Earth Sys Study Guide Ch 19,20,21
advertisement

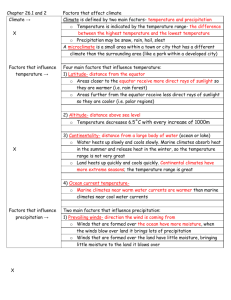
Earth Systems Study Guide-KEY Ch. 19, 20, 21 1. In which direction is air pressure exerted? Upward, downward and sideways 2. What instruments are used to measure air pressure? Mercury barometer and aneroid barometer 3. What are the forces that influence wind? Coriolis effect, pressure gradient and friction 4. What are the lines on the weather map that connect points of equal pressure called? Isobars 5. What do closely spaced isobar lines indicate? High winds 6. What do widely spaced isobars indicate? Light winds 7. Variations in air pressure from place to place are the principal cause of _wind__. 8. High-altitude, high-velocity “rivers” of air are called __jet streams__. 9. In the Northern Hemisphere, winds associated with a high-pressure system blow in what direction? clockwise outward from the center 10. Centers of low pressure are called _cyclones___. 11. High-pressure systems are usually associated with what conditions? descending air, relatively dry conditions and clear weather 12. The general movement of low-pressure centers across the United States is from __west___ to ___east____. 13. Describe the surface air movement in a Northern Hemisphere low. Inward, upward movement and counterclockwise 14. What is true about lows that move across the United States? They can produce bad weather. They move in roughly a west-to-east direction. They may require up to a week to cross the country. 15. Seasonal changes in wind direction associated with large landmasses and adjacent water bodies are called __monsoons__. 16. The only truly continuous pressure belt on Earth is the _Southern Hemisphere subpolar low___. 17. In the winter, large landmasses such as Asia develop a seasonal _high_-pressure system. 18. Near the equator, rising air is associated with a pressure zone known as the _equatorial low___. 19. If Earth did not rotate, how would air at the equator move? Air would rise and move toward the poles 20. Valley and mountain breezes are examples of __local__ winds. 21. A sea breeze usually originates during the _day_ and flows toward the __land__. 22. Winds are labeled according to the direction (?to or from?) which they blow. from 23. Which phenomenon is associated with surface temperatures in the eastern Pacific that are colder than average? La Niña 24. Which two properties characterize an air mass? temperature and moisture 25. Which type of air mass originates in northern Canada? cP 26. A cT air mass is _hot and dry_. 27. Which air masses have the greatest effect on weather conditions in much of the United States? cP and mT 28. Which air mass is the source of much of the precipitation in the central and eastern United States? mT 29. The boundary that separates different air masses is called a(n) _front_. 30. On a weather map, which type of front is shown by a line with semicircles extending from one side? Warm front 31. In which type of front is the flow of air on both sides of the front almost parallel to the line of the front? Stationary 32. When an active cold front overtakes a warm front, what type of front forms? An occluded front 33. Along a front, which type of air is always forced upwards? warmer, less dense air 34. What is the first sign of an approaching warm front? cirrus clouds 35. How does surface air flow in a middle-latitude cyclone in the Northern Hemisphere? Convergent and counterclockwise 36. A rotating column of air is called a(n) _vortex__. 37. Tornadoes are most frequent during which months? April to June 38. Hurricanes form in tropical waters between the latitudes of _5 and 20 degrees__. 39. What happens to the intensity of solar energy as latitude increases? It decreases 40. The rain shadow effect is associated with what landform? Mountains 41. Temperature decreases with elevation by an average of how many degrees per 1000 meters? 6.5°C 42. What is the weather like on the leeward side of a mountain? Dry weather 43. Increased altitude generally causes lower _temperatures___. 44. How would the climate of a coastal city differ from that of a city at the same latitude located farther inland? The coastal city would have cooler summers. 45. Which type of climate has no winters? humid tropical 46. What factor distinguishes wet tropical climates from tropical wet and dry climates? precipitation 47. Where are dry-summer tropical climates found in the United States? (What state?) California 48. What are the characteristics of marine west coast climates? mild winter, cool summers and ample rainfall throughout the year 49. Another name for a semi-arid climate is __steppe___. 50. Polar climates are characterized by _ low rates of evaporation___. 51. Which type of climate is characteristic of Antarctica? polar 52. Changes in the shape of Earth’s orbit may cause long-term changes in climate, true or false? True 53. How does volcanic ash in Earth’s atmosphere affect solar radiation? It increases the amount of solar radiation that is reflected into space. 54. A very small tilt in Earth’s axis would likely cause _ small seasonal variations in temperature___. 55. What phenomenon naturally warms Earth’s lower atmosphere and surface? the greenhouse effect 56. Describe greenhouse gases. They absorb Earth’s radiation. They are transparent to incoming solar radiation. They include carbon dioxide and water vapor. 57. Which greenhouse gas is the most powerful absorber of radiation emitted by Earth? water vapor 58. During the twentieth century, Earth’s average surface temperature __increased__. (increased or decreased). 59. Give an example of human impact on climate changes. global warming 60. Shoreline erosion and coastal flooding are two consequences of _ a global rise in sea level__.