Torts & Personal Injury Law OUTLINE
advertisement

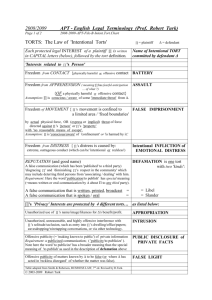
Torts & Personal Injury Law OUTLINE I. Chapter 1 - Introduction A. B. Torts -- 1. 2. Negligence 3. Strict (Absolute) Duty Breach of Duty Causation Damage/Injury Objectives 1. 2. 3. D. Intentional Elements 1. 2. 3. 4. C. Wrongful Injury Protecting (Accountability) Compensation Deterrence Tort Analysis -1. From General to Specific! 2. IRAC Issues Rule of Law Application of Law to Facts Conclusions E. General Tort topic Intentional torts Specific Tort Battery Issues framed by Tort Customer strikes clerk Rule of Law Unconsented contact = Battery Application of Law Contact was unconsented Conclusion A battery occured Resolutions 1. Alternate Dispute Resolutions (ADR) F. II. Arbitration Mediation Mini Trial Rent-A-Judge Summary Jury Trial Civil Case Chronology 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Post-Trial Complaint Answer Discovery Pre-Trial Trial Chapter 2 - Negligence - ** Failure to use Reasonable Care ** A. Elements 1. 2. 3. 4. B. **Foreseeability** 1. C. Duty Breach of Duty Causation Damage/Injury to Plaintiff Foreseeable Plaintiffs Theory Proving Breach of Duty 1. 2. **Evidence** Burden of Proof 3. Prima Facie - Burden of proof for tort met 4. Res Ipsa Loquitor - "Thing speaks for itself" D. Civil - Preponderance Criminal - Beyond Reasonable Doubt Burden on Defendant Tort wouldn't normally happen without negligence Defendant in exclusive control of objects or actions Defendant in better position to prove than Plaintiff Negligence Per Se - **Tort in violation of Statute or Ordinance** E. Causation 1. Cause in Fact -- Defendant Caused Injury 2. Substantial Factor Analysis Test for indirect causation F. Joint and Several Liability 1. 2. G. Contribution 1. H. Multiple Defendants Simultaneous OR Sequential Defendants share cost of judgment Damages - Injury suffered as a result of tortfeasor's conduct/actions 1. Compensatory - "Make the victim whole" Hedonistic (1) Joy of Life General (1) Pain and Suffering Special (1) loss of consortium (2) related expenses (3) lost wages Economic/Non-economic (1) lost wages (2) medical expenses (3) pain/humiliation (4) Nominal III. Chapter 3 -- Special Negligence Actions A. B. Vicarious - Liability of principal for agents 1. Respondeat Superior - "Let the Master Answer" 2. NOT for independent contractors 3. Scope of Employment Frolic and Detour - Responsible only for work related Coming and Going - Not counted as 'work related' 4. Motor Vehicle Liability Owner vicariously liable for ANY authorized driver's negligence Premises - Occupier/Owner 1. C. Duties of Reasonable Care - Different Trespasser - NONE Licensee + Attractive Nuisance + Invitee ++ Negligent Infliction of Emotional Distress 1. Elements Outrageous conduct Should have reasonably anticipated possible injury Significant & Reasonably Foreseeable injury Constituting Breach of Duty to victim Victim was Reasonably Foreseeable 2. Requirements Physical manifestation (1) Victim must suffer some actual physical ailment to recover Zone of Danger (1) Victim must be in foreseeable 'Zone of Danger' of tortfeasor's actions Sensory Perception (1) Victim must have seen/heard/felt event to have suffered injury Family Relationships Rule - **For Witnesses of injury (1) Victim must be related to person injured to receive damages D. Negligence Per Se - Tortfeasor's actions covered by Statute or Ordinance 1. IV. Plaintiff must be in Class of Persons Protected by Statute Chapter 4 - Defenses to Negligence A. Contributory (minority view) - Plaintiffs actions caused injury 1. Plaintiff Response - "Last Clear Chance" Plaintiff contributed BUT Defendant had "last clear chance' to avoid Plaintiff's injury B. Comparative 1. C. Assumption of Risk 1. 2. D. V. Elements Plaintiff contributed to own injuries Calculation of relative Plaintiff/Defendant % or responsibility by Triers of Fact Plaintiff assumed risk Voluntarily w/ Full appreciation of Danger involved Statutes of Limitation -- Universal and Complete Defense Chapter 5 - Intentional Torts - Injuries to Persons Intentional Tort Elements 1) Action 2) Intent 3) Injury A. Assault & Battery 1. Assault: - Intentional threat, show of force, or movement that reasonably makes a person feel in danger. Threat of harmful or offensive contact Victim apprehensive Threat is imminent 2. Battery - Actual harmful of offensive contact B. Non-consensual physical contact Contact is harmful or offensive Tortfeasor's intent (1) Intent can be Transferred to 3rd Parties Patient Dumping 1. Lack of appropriate care and unreasonable transferring of patients. [ covered under federal Emergency Treatment and Active Labor Act (EMTALA) ] C. False Imprisonment - (Confinement) 1. Elements D. Confinement w/o Consent Intent to Confine For an Appreciable time No reasonable means to escape 2. Confinement = Physical Barriers OR Express/Implied Threat 3. Shopkeeper's Privilege Can stop and detain suspected shoplifter (1) Must have reason to believe crime committed/attempted Sexual Harassment -- Workplace Discrimination based on Gender E. Spoliation of Evidence -- Deliberate spoiling, hiding, or destroying evidence relevant to a legal proceeding VI. Chapter 6 - Intentional Torts - More Injuries to Persons A. Infliction of Emotional Distress - Actions cause Mental Anguish 1. Does not require Physical Manifestation (in most Jurisdictions) B. 2. Intentional Infliction Defined (1) Outrageous Conduct (2) Conduct is intended to cause severe emotional suffering (3) Conduct causes victim's suffering 3. Negligent Infliction Defined (1) Outrageous Conduct (2) Conduct is known (or reasonably should be known) to cause severe mental anguish (3) Conduct causes victim's suffering Fraud and Misrepresentation 1. Fraud Defined (1) Making false statements w/intent to mislead (2) Statements are known by tortfeasor to be false (3) Statements made to entice victim into surrendering something of value (4) Victim must rely on statements (5) Injury to victim 2. Misrepresentation - (almost the same) Defined (1) Making false statements w/intent to mislead (2) Statements are known by tortfeasor to be false (3) Victim must rely on statements (4) Injury to Victim 3. Malicious Prosecution (Accused) Defined (1) Groundless criminal prosecution (2) Complaint made with Malice (3) Acquittal/Dismissal of Charges (4) Injury to Accused 4. Abuse of Process (Victim) Defined (1) Misuse or Threat of Misuse of Legal Processes (2) for Unlawful Objectives (3) Injury to Victim 5. Invasion of Privacy Appropriation (1) Use of name or likeness w/o consent Unreasonable Intrusion (1) Excessive or offensive invasion of seclusion and solitude Public Disclosure of Private Facts (1) Communication of Private Information w/o permission (a) ** "Reasonable Person" would find disclosure objectionable 6. False Light in the Public Eye (1) False attribution of Statements, Actions, or Opinions Defamation: Libel and Slander Elements of Libel (1) Written statement (2) False and defamatory (3) Publication to 3rd Party (4) Injury to victim's reputation in the community Elements of Slander (1) Oral statement (2) False and defamatory (3) Publication to 3rd Party (4) Injury to victim's reputation in the community Public Figures - Different standard of protection Slander Per Se - Some words/statements are slanderous by nature (1) Charge of criminal action/intent (2) Statement harmful to business (3) Implication of loathsome and communicable disease Truth and Privilege = Absolute Defense VII. Chapter 7 - Injuries to Property A. Trespass to Property 1. Elements Unauthorized entry to property Intent Interference with Plaintiff's exclusive use/enjoyment 2. "Toxic Trespass" - Same as regular - applies above or below ground Many Regulated by Environmental Statutes B. Trespass to Chattel 1. 2. C. Elements Unauthorized possession or interference of use of property Intent to dispossess or interfere Interference with Plaintiff's exclusive use/enjoyment Similar to Conversion Conversion 1. Elements Depriving owner of possession Intent to deprive or convert to own use Owner's non-consent to possession and use D. Slander to Title, Commercial Disparagement, Defamation by Computer 1. Slander of Title 2. Commercial Disparagement 3. Elements (1) False Statements about ownership of land (2) Intent to hinder or damage owner's use of property (3) Communication (publication) to 3rd Party Elements (1) False Statements about goods, services or business (2) Intent to injure ability to use good, provide services or conduct business (3) Communication (publication) to 3rd Party Defamation by Computer Elements (1) False Information about victim's Credit Rating (2) Entering such date into a computerized recordkeeping system (3) Communication (publication) to 3rd Party (4) Injury to ability to obtain credit VIII. Chapter 8 - Defenses to Intentional Torts