Law of Torts Semester Exam
advertisement

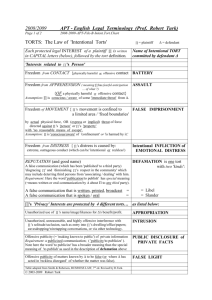
By : Lillie Gray 1st period Business Law Exam Crime- an offense against the public at large, which is therefore punishable by the government. Tort- a private wrong committed by one person against another involving one persons interference with another persons rights. Intentional Tort- occurs when a person knows and desires the consequences of his or her act. Tortfeasor- person who commits a tort. Trespass- the wrongful damage to, or interference with the property of another. Nuisance- anything that interferes with the enjoyment of life or property. False Imprisonment- when the police arrest someone without probable cause or the proper warrant. Defamation- the wrongful act of injuring another persons reputation by making false statements. Invasion of Privacy- interfering with a person’s right to be left alone, which includes the right to be free from unwanted publicity and interference with private matters. Negligence- an accidental or unintentional tort, and the failure to exercise the degree of care that a reasonable person would have exercised in the same situation. Strict Liability- an injury caused by an individuals participation in an ultra- hazardous activity; also, manufacturers or suppliers are responsible for selling goods that are responsibly dangerous. Breach of Duty- the failure to use the degree of care that would have been used by a reasonable person. Proximate Cause- the legal connection between unreasonable conduct and the resulting harm. Contributing Negligence- behavior by the plaintiff that helps cause his or her injuries. Assumption of Risks- defense in which the defendant shows that help the plaintiff new of the risk involved in an activity and still took the chance of being injured. The difference between criminal and tort laws A tort law is a private wrong committed by one person against another. In criminal law they harm not only specific individuals but the general welfare as well. Intentional Torts This occurs when a person knows and desires the consequences of his or her act. Battery 2. Trespassing 3. Nuisance Interference with contractual relations 5. Deceit 6. Conversion 7. False Imprisonment (false arrest) 8. Defamation 9. Invasion of Privacy 10. Misuse of legal procedure 11. Infliction of emotional distress 12. Assault 1. 4. Unintentional Torts A type of accident that leads to injury or death Elements of Negligence The law has established specific standards to prevent people from suing innocent parties Elements of Negligence The defendant owed the plaintiff a duty of care This failure to use the degree of care required under the circumstances The breach of duty by the defendant was the proximate cause of the injury to the plaintiff. The plaintiff suffered some actual harm or injury.