH → _AgOH + _LiNO3 • _FeCl3 + _Be3(PO4)2 _BeCl2 + _FePO4 H2 + O2 H2O 2 hydrogens + 2 oxygens 2 hydrogens 1 oxygen Notice that there are two hydrogen atoms on each side however there are two oxygen atoms in the reactants but only one in the products. To balance this we must insert a coefficient. H2 + O2 2 H2O While that evens the number of oxygen atoms – there are now four hydrogen atoms in the products. To balance the hydrogen we go back to the reactants and insert a coefficient. 2H2 + O2 2H2O Now there are equal number of atoms of hydrogen and oxygen on each side of the equation – it is now balanced. Ticket Out • Which balanced formula is correct: 1. SnO2 + H2 → Sn + H2O a. 2SnO2 + 3H2 → 2Sn + 3 H2O b. Sn3O2 + 3H2 → Sn + 2 H2O c. SnO2 + 2H2 → Sn + 2 H2O 2. Al + HCl → AlCl3 + H2 a. Al + 6HCl → AlCl3 + 3H2 b. 2Al + 3HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2 c. Al + 6HCl → AlCl3 + 3H2 Warm-up: • Write the formulas for the equation and then balance it. • Solid aluminum reacts with solid iodine to produce solid aluminum iodide. Types of Reactions • There are five types of chemical reactions: synthesis, decomposition, single-replacement, double-replacement, and combustion. • Replacement reactions are sometimes called displacement reactions. • Synthesis reactions are also called combination reactions. Synthesis or Combination • Synthesis is a reaction in which two or more substances react to produce a single product. A + B AB Na + Cl2 2NaCl Decomposition Reactions • Decomposition reactions occur when a single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances. AB A + B or ABC A + BC 2HI H2 + I2 2Mg(ClO3)2 2MgCl2 + 3O2 Single-Replacement Reactions • A reaction in which the atoms of one element replace the atoms of another element in a compound. A + BC AC + B Mg + Zn(NO3)2 Mg(NO3)2 + Zn Double-Replacement Reactions • A reaction involving the exchange of positive ions between two ionic compounds dissolved in water. AB + CD AD + CB 2NaOH + CuCl2 2NaCl + Cu(OH)2 Combustion Reactions • In a combustion reaction, oxygen combines with a substance and releases energy in the form of heat and light. CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O *All hydrocarbons contain carbon and hydrogen and burn in oxygen to yield the same products – CO2 and H2O Heat Content Changes • An exothermic reaction occurs when more energy is released forming new bonds than is required to break bonds in the initial reactants. *These reactions tend to feel warm. • An endothermic reaction occurs when a greater amount of energy is required to break the existing bonds in the reactants than is released when the new bonds form in the products. *These reactions tend to feel cold.