Nervous Tissue (2)
advertisement

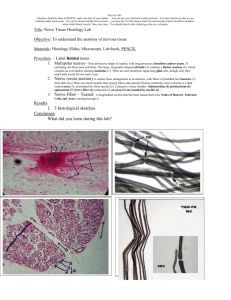
Nerve Tissue Al-Maarefa College Nerve Tissue • Cells have very high ability to – Respond to stimuli – Transmit impulses Nerve Tissue Nerve Tissue • NEURON is the main nerve cell) Nerve Tissue • NEURON is the main nerve cell – Cell Body(3) – Dendrites (5) – Axon(1) Motor Neurone Motor Neurone • Cell body • Dendrites • Axon – Covered by Myelin sheath Neuron • Multipolar Kuehnel, Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy Neuron's – cerebral cortex Kuehnel, Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy Neuron's – spinal cord Kuehnel, Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy Nerve and Reflex Arc Nerve Fiber (Axon) • Nerve fibers are long nerve cell processes (axon cylinder, axon) with a surrounding membrane • Schwann cells (neurolemmocytes, peripheral glial cells) enfold the axon and form an insulating cover known as Schwann’s sheath (neurolemma). Stain: osmium tetroxide; magnification: × 1000 Kuehnel, Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy Nerve Fiber (Axon) • Myelinated nerve fiber, i.e., the axon is covered by a myelin sheath, which is rich in lipids. • Every 0.8 to 1.0 mm, a node of Ranvier subdivides the myelin sheath into segments or internodes. Stain: osmium tetroxide; magnification: × 1000 Kuehnel, Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy Sciatic nerve – cross section • • • • • • 1 Fascicle (nerve fiber bundle) 2 Perineurium 3 Epineurium 4 Artery 5 Vein 6 Adipose tissue Stain: alum hematoxylin; magnification: × 10 Kuehnel, Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy Glial Cells • Glial cells (Neuroglia) or (Glia) • (Greek "glue” • Non-neuronal cells that: 1- maintain homeostasis, 2- form myelin, 3- provide support and protection for the brain's neurons • They occupy the entire space between neurons and separate nerve cells from blood vessels Glial Cells - Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Surround neurons and hold them in place Supply nutrients and oxygen to neurons Insulate one neuron from another Destroy pathogens and remove dead neurons Glial Cells - Types • Astrocytes (macroglia) • Oligodendrocytes • Microgliocytes Astrocytes • Most abundant • Deal with homeostasis – relate to vessels Kuehnel, Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy • are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including : • 1- biochemical support of endothelial cells that form the blood–brain barrier, • 2- provision of nutrients to the nervous tissue, • 3-maintenance of extracellular ion balance, • 4- and a role in the repair and scarring process of the brain and spinal cord following traumatic injuries Astrocytes and nerve cells Kuehnel, Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy Microglia Microglia: Microglia are the main resident immunological cells the CNS • Oligodendrocytes: – Closely related to neurons – Provide myelin protection for CNS neurons Neurons and glial cells Kuehnel, Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy Neuron and glial cells Kuehnel, Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy Summary • Nerve Tissue Cells: – Neurons: • Myelinated • Non-myelinated Summary • Nerve Tissue Cells: – Neurons: • Myelinated • Non-myelintaed – Neuroglial cells: • Astrocytes • Microglia • Oligodendrocytes