Chapter 2
advertisement

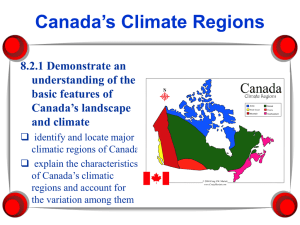
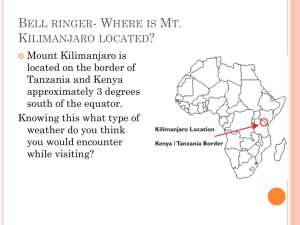
Introduction to Geography Chapter 2: Weather and Climate Weather and Climate ► Weather Day-to-day variations in temperature and precipitation ► Climate Statistical summary of weather conditions through time Solar Energy ► Radiant energy from sun Small amount intercepted by Earth ► Powers circulation of atmosphere & oceans ► Supports life on Earth ► Varies across Earth’s surface Insolation ► Amount of energy intercepted by Earth ► 2 factors Intensity of solar radiation ► Angle of incidence Duration of sunlight ► Varies by season Intensity of Solar Radiation ► Varies daily & seasonally ► Seasonal angle depends on latitude ► Tilt of Earth’s axis = 23.5 degrees Total Insolation ►Total amount of solar radiation from seasonal changes in: Length of daylight Distance from the Sun ►Tropical areas ►High latitudes World Temperatures—January World Temperatures—July Storage of Heat ► Variable ability to store heat depends on material ► Water absorbs and releases more heat than land ► Therefore… Greater seasonal difference in temperatures in mid-continent areas in high latitudes (Asia, North America) Moderate climates near water Heat Transfer Responsible for movement of energy from place to place on Earth ► Radiation (radiant energy): energy transmitted by electromagnetic waves (heat, light, radio, TV) ► Wave length ► Shortwave: ► Insolation ► Passes through atmosphere Longwave: ► Energy reradiated from Earth ► Most blocked by atmosphere (greenhouse effect) Greenhouse Effect ► Greenhouse gases Transparent to shortwave but absorb longwave Water vapor, carbon dioxide, ozone, methane Increased greenhouse gases = increased global warming ► Additions by human activities, probably global warming ► Latent Heat Exchange ► Transfers energy from low to high latitudes ► Causes precipitation ► Two types Sensible ►Detectable by touch Latent ►“In storage” in water & water vapor ►Latent heat exchange Heat Exchange & Atmospheric Circulation ► Evaporation of water from surface of the oceans ► Water vapor rises in the atmosphere ► Converted to water (rain) or ice (snow) ► Powered by convection: movement of fluid when heated ► Advection = horizontal movements of air AKA wind Condensation ► Conversion of water from vapor to liquid ► Capacity of air to hold water vapor: Depends on temperature ► Condensation ► Cooling = clouds air Causes increase in relative humidity Saturation point = condensation Cooling beyond saturation condensation (clouds) Relative Humidity ►Relative humidity: actual water content of air, expressed as percentage of what air could hold ► Fluctuates as temperature changes Temperature Relative Humidity 86 degrees F 50% if holds half water vapor possible 71 degrees F 75% 60 degrees F 100% Convectional Precipitation ► Adiabatic cooling: cooling of warmed air as it rises (1ºC per 100 meters; 5.5ºF. per 1000 feet) ► “Normal” precipitation ► ALL air holds water Depends on temperature ► Responsible for large portion of precipitation Orographic Precipitation ►Air forced to rise ►Adiabatic cooling ► Rain on windward side ► Desert on leeward side: Rain shadow ► Examples Cascades & Sierras Rockies over mountains from expansion Frontal Precipitation ► Air forced up boundary between cold & warm air ► Front: boundary between two large air masses ► Cold air advancing = cold front ► Warm air advancing = warm front Air Masses ► Air mass Region of air with similar characteristics ► Air masses form if air remains over a uniform surface long enough for it to acquire uniform properties ► In North America Continental polar air (cold) Maritime tropical air (warm) Fronts ► Cold front Cold air mass moves towards warm air mass ► Warm front Warm air mass moves towards cooler air mass Pressure and Winds ► Dependent on conditions Varies with altitude ► Measured with barometer ► Pressure gradient Difference in pressure between two places Air moves from high to low pressure Coriolis Effect ►Deflection of wind above rotating Earth N Hemisphere: to the right S Hemisphere: to the left ►Cells rotating clockwise & counterclockwise Global Circulation ► 4 zones Intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ) ► Warm air rising ► Convectional precipitation ► Trade winds Subtropical high-pressure zones ► Descending of air from ITCZ ► Areas of dry, bright sunshine, little precipitation Midlatitude low-pressure zones ► Converging warm & cold air ► Polar front ► Westerlies Polar high-pressure zones ► Dense air, high pressure ► Little precipitation & cold Worldwide Pressure and Winds (January) Worldwide Pressure and Winds (July) Ocean Circulation Patterns ► Wind creates waves and currents ► Gyres Wind-driven circular flows ► El Niño Occasional shifts in ocean circulation Storms ► Cyclones Large low pressure areas Winds ► Counterclockwise ► Clockwise in S Hemisphere Cyclone: low pressure cell ► Air converges & ascends Anticyclone: high pressure cell ► Air descends & diverges in N Hemisphere Hurricanes ► Tropical Cyclones Need warm, moist air ► Most powerful over oceans Storm surge ► Elevated sea level in center of storm Regional Names ► Hurricanes ► Typhoons ► Tropical cyclones Tropical Disturbances ► Tropical depressions Winds 38 mph or less ► Tropical storm Winds 39-73 mph ► Tropical Cyclone (Hurricane) Winds 74 mph and above Hurricane Katrina August 28, 2005 Hurricane Names ► Cyclone is named when winds hit 39mph Began in 1953 ► Originally just used female names Alternation began in 1979 ► Use a 6 year rotation list http://www.nhc.noaa.gov/aboutnames.shtml Retired names ►http://www.nhc.noaa.gov/retirednames.shtml 31 Hurricanes ► Eye Non-stormy hurricane center ► Eyewall Zone at edge of eye where wind speeds are highest ► Eyewall replacement Process where new wall of storms surrounds wall of storms circling the eye ► Spiral rainbands Intense bands of T-storms rotating counterclockwise around storm 32 Storms ► Midlatitude cyclones Large migratory lowpressure system in the mid-latitudes, moving in the direction of the westerlies Responsible for majority of day-to-day weather changes Bring precipitation to much of world’s population Climate ► Summary of weather conditions over long period ► Influences Hours of daylight Precipitation Temperature Winds Pollution ► Changes over time ► Humans and climate ► 2 primary measures Temperature Precipitation Air Temperature ►Changes with elevation (6.4ºC per 1000 meters; 3.5ºF. per 1000 feet) ►Affected by: Topography Proximity to oceans Water availability Precipitation ►Variability over time and space Worldwide variation = 0-120 inches ► Reliability & regularity Classifying Climate ► Include temperature and precipitation, effects of temperature on water availability to plants ► Wladimir Köppen, German geographer (1918) Used distribution of plants Advantage of effect on other environmental factors 5 basic climate types with subdivisions Most widely used system Classifying Climate Climate Regions ► Horizontal bands based on latitude ► Climate regions similar to Bioregions Temperature and precipitation maps ► Other influences Continents Mountains Humid Low-Latitude Tropical Climates (A) ► Warm & humid all year ► Humid tropical (Af, Am) +/- 10 degrees N/S of equator Little seasonal temp. variation High temps; rain ► Seasonally humid tropical climates (Aw) Concentrated rainfall ► Seasonal shifts of ITCZ Dry Climates (B) ► Dry climates, BW & BS 35% of Earth’s land area & 10% of Earth’s population Border low-latitude humid climates on North and South ► Desert climates (BWh, BWk) Warm and dry Subtropics ► Semi-arid climates (BSh, BSk) Transition areas between deserts & humid areas Grasslands, steppes Seasonal temp. contrasts Warm Midlatitude Climates (C) ► Seasonal temp variation & less precipitation Must be able to survive cold season ► Weather ► related to fronts & temp. Humid subtropical (Cfa, Cw) 25-40°N/S on E side of continents ► Marine west coast (Cfb, Cfc) Continental west coasts, 35-65°N/S Mild climates ► Mediterranean climates (Cs) Dry summers with seasonal precipitation Cold Midlatitude Climates (D) ► Humid continental climates (Dfa, Dwa, Dfb, Dwb) Strong contrasts Remote from oceans Interior & eastern side of Northern Hemisphere Continents (35-60 degrees) ► Subarctic climates (Dfc, Dwc, Dfd, Dwd) Northern edge of humid continental climates No agriculture Northern Hemisphere only Vegetation: Boreal forests Polar Climates (E) ► High-latitude climates ► Low temps ► Extreme seasonal variability ► Tundra climate (ET) Permafrost Tundra ► Ice-cap climates (EF) Near poles & high altitudes at low latitudes Climate Change ►3 hypotheses ► Astronomical Variations of Earth’s orbit Sunspots ► Geologic Continental drift Volcanic eruptions Mountain ranges ► Human Atmosphere Vegetation Climate Change ►Time scale of observations determine what patterns of change stand out in the record ►Determining Climates of the Past Dendrochronology Oxygen isotope analysis of oceanic sediments Ice cores Pollen analysis 46 47 Global Warming ► 20th c. warming: 1º C (1.8º F.) Link with increased carbon dioxide (CO2) ► Evidence of global warming Computer models & historic climate data ► Consequences of global warming Rise in sea level & increase in extreme weather ► Dealing with global warming Develop means to adapt & measures to counteract effects End of Chapter 2