Grammar Review - Mrs-Wilmarths-Wiki
advertisement

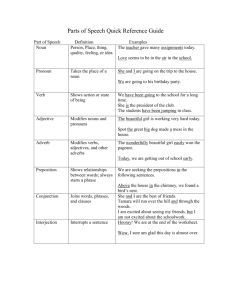
Nouns •Name a person, place, thing, or idea. •There are two types: Common & Proper •The first letter of a proper noun is capitalized because it names a specific person, place, thing, idea Pronouns replace a noun Every pronoun needs a clear antecedent, and the pronoun must agree with its antecedent. Commonly used pronouns are: I, you, he, she, it, we, they, your, yours, our, ours, mine, me, my, us, them, his, her, hers, their, theirs, its Demonstrative: This, that, these, those Interrogative: who, whom, whose, which, what Indefinite: Any, another, anybody, anyone, anything, each, either, everybody, everyone, everything, neither, no one, one, someone, both, few, many, several, some, none, all, most *Remember, to function as a pronoun, a word must be replacing another. Identify the pronoun & its antecedent 1. All of these computers have their drawbacks. 2. People trying to reduce their salt intake should avoid canned foods. 3. At the men’s bowling tournament, one of the bowlers hurt his ankle. 4. Mr. Mass told the students “Anyone looking for a book can take one from this pile.” 5. Jill told Matt that she had to get more sleep. 6. “You need to get a new notebook,” Kate told Jenny. Fill in the pronoun that agrees with the antecedent 1.Anyone can get __ name in the news. 2.None of the checks were cashed;___ finally expired. 3. A person should insure ____ valuables. 4. The code breakers shared ___ secrets. 5. San Diego and San Jose get ___ names from Spanish. 6. Either Eleanor Roosevelt or Ellen Wilson is believed to have covered for ___ husband during presidential emergencies. • • • • • • • Verbs show action or state of being. Action Verbs can have helping (or auxiliary) verbs to help denote tense. Linking verbs connect the subject to a word that modifies or renames it. Common linking verbs are: am, is, are, was, were, be, being, been, seems, appears, looks When unsure if a verb is an action or linking verb, replace the complete verb with is or are. If the meaning remains the same, it is a linking verb. Katie appeared ill. Katie appeared out of thin air. As we have already discussed, adjectives modify nouns and pronouns Adjectives answer the questions: What kind?, which one?, how many?, or how much? Generally, adjectives come before the nouns or pronouns that they modify, but at times, they can come after. There are also words that appear to be pronouns, but function as adjectives, such as this, that, these, those, my, your, his, its, our, theirs, what, which, whose. So, one must determine how the word is functioning in a sentence. as we have already discussed, adverbs modify verbs, adverbs, and adjectives Often times, adverbs are formed by adding an –ly ending to an adjective. Adverbs answer the questions: Where? , In what way?, When?, or To what extent? Many prepositions can function as adverbs. One must remember that all prepositions must have an object, if it does not it is an adverb. A preposition shows a relationship between its object and other words in a sentence. The preposition may be in the form of one word (at, by, in, on, etc.) or in the form of a phrase that functions as a unit (in front of, by way of, etc.). Some of the relationships that prepositions express are place or position, time, manner, direction, and agent. Once a prepositional phrase is formed, it acts as either an adverb or adjective to modify another word in the sentence. John came out of the house and went to the store. He went in and bought a box of chocolate chip cookies. The cookies were hard and bland, so John decided to make some homemade cookies. The new cookies were so chocolaty and melted in John’s mouth. Conjunctions, unlike prepositions that show relationships between words, make direct connections between words. There are three kinds of conjunctions: Coordinating, correlative, and subordinating. Three types of conjunctions are Coordinating conjunctions connect similar words or groups of words. The seven coordinating conjunctions are and, but, for, nor, or, so, yet. Correlative conjunctions are always used in pairs and connect similar words or groups of words. The correlative conjunctions are both...and, either...or, neither...nor, not only...but also, whether...or. Subordinating conjunctions connect two complete ideas by making one of the ideas subordinate, or less important than, the other. Frequently used subordinating conjunctions are after, although, as, as if, as long as, as though, because, before, even if, even though, if, in order that, now that, since, so that, than, though, till, unless, until, when, whenever, where, wherever, and while. Since we couldn’t go swimming, we watched a movie. It will rain as it is dark and cloudy. Although he knew it was difficult, he still tried. She wouldn’t cry unless she was hurt Whether or not I am going, it is none of your business. I have prepared for the test, so I should do well. Jean recycled not only consistently but also carefully. Kim and Jane are going to the concert, but Joey cannot. Because many words can be used as conjunctions, prepositions, or adverbs, students must determine how the word is used in a sentence to determine its part of speech. An interjection is a word that expresses a feeling or emotion and functions independently in a sentence. Examples of interjections are Oh no, alas, hey, ouch, wow. Interjections are seldom used in formal writing. Examples: Ouch! I am never going to give blood again. I wanted to do well on this test, but alas, I failed. Verbals: A generic term for words that look like verbs, but function as another part of speech Participles: look like verbs, but function as an adjective Gerunds: Has an –ing ending like a verb, but functions as a noun Infinitives: to+ a verb and is used as a noun or a modifier Playing baseball at Yankee Stadium was Matt’s ultimate fantasy. Jim's confusing message did nothing to solve the mystery. To dance on stage in New York is my only dream. The politician's broken promises were all that the voters remembered. I always seem to forget my purse after lunch. Playing the tuba made Orin feel as if his world was perfect. Brenda seemed surprised with the team's decision to withdraw. What questions do adjectives answer? What questions do adverbs answer? What are the three types of conjunctions? What does each do? What are the two most important thing to remember about pronouns? What does a preposition need to be a preposition? What is the trick to use if you are unsure if a verb is action or linking What part of speech is never used in formal writing? What jobs do prepositional phrases perform? What is a verbal? What are the three kinds of verbals and what does each do? Identify the pronoun and its antecedent Playing the tuba made Orin feel as if his world was perfect. The players on the team were happy because they won. One of the students forgot his music. There, in the corner, sat the students waiting for their parents. Fill in the appropriate pronoun. Each of the boys remembered that ___ had a test today. Neither Mike nor James got ___ paper signed Everyone in the class earned a 90 on ____ test. “All of you must pass the senior project because the state mandates it,” Mr. Forgione told the students. Identify the part of speech for each word. Caring for a pet is fun, but it is very hard work. One of the students from each row should quickly pass out the books.