EC102: Class 1
advertisement

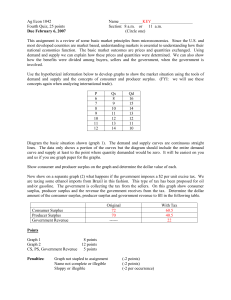
EC102: CLASS 7 Christina Ammon Overview Fill out evaluation Moodle Quiz 7 If time: one question from old problem set Question 1 In this figure consumer surplus, producer surplus and total surplus are respectively represented as areas: • A, B, A+B • A, B, A-B • B, A, A+B • A, A+B, B Question 2 When quantity grows from Xa to X1, the changes in the benefit from consuming and total surplus are respectively given by: • G, G+F • F, F+G • G+F, G • -G, F+G Question 3 Total surplus is maximized at the perfectly competitive equilibrium because changing quantity: • From X1 to Xa and from X1 to Xh reduces consumer surplus • From X1 to Xa and from X1 to Xh reduces total surplus • From Xa to X1 and from Xh to X1 reduces total surplus • From Xa to X1 and from Xh to X1 reduces consumer surplus Question 3 Move from X1 to Xa 1. • • • Consumption decreases from X1 to Xa => consumer surplus falls by G+F Production decreases from X1 to Xa=> total cost of production decreases by the F. Total surplus decreases by (G+F)-F=G. Move from X1 to Xh 2. • • • Consumption increases from X1 to Xh =>consumer surplus increases by I Production increases from X1 to Xh => total costs of production increase by J+I Total surplus decreases by (J+I)-I=J. So, if we change the quantity supplied, total output falls Question 4 In the figure the tax is represented by: • The vertical distance between S’ and S • The horizontal distance between S’ and S • The difference between p2 and p1 • The distance between e2 and e1 Question 5 The figure shows that the tax: • Increases consumer surplus, decreases producer surplus, and decreases total surplus • Decreases consumer surplus, decreases producer surplus, and decreases total surplus • Decreases consumer surplus, increases producer surplus, and decreases total surplus • Decreases consumer surplus, increases producer surplus, and increases total surplus Consumer Surplus Producer Surplus Question 6 Market failure is: A situation in which an economy with freely operating markets may fail to generate an efficient allocation of resources A situation in which an economy with regulated markets may fail to generate an efficient allocation of resources A situation in which an economy with freely operating markets may fail to generate a fair allocation of resources A situation in which an economy with regulated markets may fail to generate a fair allocation of resources Monopoly How does it compare to perfect competition? Perfect competition assumptions: • Many, small buyers • Many, small sellers • Output is homogeneous • Perfect information • There are no barriers to entry This implies for the equilibrium: • Sellers are price takers • Buyers are price takers • Profits are zero in the long run • Sellers do not behave strategically Question 7 “And how are monopolies lost? Think about it. Some very good product people invent some very good products, and the company achieves a monopoly. But after that, the product people aren’t the ones that drive the company forward anymore. Because what’s the point of focusing on making the product even better when the only company you can take business from is yourself?” Question 1 h Assume now that the two goods are “leisure” and “consumption”: Explain the equation for the budget constraint between leisure and consumption. 2. Use the appropriate diagram to show how the optimal amount of labour supply can be derived in the setting of leisureconsumption model. 3. Use the appropriate diagram to show how this equilibrium choice would be affected if the wage were reduced. 4. Discuss how the supply curve of labour can be derived using information about the leisure demand curve. What determines whether it will slope upwards or downwards? 1. Question 1h What is the labour supply curve? What is the relationship between leisure demanded and labour supplied? Hence, we can find the labour supply curve by finding the optimal amount of leisure demanded (and hence labour supplied) at different wage rates Shape depends on the income or substitution effect • • Income effect Substitution effect Graphs How do we often assume the labour supply curve to look like?