the zeros are - s3.amazonaws.com
advertisement

6.7
Pg.366
This ppt includes 7 slides consisting of a
Review and
3 examples
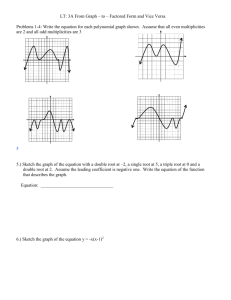
Find all the zeros:
f(x)=x3+x2-2x-2
Answer: - 2 , 2 ,-1
F(x)= x3 – 6x2 – 15 x + 100 = (x + 4)(x – 5)(x – 5)
the zeros are: -4, 5, 5
5 is a repeated solution
A polynomial to the nth degree will have n zeros.
(should be 3 total! degree 3)
CT = ±1 ±2 ±3 ±4 ±6 ±8 ±12 ±16 ±24 ±48
LC
±1
Graph the equation and you’ll see only 1 real zero:
Look in the table and you will find -3 is the only zero in the table, SO use synthetic division
with -3
1
-3
1
3
-3
16
0
0
16
x2 + 16 = 0
x2 = -16
x = ±√-16 = ±4i
The three zeros are -3, 4i, -4i
48
-48
0
F(x)=
(x-1)(x-(-2+i))(x-(-2-i))
F(x)= (x-1)(x+2-i)(x+2+i)
f(x)= (x-1){(x+2)-i} {(x+2)+i}
F(x)= (x-1){(x+2)2-i2}
Foil
F(x)=(x-1)(x2 + 4x + 4 –(-1))Take care of i2
F(x)= (x-1)(x2 + 4x + 4 + 1)
F(x)= (x-1)(x2 + 4x + 5)
Multiply
F(x)= x3 + 4x2 + 5x – x2 – 4x – 5
f(x)= x3 + 3x2 + x - 5
Note:
2+i means 2-i is also a zero
F(x)= (x-4)(x-4)(x-(2+i))(x-(2-i))
F(x)= (x-4)(x-4)(x-2-i)(x-2+i)
F(x)= (x2 – 8x +16)((x-2)-i)((x-2)+i)
F(x)= (x2 – 8x +16)((x-2)2-i2)
F(x)= (x2 – 8x +16)(x2 – 4x + 4 –(-1))
F(x)= (x2 – 8x +16)(x2 - 4x + 5)
F(x)= x4–4x3+5x2–8x3+32x2-40x+16x2-64x+80
F(x)= x4-12x3+53x2-104x+80
Under
y= type in the equation.
Go to second; calc; 2:zero
Left bound: you need to place the cursor to
the left of the intersection and press enter.
Right bound: you need to place the cursor to
the right of the intersection and press enter;
and enter again.
At the bottom of the window “zero” will
appear x = # This is your real zero.
Assignments
will be made in class and placed
on the web page under lesson plans.