Sample Level 3 Certificate in Counselling Mark Scheme
advertisement

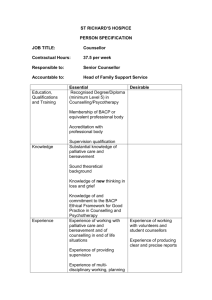
Level 3 Counselling Theory Series: Sample AIM Awards Level 3 Counselling Counselling Theory Marking Scheme No. Question Accepted Responses* Marks Available a State which of the three main approaches most likely to use this concept. Conditions of worth “Humanistic” and/or “Person-Centred” 1 mark b Negative Automatic Thoughts “Cognitive-Behavioural” 1 mark c Drive Theory “Psychodynamic” 1 mark 2 Give an example of a theorist well known for developing this approach. a Cognitive-Behavioural ‘(Aaron) Beck or ‘(Albert) Ellis 1 mark b Humanistic ‘(Carl) Rogers’ or ‘(Abraham)Maslow’ 1 mark c Psychodynamic ‘(Sigmund) Freud’ or ‘(Carl) Jung’ or ‘(Melanie) Klein’ 1 mark 3 For each definition state the key theoretical concept you believe is being defined. 1 “To sense the client’s private world as if it were your own, but without ever losing the “as if” quality…” 1 Version Final Assessment Criterion covered by this question 1.1, 1.3 1.2 1.2, 1.3 ‘Empathy’ or ‘Empathetic understanding’ 1 mark Level 3 4 5 Counselling Theory Series: Sample 2 “The phenomenon in counselling and therapy whereby the client unconsciously relates to the counsellor/therapist as if to a significant person… from the past” 3 “the client’s self-obstruction in relation to change through discovery of painful or unconscious material” 4 “client and counsellor examining evidence together about the client’s beliefs” For each of the definitions provided previously, state which of the main three approaches to counselling is most likely to use the concept of being defined 1 Transference 1 mark Resistance 1 mark Collaborative empiricism 1 mark Humanistic 1 mark 2 Psychodynamic 1 mark 3 Psychodynamic 1 mark 4 Cognitive-Behavioural 1 mark State which of the three main approaches to counselling is most likely to use the intervention being described 1 Interpretation of the transference 2 Communication of empathetic understanding Version Final 1.3 1.3 Psychodynamic 1 mark Humanistic 1 mark Level 3 Counselling Theory 3 Identifying dysfunctional thinking 6 a Carl Rogers once said that for constructive personality change to occur during counselling, it is necessary that certain conditions exist and continue over a period of time. He also said that no other conditions are necessary. State and briefly describe the conditions to which Rogers was referring. Version Final Series: Sample Cognitive-Behavioural 1 mark 2.1, 2.2 Accept the following: Counsellor and client are in psychological contact. Client is in a state of incongruence/vulnerable/ anxious Counsellor is congruent/integrated/genuine in the relationship Counsellor experiences unconditional positive regard for the client Counsellor experiences empathetic understanding of the client’s internal frame of reference and tries to communicate this experience to the client The communication to the client of the therapist’s empathetic understanding and unconditional positive regard is to a minimal degree achieved. Up to 6 marks. 1 mark for each condition accurately defined. Level 3 Counselling Theory Series: Sample For each condition, accept any clear description in which words in bold appear. Use professional judgment and accept other responses which show understanding of relevant concept. Reject if incoherent or unconvincing Version Final Level 3 b Counselling Theory Discuss the idea that no other conditions are necessary, giving reasons to support your view. Version Final Series: Sample Discussion of idea provided. Up to 4 marks available 4 marks Evaluative. Substantial and convincing understanding shown, discussing both the pros and cons of idea under discussion. 3 or more convincing reasons given 3 marks Evaluative. Substantial and convincing understanding shown, discussing both the pros and cons of idea under discussion. 2 convincing reasons given 2 marks Some discussion. Clear understanding shown, able to defend one side of argument. 2 convincing reasons given 1 mark Some discussion. Clear understanding shown, able to defend one side of argument. 1 convincing reason given 0 marks Responses which are merely descriptive or show very limited or ambiguous understanding Level 3 Counselling Theory Series: Sample 7 A phobia could be described as a persistent irrational fear and avoidance of certain situations. a Which of the three main approaches to counselling (Cognitive-Behavioural, Humanistic, Psychodynamic) is often said to be most effective in helping clients with phobias? Cognitive-Behavioural 1 mark b Discuss and give reasons for and against the idea that this approach is the most effective with phobias. Discussion of idea provided. Up to 4 marks available 4 marks Evaluative. Substantial and convincing understanding shown, discussing both the pros and cons of idea under discussion. 3 or more convincing reasons given 3 marks Evaluative. Substantial and convincing understanding shown, discussing both the pros and cons of idea under discussion. 2 convincing reasons given 2 marks Some discussion. Clear understanding shown, able to defend one side of argument. 2 convincing reasons given 1 mark Some discussion. Version Final 2.1, 2.2 Level 3 Counselling Theory Series: Sample Clear understanding shown, able to defend one side of argument. 1 convincing reason given 0 marks Responses which are merely descriptive or show very limited or ambiguous understanding 8 a As she listens to one particular client over the course of a number of sessions, a counsellor repeatedly feels very angry. As soon as the session is over, the feeling of anger disappears. She is puzzled by this reaction, since she is not aware of any obvious reason for it. Nothing this client says or does seems likely to provoke this reaction. She takes this issue to her supervisor, who favours a psychodynamic approach. Which theoretical concept might this counsellor’s supervisor suggest as helpful in understanding this experience? 2.1, 2.2 Accept: ‘Counter-transference or ‘Projective Identification’ 1 mark Reject: ‘Transference’ b Discuss and give reasons why the supervisor might say this, and why it might or might not assist the counsellor. Version Final Discussion of reasons provided. Up to 4 marks available 4 marks Evaluative. Substantial and convincing understanding shown, discussing both the pros and cons of idea under Level 3 Counselling Theory Series: Sample discussion. 3 or more convincing reasons given 3 marks Evaluative. Substantial and convincing understanding shown, discussing both the pros and cons of idea under discussion. 2 convincing reasons given 2 marks Some discussion. Clear understanding shown, able to defend one side of argument. 2 convincing reasons given 1 mark Some discussion. Clear understanding shown, able to defend one side of argument. 1 convincing reason given 0 marks Responses which are merely descriptive or show very limited or ambiguous understanding *The accepted responses are not exclusive, examiners are expected to use their professional judgement to give credit to other equally acceptable responses that address the question. Version Final Level 3 Counselling Theory Distribution of marks: Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Total Version Number of marks 3 3 4 4 3 10 5 5 37 Final Criteria Covered 1.2, 1.3 1.2 1.2, 1.3 1.3 1.3 2.1, 2.2 2.1, 2.2 2.1, 2.2 Weighting (%) 8% 8% 11.5% 11.5% 8% 27% 13% 13% Series: Sample Level 3 Counselling Theory Series: Sample This assessment is designed to assess the indicated assessment criteria indicated in the unit below. Writers will ensure: All assessment criteria are covered in the assessment There is balancing of the distribution of marks across the assessment criteria (marks do not have to be evenly split across all questions, but there should be a reasonable balance, some criteria may carry more weight than others) Shaded assessment criteria are not assessed by this examination Unit Credit Value: Unit Level: Unit Guided Learning Hours: Ofqual Unit Reference Number: 9 Three 45 F/506/3053 LEARNING OUTCOMES The learner will: 1. Understand the key concepts in the main approaches to counselling 2. Understand the strengths and limitations of the main approaches to counselling 3. Understand the strengths and limitations of an integrative approach to counselling ASSESSMENT CRITERIA The learner can: 1.1. Explain the view taken of the development and perpetuation of psychological problems as seen by each of the approaches 1.2. Distinguish between the nature and process of therapeutic change as seen by each of the approaches 1.3. Summarise the key therapeutic interventions typical of each of the approaches 2.1. Explain the key strengths for each of the approaches 2.2. Explain the key limitations for each of the approaches 3.1. Describe an integrative approach to counselling 3.2. Discuss the potential advantages for practice of an integrative approach to counselling 3.3. Discuss the potential disadvantages for practice of an integrative approach to counselling The qualification specification contains full information on the qualification. Version Final